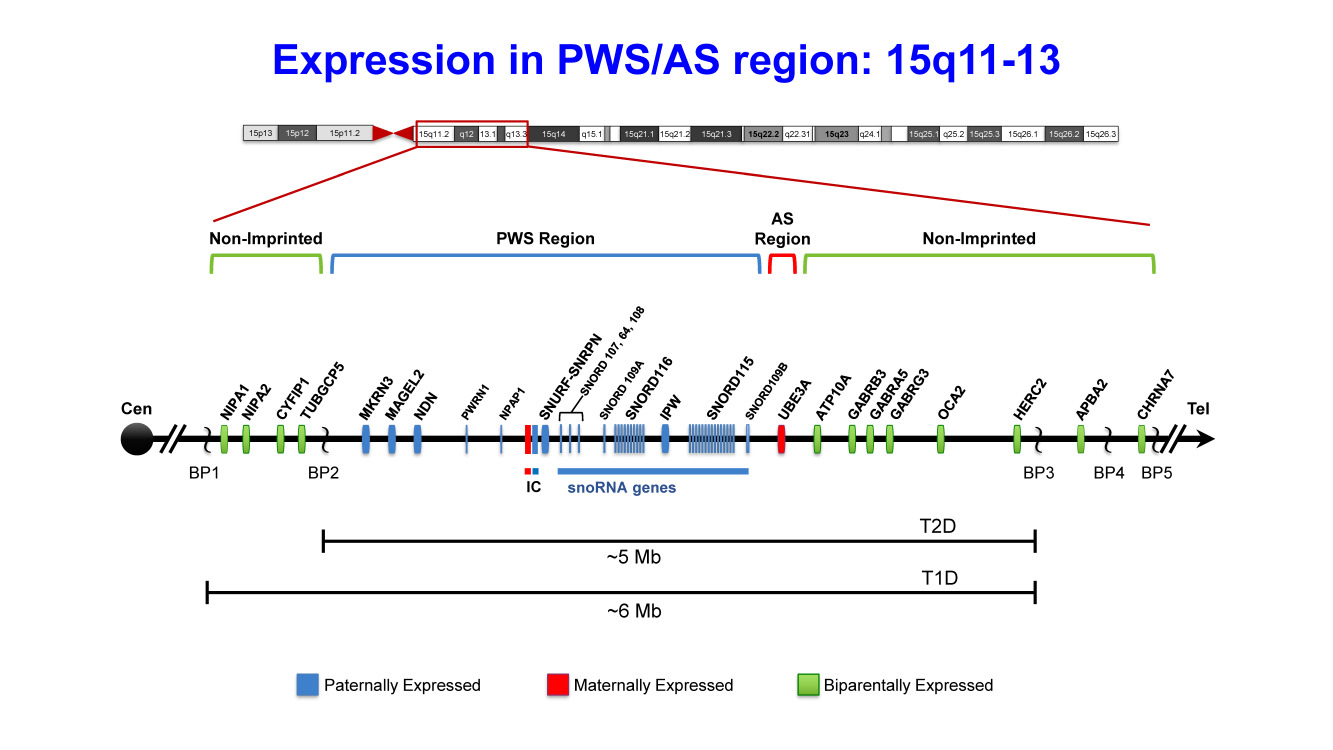
Summary of the genetic and expression map of chromosome region 15q11.2-q13.3
The Prader-Willi syndrome (PWS) critical region (shown in blue) has several paternally (PWS region) expressed genes (MKRN3, MAGEL2, NDN, PWRN1, NPAP1, and SNURF-SNRPN), a family of paternally expressed small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) genes, and IPW, a long noncoding RNA. Three of these genes (SNURF-SNRPN, MAGEL2, and NDN) have differentially methylated CpG islands in their promoter region that are methylated on the repressed maternal alleles. Only UBE3A (shown in red), associated with Angelman syndrome (AS), has preferential maternal-only expression, and this imprinted expression is limited to certain tissue-specific regions (specifically the brain). The imprinting center (IC) has a bipartite structure with an AS (maternal, shown in red) and a PWS (paternal, shown in blue) component. The PWS shortest region of deletion overlap (PWS-SRO) has been localized to a 4.3-kb region that includes the promoter, CpG island, exon 1, and a small part of intron 1 of bicistronic SNURF-SNRPN. The AS-SRO lies approximately 35 kb proximal to exon 1 of SNURF-SNRPN. The bipartite IC lies within the 2.5-Mb PWS/AS imprinted region. The cluster of GABA receptor genes (GABRB3, GABRA5, and GABRG3), ATP10A, OCA2 (pathogenic variants of which cause oculocutaneous albinism type 2), and HERC2 are not imprinted and have biparental expression (shown in green). The jagged vertical lines denote the three common 5- to 6-Mb PWS and AS deletion breakpoints: BP1, BP2, and BP3. On rare occasions there will be a distal breakpoint at BP4 or BP5. Between BP1 and BP2 lie four additional, nonimprinted genes: NIPA1, NIPA2, CYFIP1, and TUBGCP5. Type 1 and type 2 deletions account for more than 90% of the deletions identified in individuals with PWS. Type 1 deletions (T1D) extend from BP1 to BP3, and type 2 deletions (T2D) extend from BP2 to BP3. Note that there are more copies of SNORD116 (approximately 24 copies) and SNORD115 (approximately 47 copies) than are shown, and the map has not been precisely drawn to scale. The map order was determined by the latest human genome assembly (UCSC Genome Browser,GRCh38/hg38).