Summary
Clinical characteristics.
The PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome (PHTS) includes Cowden syndrome (CS), Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome (BRRS), PTEN-related Proteus syndrome (PS), and PTEN-related Proteus-like syndrome.
CS is a multiple hamartoma syndrome with a high risk for benign and malignant tumors of the thyroid, breast, kidney, and endometrium. Affected individuals usually have macrocephaly, trichilemmomas, and papillomatous papules, and present by the late 20s. The lifetime risk of developing breast cancer is 85%, with an average age of diagnosis between 38 and 46 years. The lifetime risk for thyroid cancer (usually follicular, rarely papillary, but never medullary thyroid cancer) is approximately 35%. The lifetime risk for renal cell cancer (predominantly of papillary histology) is 34%. The risk for endometrial cancer may approach 28%.
BRRS is a congenital disorder characterized by macrocephaly, intestinal hamartomatous polyposis, lipomas, and pigmented macules of the glans penis.
PS is a complex, highly variable disorder involving congenital malformations and hamartomatous overgrowth of multiple tissues, as well as connective tissue nevi, epidermal nevi, and hyperostoses.
Proteus-like syndrome is undefined but refers to individuals with significant clinical features of PS who do not meet the diagnostic criteria for PS.
Diagnosis/testing.
The diagnosis of PHTS is established in a proband by identification of a heterozygous germline PTEN pathogenic variant on molecular genetic testing.
Management.
Treatment of manifestations: Treatment for the benign and malignant manifestations of PHTS is the same as for their sporadic counterparts. Topical agents (e.g., 5-fluorouracil), curettage, cryosurgery, or laser ablation may alleviate the mucocutaneous manifestations of CS but are rarely utilized; cutaneous lesions should be excised only if malignancy is suspected or symptoms (e.g., pain, deformity, increased scarring) are significant.
Surveillance: To detect tumors at the earliest, most treatable stages:
Children (age <18 years). Yearly thyroid ultrasound from the time of diagnosis (earliest reported at age 7 years) and skin check with physical examination
Adults. Yearly thyroid ultrasound and dermatologic evaluation
Women beginning at age 30 years. Monthly breast self-examination; annual breast screening (at minimum mammogram; MRI may also be incorporated). Starting by age 35 years, consider transvaginal ultrasound or endometrial biopsy.
Men and women. Colonoscopy beginning at age 35 years with frequency dependent on degree of polyposis identified or family history of early-onset colon cancer (before age 40); biennial (every 2 years) renal imaging (CT or MRI preferred) beginning at age 40 years
Those with a family history of a particular cancer type at an early age. Consider initiating screening 5 to 10 years prior to the youngest age of diagnosis in the family.
Evaluation of relatives at risk: When a PTEN pathogenic variant has been identified in a proband, molecular genetic testing of asymptomatic at-risk relatives can identify those who have the family-specific pathogenic variant and warrant ongoing surveillance.
Genetic counseling.
PHTS is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Because CS is likely underdiagnosed, the actual proportion of simplex cases (defined as individuals with no obvious family history) and familial cases (defined as ≥2 related affected individuals) cannot be determined. The majority of CS cases are simplex. Perhaps 10%-50% of individuals with CS have an affected parent. Each child of an affected individual has a 50% chance of inheriting the pathogenic variant and developing PHTS. Once a PTEN pathogenic variant has been identified in an affected family member, prenatal testing for a pregnancy at increased risk is possible.
Diagnosis
Suggestive Findings
The PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome (PHTS) includes Cowden syndrome (CS), Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome (BRRS), PTEN-related Proteus syndrome (PS), and PTEN-related Proteus-like syndrome.
PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome (PHTS) should be suspected in individuals with the following clinical features.
Cowden Syndrome (CS)
Based on more than 3,000 prospectively accrued cases of CS or Cowden-like syndrome (CLS) from the community, a scoring system (which can be found online) that takes into account phenotype and age at diagnosis has been developed. The scoring system allows input of clinical information on an individual suspected of having CS/CLS and subsequently generates the prior probability of finding a PTEN pathogenic variant.
In adults, a clinical threshold score of ten or more leads to a recommendation for referral to a genetics professional to consider PHTS.
In children, macrocephaly and one or more of the following leads to the consideration of PHTS:
Autism or developmental delay
Dermatologic features including lipomas, trichilemmomas, oral papillomas, or penile freckling
Vascular features, such as arteriovenous malformations or hemangiomas
Gastrointestinal polyps
Pediatric-onset thyroid cancer or germ cell tumors
Additionally, consensus clinical diagnostic criteria for CS have been developed [Eng 2000]. The National Comprehensive Cancer Network publishes updated clinical diagnostic criteria on a yearly basis. However, the CS scoring system discussed in this section has been shown to be more accurate than the NCCN diagnostic criteria [Tan et al 2011].
Consensus clinical diagnostic criteria have been divided into three categories: pathognomonic, major, and minor.
Pathognomonic criteria
Adult Lhermitte-Duclos disease, defined as the presence of a cerebellar dysplastic gangliocytoma [
Zhou et al 2003a]
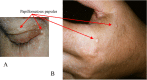
Mucocutaneous lesions:
Papillomatous papules in the periocular region (A) and on the dorsum of the hand (B)
Major criteria
Breast cancer
Epithelial thyroid cancer (non-medullary), especially follicular thyroid cancer
Macrocephaly (occipital frontal circumference ≥97th percentile)
Endometrial carcinoma
Minor criteria
Other thyroid lesions (e.g., adenoma, multinodular goiter)
Intellectual disability (IQ ≤75)
Hamartomatous intestinal polyps
Fibrocystic disease of the breast
Lipomas
Fibromas
Genitourinary tumors (especially renal cell carcinoma)
Genitourinary malformation
Uterine fibroids
A clinical diagnosis of CS is established if an individual meets any one of the following criteria:
Pathognomonic mucocutaneous lesions including one of the following:
Six or more facial papules, of which three or more must be trichilemmomas
Cutaneous facial papules and oral mucosal papillomatosis
Oral mucosal papillomatosis and acral keratoses
Six or more palmoplantar keratoses
Two or more major criteria
One major and three or more minor criteria
Four or more minor criteria
In a family in which one individual meets the diagnostic criteria for CS listed above, other relatives are considered to have a clinical diagnosis of CS if they meet any one of the following criteria:
A pathognomonic criterion
Any one major criterion with or without minor criteria
Two minor criteria
History of Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome
Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba Syndrome (BRRS)
Diagnostic criteria for BRRS have not been set but are based heavily on the presence of the cardinal features of macrocephaly, hamartomatous intestinal polyposis, lipomas, vascular malformations, and pigmented macules of the glans penis [Gorlin et al 1992].
Establishing the Diagnosis
The diagnosis of PHTS is established in a proband by identification of a heterozygous germline pathogenic variant in PTEN on molecular genetic testing (see Table 1).
Molecular genetic testing approaches can include a combination of gene-targeted testing (single-gene testing, multigene panel) and comprehensive
genomic testing (exome sequencing, genome sequencing) depending on the phenotype.
Gene-targeted testing requires that the clinician determine which gene(s) are likely involved, whereas genomic testing does not. Individuals with the distinctive findings described in Suggestive Findings are likely to be diagnosed using gene-targeted testing (see Option 1), whereas those with a phenotype indistinguishable from many other inherited disorders with macrocephaly, developmental delay, and/or early-onset tumors are more likely to be diagnosed using genomic testing (see Option 2).
Option 1
Single-gene testing. Sequence analysis of PTEN is performed first and followed by gene-targeted deletion/duplication analysis if no pathogenic variant is found. If a pathogenic variant is not identified with deletion/duplication analysis, perform sequence analysis of the PTEN promoter region for variants that decrease PTEN gene expression.
Note: In individuals with Cowden syndrome (CS) and Cowden-like syndrome (CLS), also consider a germline KLLN epimutation and SDHB-D analysis including PIK3CA, AKT1 [Orloff et al 2013], SEC23B [Yehia et al 2015], and WWP1 [Lee et al 2020] (see Differential Diagnosis, Considerations in individuals with non-PHTS CS and CLS).
A multigene panel that includes PTEN and other genes of interest (see Differential Diagnosis) may also be considered. Note: (1) The genes included in the panel and the diagnostic sensitivity of the testing used for each gene vary by laboratory and are likely to change over time. (2) Some multigene panels may include genes not associated with the condition discussed in this GeneReview; thus, clinicians need to determine which multigene panel is most likely to identify the genetic cause of the condition while limiting identification of variants of uncertain significance and pathogenic variants in genes that do not explain the underlying phenotype. (3) In some laboratories, panel options may include a custom laboratory-designed panel and/or custom phenotype-focused exome analysis that includes genes specified by the clinician. (4) Methods used in a panel may include sequence analysis, deletion/duplication analysis, and/or other non-sequencing-based tests.
For an introduction to multigene panels click here. More detailed information for clinicians ordering genetic tests can be found here.
Option 2
Comprehensive
genomic testing does not require the clinician to determine which gene is likely involved. Exome sequencing is most commonly used; genome sequencing is also possible.
For an introduction to comprehensive genomic testing click here. More detailed information for clinicians ordering genomic testing can be found here.
Table 1.
Molecular Genetic Testing Used in PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome
View in own window
| Gene 1 | Method | Proportion of Probands by Phenotype with a Pathogenic Variant 2 Detectable by Method |
|---|
| CS | BRRS | PLS | PS |
|---|
|
PTEN
| Sequence analysis of coding region 3 | 25%-80% | 60% | 50% 4 | 20% 4 |
| Deletion/duplication analysis 5 |
3% 6
| 11% 7 | Unknown | Unknown |
| Sequence analysis of promoter region 3 | 10% 7 | Rare 7 | Unknown | Unknown |
BRRS = Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome; CS = Cowden syndrome; PLS = Proteus-like syndrome; PS = PTEN-related Proteus syndrome
- 1.
- 2.
- 3.
Sequence analysis detects variants that are benign, likely benign, of uncertain significance, likely pathogenic, or pathogenic. Variants may include small intragenic deletions/insertions and missense, nonsense, and splice site variants; typically, exon or whole-gene deletions/duplications are not detected. For issues to consider in interpretation of sequence analysis results, click here.
- 4.
Data suggest that up to 50% of individuals with a Proteus-like syndrome and 20% of individuals who meet the clinical diagnostic criteria of Proteus syndrome have PTEN pathogenic variants [Yehia & Eng 2018, Yehia et al 2019].
- 5.
Gene-targeted deletion/duplication analysis detects intragenic deletions or duplications. Methods used may include a range of techniques such as quantitative PCR, long-range PCR, multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA), and a gene-targeted microarray designed to detect single-exon deletions or duplications.
- 6.
- 7.
Clinical Characteristics
Clinical Description
PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome (PHTS) is characterized by hamartomatous tumors and germline PTEN pathogenic variants. Clinically, PHTS includes Cowden syndrome (CS), Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome (BRRS), PTEN-related Proteus syndrome (PS), and PTEN-related Proteus-like syndrome.
CS is a multiple hamartoma syndrome with a high risk for benign and malignant tumors of the thyroid, breast, and endometrium. Renal cell carcinoma and colorectal carcinoma have also been shown to be in the PHTS spectrum.
BRRS is a congenital disorder characterized by macrocephaly, intestinal polyposis, lipomas, vascular malformations, and pigmented macules of the glans penis.
PS is a complex, highly variable disorder involving congenital malformations and overgrowth of multiple tissues.
Proteus-like syndrome is undefined but refers to individuals with significant clinical features of PS who do not meet the diagnostic criteria for PS.
Cowden Syndrome (CS)
More than 90% of individuals with CS have some clinical manifestation of the disorder by the late 20s [Nelen et al 1996, Eng 2000]. By the fourth decade, 99% of affected individuals develop the mucocutaneous stigmata (primarily trichilemmomas and papillomatous papules) as well as acral and plantar keratoses. In addition, individuals with Cowden syndrome usually have macrocephaly and dolichocephaly.
Hamartomatous and mixed gastrointestinal polyps, seen frequently in the majority of people with PHTS, do confer an increased risk for colorectal cancers [Heald et al 2010].
Based on anecdotal observations, glycogenic acanthosis in the presence of features of CS appears to be associated with a high likelihood of finding a PTEN pathogenic variant [McGarrity et al 2003].
Tumor risk. Individuals with CS are at high risk for breast, thyroid, renal, and endometrial cancers. As with other hereditary cancer syndromes, the risk for multifocal and bilateral (in paired organs such as the breasts) cancer is increased. Individuals with a germline PTEN pathogenic variant have a seven-fold increased risk of developing a second primary malignant neoplasm as compared to the general population [Ngeow et al 2014]:
Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba Syndrome (BRRS)
Common features of BRRS, in addition to those mentioned above, include high birth weight, developmental delay, and intellectual disability (50% of affected individuals), a myopathic process in proximal muscles (60%), joint hyperextensibility, pectus excavatum, and scoliosis (50%) [Gorlin et al 1992].
Individuals with BRRS and a PTEN pathogenic variant are thought to have the same cancer risks as individuals with CS but formal study has not been performed. Note: It is not clear whether these risks apply to individuals with BRRS who do not have a PTEN pathogenic variant.
The gastrointestinal hamartomatous polyps in BRRS (seen in 45% of affected individuals) may occasionally be associated with intussusception, but rectal bleeding and oozing of "serum" is more common. These polyps are not believed to increase the risk for colorectal cancer. PHTS hamartomatous polyps are different in histomorphology from the polyps seen in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
Clinical Implications of All PHTS Phenotypes
The two most serious clinical manifestations in individuals with germline PTEN pathogenic variants are organ-specific cancers and neurodevelopmental disorders, including autism spectrum disorder (ASD).
PTEN-related lifetime neoplasia risks. Regardless of clinical diagnosis, individuals with a germline PTEN pathogenic variant are thought to have the same cancer risks as individuals with CS [Tan et al 2012].
Neurodevelopmental disorders. Neurodevelopmental phenotypes such as megalencephaly, ASD, and developmental delay have been reported in individuals with PHTS [Goffin et al 2001, Butler et al 2005, Hansen-Kiss et al 2017]. Germline PTEN pathogenic variants have been identified in 10%-20% of individuals with ASD and macrocephaly [Yehia et al 2020]. The extent of macrocephaly observed in PTEN-related ASD is often more severe than in individuals with macrocephalic ASD unrelated to PTEN [Mester et al 2011]. Individuals with PTEN-related ASD show increases in cortical white matter and a distinctive neurocognitive and behavioral phenotype including delayed language development, poor working memory and processing speed, and adaptive and sensory abnormalities [Frazier et al 2015, Busch et al 2019].
Genotype-Phenotype Correlations
For purposes of PTEN genotype-phenotype analyses, a series of 37 unrelated probands with CS were ascertained by the operational diagnostic criteria of the International Cowden Consortium, 1995 version [Nelen et al 1996, Eng 2000]. Association analyses revealed that families with CS and a germline PTEN pathogenic variant are more likely to develop malignant breast disease than are families who do not have a PTEN pathogenic variant [Marsh et al 1998]. In addition, pathogenic missense variants and others 5' to or within the phosphatase core motif appeared to be associated with involvement of five or more organs, a surrogate phenotype for severity of disease [Marsh et al 1998].
More than 90% of families that included individuals with CS and also individuals with BRRS were found to have a germline PTEN pathogenic variant. The mutational spectra of BRRS and CS have been shown to overlap. No difference in mutation frequencies was observed between BRRS occurring in a single individual in a family and BRRS occurring in multiple family members.
An individual presenting as a simplex case (i.e., one with no known family history) of Proteus-like syndrome comprising hemihypertrophy, macrocephaly, lipomas, connective tissue nevi, and multiple arteriovenous malformations was found to have a germline p.Arg335Ter
PTEN pathogenic variant and the same somatic pathogenic variant (p.Arg130Ter) in three separate tissues, possibly representing germline mosaicism [Zhou et al 2000]. Both pathogenic variants have been previously described in individuals with clinical features of CS and BRRS.
Two of nine individuals who met the clinical diagnostic criteria of Proteus syndrome and three of six with Proteus-like syndrome were found to have germline PTEN pathogenic variants. Subsequently multiple individuals with germline PTEN pathogenic variants who met the clinical diagnostic criteria of Proteus syndrome have been reported [Yehia & Eng 2018].
Penetrance
More than 90% of individuals with CS have some clinical manifestation of the disorder by the late 20s [Nelen et al 1996, Eng 2000, Yehia et al 2020]. By the fourth decade, 99% of affected individuals develop the mucocutaneous stigmata, primarily trichilemmomas and papillomatous papules, as well as acral and plantar keratoses. (See also Clinical Description, Cowden Syndrome for the age at which specific manifestations are likely to become evident.)
Nomenclature
Cowden syndrome, Cowden disease, and multiple hamartoma syndrome have been used interchangeably.
Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome, Bannayan-Ruvalcaba-Riley syndrome, Bannayan-Zonana syndrome, and Myhre-Riley-Smith syndrome refer to a similar constellation of signs that comprise what the authors refer to as BRRS. When a PTEN pathogenic variant is found, the gene-related name, PHTS, should be used.
One form of Proteus-like syndrome, with a clinical presentation similar to that first described by Zhou et al [2000] and with a germline PTEN pathogenic variant, was termed SOLAMEN (segmental overgrowth, lipomatosis, arteriovenous malformation, and epidermal nevus) syndrome [Caux et al 2007]. This is not useful, especially in the molecular era, as any phenotype associated with a PTEN pathogenic variant should be termed PHTS with all its implications for clinical management [Yehia et al 2020].
Prevalence
Because the diagnosis of CS is difficult to establish, the true prevalence is unknown. The prevalence estimate of 1:200,000 [Nelen et al 1999] is likely low. Because of the variable and often subtle external manifestations of CS and BRRS, many individuals remain undiagnosed [Yehia et al 2020].
Management
Evaluations and Surveillance Guidelines Following Initial Diagnosis
To establish the extent of disease and needs of an individual diagnosed with PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome (PHTS), the evaluations summarized in Table 4 (if not performed as part of the evaluation that led to the diagnosis) are recommended. The most serious consequences of PHTS relate to the increased risk of cancers including breast, thyroid, endometrial, renal, and to a lesser extent, colon. In this regard, the most important aspect of management of any individual with a PTEN pathogenic variant is increased cancer surveillance to detect any tumors at the earliest, most treatable stages. Current suggested screening and surveillance by age are detailed in Table 4.
Table 4.
Recommended Evaluations and Surveillance Following Initial Diagnosis in Individuals with PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome
View in own window
| System/Concern | Evaluation & Surveillance 1 |
|---|
|
General
| Complete medical history & family history for features of PHTS Annual comprehensive physical exam starting at age 18 yrs, or 5 yrs before youngest age of diagnosis of a component cancer in family (whichever comes 1st), w/particular attention to thyroid exam Encourage education re signs & symptoms of cancer.
|
|
Breast (female)
| Starting at age 18 yrs: consistent breast awareness & self-exam; report changes to health care provider. Starting at age 25 yrs 2: clinical breast exam every 6-12 mos Starting at ages 30-35 yrs 2: annual mammogram w/consideration of tomosynthesis & breast MRI w/contrast Discuss mastectomy as needed.
|
|
Thyroid
| Starting at age of diagnosis (youngest thyroid cancer reported: age 7 yrs): annual thyroid US |
|
Kidney
|
|
|
Endometrium
| Consider endometrial cancer screening by age 35 yrs. Encourage education & prompt response to symptoms (e.g., abnormal bleeding). Consider endometrial biopsy screening every 1-2 yrs. Transvaginal US in postmenopausal women at clinician's discretion & as needed Discuss hysterectomy on completion of childbearing & as needed.
|
|
Colon
| Starting at age 35 yrs 2: colonoscopy every 5 yrs; more frequently if person is symptomatic or polyps are found |
|
Dermatologic
| Annual dermatologic exams are recommended (incl for cutaneous melanoma). |
|
Developmental
| Starting at age of diagnosis: at clinician's recommendation, consider psychomotor assessment in children; brain MRI if symptomatic Eval for early intervention / special education where indicated
|
Genetic
counseling
| By genetics professionals 3 To inform affected persons & their families re nature, MOI, & implications of PHTS to facilitate medical & personal decision making Refer to psychosocial support as needed (e.g., to address the diagnosis, family planning, risk-reducing mastectomy).
|
MOI = mode of inheritance; PHTS = PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome; US = ultrasound
- 1.
Adapted with permission from the NCCN Guidelines® for Genetic/Familial High-Risk Assessment: Breast and Ovarian V.1.2021. © 2021 National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Inc. All rights reserved. The NCCN Guidelines and illustrations herein may not be reproduced in any form for any purpose without the express written permission of the NCCN. Accessed December 27, 2020. To view the most recent and complete version of the guideline, go online to NCCN.org (no-fee registration and login required). NCCN makes no warranties of any kind whatsoever regarding their content, use or application and disclaims any responsibility for their application or use in any way.
- 2.
For individuals with a family history of a particular cancer type at an early age, screening should be considered five to ten years prior to the youngest diagnosis in the family.
- 3.
Medical geneticist, certified genetic counselor, or certified advanced genetic nurse
Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba Syndrome (BRRS)
Note: Screening recommendations have not been established for BRRS. Given recent molecular epidemiologic studies, however, individuals with BRRS and a germline PTEN pathogenic variant should undergo the same surveillance as individuals with CS (see Table 4). Individuals with BRRS should especially be monitored for complications related to gastrointestinal hamartomatous polyposis (which can be more severe than in individuals with CS) and musculoskeletal features such as hypotonia and scoliosis.
Proteus Syndrome / Proteus-Like Syndrome
Note: Although the observation of germline PTEN pathogenic variants in a minority of individuals who meet the clinical diagnostic criteria for Proteus syndrome and Proteus-like syndrome is relatively new, clinicians should consider instituting the above surveillance recommendations for individuals with these disorders who have germline PTEN pathogenic variants.
Treatment of Manifestations
Table 5.
Treatment of Manifestations in Individuals with Cowden Syndrome and Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba Syndrome
View in own window
| Manifestation/Concern | Treatment | Considerations/Other |
|---|
Mucocutaneous
lesions
| Asymptomatic lesions: observation alone is prudent. | Cutaneous lesions should be excised only if malignancy is suspected or symptoms (e.g., pain, deformity, ↑ scarring) are significant. |
| Symptomatic lesions: topical agents (e.g., 5-fluorouracil), curettage, cryosurgery, or laser ablation may provide only temporary relief [Hildenbrand et al 2001]. | Surgical excision is sometimes complicated by keloid formation & recurrence (often rapid) of the lesions [Eng, unpublished data]. |
Developmental
delay
| As needed:
| |
Breast disease /
neoplasia
| Treatment per breast cancer specialist | |
|
Thyroid disease
| Thyroid US to monitor for ↑ in size of nodules, or multinodular goiter If results of fine needle aspirate are suspicious for malignancy, perform total thyroidectomy.
| Sub-total thyroidectomies will → regrowth of thyroid w/similar cancer risks. |
|
Endometrial disease
| Multiple fibroids are treated w/total abdominal hysterectomy. | Single fibroid removals → dramatic recurrences. |
Gastrointestinal
neoplasias
| Endoscopy w/removal of polyps per gastroenterologist | |
|
Renal cell carcinoma
| Standard treatment | |
Treatment of Manifestations in Individuals with Proteus Syndrome / Proteus-Like Syndrome
Individuals with a germline PTEN pathogenic variant should follow management recommendations for CS and BRRS (see Table 5). Also see Proteus Syndrome, Management.
Prevention of Primary Manifestations
Some women at increased risk for breast cancer consider prophylactic mastectomy, especially if breast tissue is dense or if repeated breast biopsies have been necessary. Prophylactic mastectomy reduces the risk of breast cancer by 90% in women at high risk [Hartmann et al 1999]. Note: The recommendation of prophylactic mastectomy is a generalization for women at increased risk for breast cancer from a variety of causes, not just from PHTS.
No direct evidence supports the routine use of agents such as tamoxifen or raloxifene in individuals with PHTS to reduce the risk of developing breast cancer. Physicians should discuss the limitations of the evidence and the risks and benefits of chemoprophylaxis with each individual. In addition, the clinician must discuss the increased risk for endometrial cancer associated with tamoxifen use in a population already at increased risk for endometrial cancer.
Agents/Circumstances to Avoid
Because of the propensity for rapid tissue regrowth and the propensity to form keloid tissue, it is recommended that cutaneous lesions be excised only if malignancy is suspected or symptoms (e.g., pain, deformity) are significant.
Evaluation of Relatives at Risk
It is appropriate to clarify the genetic status of at-risk relatives of an affected individual by molecular genetic testing for the PTEN pathogenic variant identified in the proband. Family members who have the familial PTEN pathogenic variant (and therefore have PHTS) are in need of initial evaluation and ongoing surveillance.
Molecular testing is appropriate for at-risk individuals younger than age 18 years, given the possible early disease presentation in individuals with BRRS and PTEN-related Proteus syndrome. In individuals with PHTS, the earliest documented breast cancer and thyroid cancer are at age 17 years and at age seven years, respectively.
Family members who have not inherited the PTEN pathogenic variant and their subsequent offspring have cancer risks similar to the general population.
See Genetic Counseling for issues related to testing of at-risk relatives for genetic counseling purposes.
Therapies Under Investigation
Although mTOR inhibitors show promise for treatment of malignancies in individuals who have a germline PTEN pathogenic variant, use should be limited to clinical trials. A Phase II open-label clinical trial (NCT00971789) utilized the mTOR inhibitor sirolimus in adults with PHTS and showed evidence of improvement of symptoms throughout the duration of the trial [Komiya et al 2019]. Another double-blind drug-placebo cross-over clinical trial with the mTOR inhibitor everolimus is completing accrual of pediatric, adolescent, and young adults with germline PTEN pathogenic variants and autism spectrum disorder (NCT02461446).
Search ClinicalTrials.gov in the US and EU Clinical Trials Register in Europe for access to information on clinical studies for a wide range of diseases and conditions.
Genetic Counseling
Genetic counseling is the process of providing individuals and families with
information on the nature, mode(s) of inheritance, and implications of genetic disorders to help them
make informed medical and personal decisions. The following section deals with genetic
risk assessment and the use of family history and genetic testing to clarify genetic
status for family members; it is not meant to address all personal, cultural, or
ethical issues that may arise or to substitute for consultation with a genetics
professional. —ED.
Mode of Inheritance
Cowden syndrome and Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome are autosomal dominant disorders caused by either an inherited or a de novo PTEN pathogenic variant.
PTEN-related Proteus syndrome and Proteus-like syndrome are also autosomal dominant disorders but are almost always caused by a de novo pathogenic variant.
Risk to Family Members
Parents of a proband
Cowden syndrome (CS). Because CS is likely underdiagnosed, the actual proportion of simplex cases (defined as individuals with no obvious family history) and familial cases (defined as ≥2 related affected individuals) cannot be determined. Based on practical experience, about 50% of individuals diagnosed with CS have an affected relative [Author, unpublished data].
De novo PTEN pathogenic variants occur in 10%-44% of PHTS probands [
Mester & Eng 2012].
Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome (BRRS). The majority of evidence suggests that
PTEN pathogenic variants occur in both simplex and familial occurrences of BRRS [
Mester & Eng 2012,
Yehia & Eng 2018].
PTEN-related Proteus syndrome and Proteus-like syndrome. Virtually all individuals have a de novo pathogenic variant.
If the proband appears to be the only affected family member, molecular genetic testing is recommended for the parents of the proband to confirm their genetic status and to allow reliable recurrence risk counseling.
If the pathogenic variant identified in the proband is not identified in either parent, the following possibilities should be considered:
The proband has a
de novo pathogenic variant. Note: A pathogenic variant is reported as "
de novo" if: (1) the pathogenic variant found in the proband is not detected in parental DNA; and (2) parental identity testing has confirmed biological maternity and paternity. If parental identity testing is not performed, the variant is reported as "assumed
de novo" [
Richards et al 2015].
The proband inherited a pathogenic variant from a parent with germline (or somatic and germline) mosaicism.* Note: Testing of parental leukocyte DNA may not detect all instances of somatic mosaicism.
* A parent with somatic and germline mosaicism for a PTEN pathogenic variant may be mildly/minimally affected.
The family history of many individuals diagnosed with PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome (PHTS) may appear to be negative because of failure to recognize the disorder in family members, early death of the parent before the onset of symptoms, or late onset of the disorder in a heterozygous parent. Therefore, an apparently negative family history cannot be confirmed unless molecular genetic testing has demonstrated that neither parent is heterozygous for the pathogenic variant identified in the proband.
Sibs of a proband. The risk to the sibs of the proband depends on the genetic status of the parents:
If a parent of the proband has the
PTEN pathogenic variant identified in the proband, the risk to the sibs of inheriting the variant is 50%. The
penetrance of PHTS is close to 99% by the 30s in individuals with a
PTEN pathogenic variant.
If the
PTEN pathogenic variant identified in the proband cannot be detected in the leukocyte DNA of either parent, the recurrence risk to sibs is slightly greater than that of the general population because of the possibility of parental germline mosaicism [
Pritchard et al 2013].
If the parents have not been tested for the PTEN pathogenic variant but are clinically unaffected and are in their thirties, the risk to the sibs of a proband appears to be low. However, sibs of a proband with clinically unaffected parents are still presumed to be at increased risk for PHTS because of the possibility of age-related penetrance in a heterozygous parent or parental germline mosaicism.
Offspring of a proband. Each child of an individual with PHTS has a 50% chance of inheriting the PTEN pathogenic variant.
Other family members. The risk to other family members depends on the status of the proband's parents: if a parent has the PTEN pathogenic variant, his or her family members may be at risk.
Prenatal Testing and Preimplantation Genetic Testing
Once the PTEN pathogenic variant has been identified in an affected family member, prenatal and preimplantation genetic testing are possible.
Differences in perspective may exist among medical professionals and within families regarding the use of prenatal testing. While most centers would consider use of prenatal testing to be a personal decision, discussion of these issues may be helpful.
Molecular Genetics
Information in the Molecular Genetics and OMIM tables may differ from that elsewhere in the GeneReview: tables may contain more recent information. —ED.
Table A.
PTEN Hamartoma Tumor Syndrome: Genes and Databases
View in own window
Data are compiled from the following standard references: gene from
HGNC;
chromosome locus from
OMIM;
protein from UniProt.
For a description of databases (Locus Specific, HGMD, ClinVar) to which links are provided, click
here.
Molecular Pathogenesis
While much functional research has been accomplished, complete function of PTEN is not yet fully understood. PTEN belongs to a subclass of phosphatases called dual-specificity phosphatases that remove phosphate groups from tyrosine as well as serine and threonine. In addition, PTEN is the major phosphatase for phosphoinositide-3,4,5-triphosphate, and thus downregulates the PI3K/AKT pathway [Yehia et al 2019].
The PTEN protein localizes to specific nuclear and cytoplasmic components. The wild type protein is a major lipid phosphatase that downregulates the PI3K/AKT pathway to cause G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. In addition, the protein phosphatase appears to play an important role in inhibition of cell migration and spreading, as well as downregulating several cell cyclins. It appears that nuclear PTEN mediates cell cycle arrest, while cytoplasmic PTEN is required for apoptosis [Yehia & Eng 2018, Yehia et al 2019].
Germline pathogenic variants have been found throughout PTEN and include missense, nonsense, and splice site variants, small deletions, insertions, and large deletions. More than 150 unique pathogenic variants are currently listed in the Human Gene Mutation Database (see Table A). Nearly 40% of pathogenic variants are found in exon 5, which encodes the phosphate core motif [Yehia et al 2019]. Most pathogenic variants are unique, although a number of recurrent pathogenic variants have been reported, particularly those in Table 6.
Mechanism of disease causation. The majority (76%) of germline pathogenic variants in PTEN predict either truncated PTEN protein, lack of protein (haploinsufficiency), or dysfunctional protein. Many missense variants are functionally null and several act as dominant negatives [Papa et al 2014]. When PTEN is absent, decreased, or dysfunctional, phosphorylation of AKT1 is uninhibited, leading to the inability to activate cell cycle arrest and/or to undergo apoptosis. In addition, through lack of protein phosphatase activity, the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is dysregulated, leading to abnormal cell survival [Yehia et al 2019].
PTEN-specific laboratory technical considerations.
PTEN has a highly homologous pseudogene (PTENP1) on chromosome 9 [Dahia et al 1998]. Special consideration should be taken when designing PTEN-specific primers to ensure specificity and to avoid cross-amplification of this pseudogene [Ngeow & Eng 2016].
Table 6.
Notable PTEN Pathogenic Variants
View in own window
| Reference Sequences | DNA Nucleotide Change | Predicted Protein Change | Comment [Reference] |
|---|
NM_000314.8
NP_000305.3
| c.388C>T | p.Arg130Ter |
Recurrent pathogenic variants [Yehia et al 2019]
|
| c.697C>T | p.Arg233Ter |
| c.1003C>T | p.Arg335Ter |
Variants listed in the table have been provided by the authors. GeneReviews staff have not independently verified the classification of variants.
GeneReviews follows the standard naming conventions of the Human Genome Variation Society (varnomen.hgvs.org). See Quick Reference for an explanation of nomenclature.
Cancer and Benign Tumors
Sporadic cancers (including endometrial cancer, prostate cancer, glioblastoma) occurring as single tumors in the absence of any other findings of PHTS frequently harbor somatic variants in PTEN that are not present in the germline. Somatic PTEN variants and loss of gene expression are frequently found in both endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinoma and precancerous endometrial lesions (intraepithelial neoplasia) [Mutter et al 2000]. In these circumstances predisposition to these tumors is not heritable.
Chapter Notes
Author Notes
Dr Eng is the chair and coordinator of the International Cowden Syndrome Consortium, founding Chairwoman of the Cleveland Clinic Genomic Medicine Institute, and a primary researcher in the field of PTEN-related disorders. Dr Yehia is an Ambrose Monell Foundation Cancer Genomic Medicine Fellow at the Cleveland Clinic Genomic Medicine Institute. The Cleveland Clinic Genomic Medicine Institute program features the only multidisciplinary Cowden Syndrome center in the US, with ongoing clinical and molecular research protocols in PHTS.
Acknowledgments
We are eternally grateful to the many patients and families who have participated in our research and who continue to educate us in the ever-broadening clinical spectrum of PHTS, without which this review and these management recommendations could not have been written. Our PHTS research has been continuously supported by the American Cancer Society and the Doris Duke Distinguished Clinical Scientist Award, and, recently, by the National Cancer Institute. Dr Charis Eng is the Sondra J and Stephen R Hardis Chair of Cancer Genomic Medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
Author History
Charis Eng, MD, PhD (2001-present)
Heather Hampel, MS; Ohio State University (2001-2006)
Robert Pilarski, MS; Ohio State University (2001-2006)
Jennifer L Stein, MS, CGC; Cleveland Clinic (2006-2009)
Lamis Yehia, PhD (2021-present)
Kevin M Zbuk, MD; Cleveland Clinic (2006-2009)
Revision History
11 February 2021 (sw) Comprehensive update posted live
2 June 2016 (sw) Comprehensive update posted live
23 January 2014 (me) Comprehensive update posted live
19 April 2012 (ce) Somatic
AKT1 pathogenic variants reported to result in Proteus syndrome [
Lindhurst et al 2011]
21 July 2011 (me) Comprehensive update posted live
5 May 2009 (me) Comprehensive update posted live
10 January 2006 (me) Comprehensive update posted live
19 May 2004 (ce) Revision: Genetic Counseling
17 December 2003 (me) Comprehensive update posted live
23 May 2003 (ce) Revision: Differential Diagnosis
29 November 2001 (me) Review posted live
10 July 2001 (ce) Original submission