NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
National Center for Biotechnology Information (US). Genes and Disease [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 1998-.
Alport syndrome (AS) is a genetic disease in which a collagen mutation affects the kidneys, the ears, and the eyes. The syndrome was named for Dr. Alport who in 1927 described a British family in which many members developed renal disease as well as deafness. He noted that affected men in the family died as a result of their kidney problems, whereas females were less affected and lived until old age.
It is now known that most cases of AS are caused by a mutation in the collagen gene COL4A5. This gene encodes for the alpha-5 chain of collagen type IV and is located on the X chromosome. Because women have two X chromosomes (XX), affected women usually have one normal copy and one abnormal copy of the gene. Men only have one copy of the X chromosome (XY). If they inherit the COL4A5 mutation, this abnormal copy of the gene is the only copy they have and the effects are more severe.
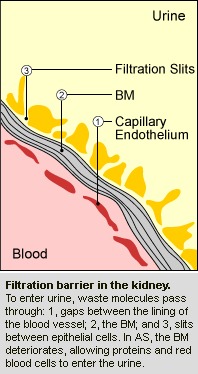
Type IV collagen is found in basement membranes (BM), which are selective barriers between cells. In the kidney, the glomerular BM filters waste products into the urine while keeping useful molecules within the blood stream. In AS, the abnormal collagen disrupts this filter, leading to the loss of proteins and red blood cells into the urine. Blood in the urine (hematuria) is a sign common to all types of AS. In the ear, abnormal collagen in the cochlea results in a progressive deafness in which the ability to hear high tones is lost first. Abnormal collagen can also affect the lens of the eye.
Currently, renal failure due to AS is treated by dialysis or, for some, renal transplantation. However, gene therapy may one day be able to provide a cure for AS by replacing the faulty COL4A5 gene.
Related diseases
- Genome view see gene locations
- Entrez Gene collection of gene-related information
- BLink related sequences in different organisms
- Research articles online full text
- Books online books section
- OMIM catalog of human genes and disorders
- GeneReviews a medical genetics resource
- National Kidney Foundation further information
- GeneLocus Links
- Alport syndrome - Genes and DiseaseAlport syndrome - Genes and Disease
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
