NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Wang Z, Pianosi P, Keogh K, et al. The Clinical Utility of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) in Asthma Management [Internet]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2017 Dec. (Comparative Effectiveness Reviews, No. 197.)

The Clinical Utility of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) in Asthma Management [Internet].
Show details
Figure D.1
Pooled sensitivity, specificity and HSROC curve for diagnosis of asthma when FeNO cutoff <=20 ppb.
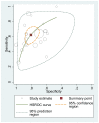
Figure D.2
Pooled sensitivity, specificity and HSROC curve for diagnosis of asthma when FeNO cutoff between 20 and 30 ppb.
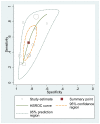
Figure D.3
Pooled sensitivity, specificity and HSROC curve for diagnosis of asthma when FeNO cutoff between 30 and 40 ppb.
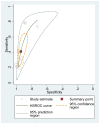
Figure D.4
Pooled sensitivity, specificity and HSROC curve for diagnosis of asthma when FeNO cutoff larger than 40 ppb.
Figure D.5
Asthma Control Test score – FeNO versus other tests in guiding asthma treatments in children and adults. Some estimates were extracted from 2 Cochrane systematic reviews because data were not reported in published trial reports.
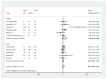
Figure D.6
FEV1% - FeNO versus other tests in guiding asthma treatments in children and adults. Some estimates were extracted from 2 Cochrane systematic reviews because data were not reported in published trial reports.
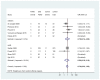
Figure D.7
Hospitalizations - FeNO versus other tests in guiding asthma treatments in children and adults. Some estimates were extracted from 2 Cochrane systematic reviews because data were not reported in published trial reports.
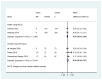
Figure D.8
Quality of life - FeNO versus other tests in guiding asthma treatments in children and adults. AQLQ: Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire; PACQLQS: Pediatric Asthma Caregiver Quality of Life Questionnaire with Standardized activities. Some estimates were (more...)
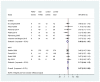
Figure D.9
Exacerbations requiring steroids - FeNO versus other tests in guiding asthma treatments in children and adults. Some estimates were extracted from 2 Cochrane systematic reviews because data were not reported in published trial reports.
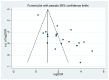
Figure D.10
Funnel plot for FeNO cutoffs <20 ppb.
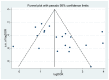
Figure D.11
Funnel plot for FeNO cutoffs 20–30 ppb.
- Figures - The Clinical Utility of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) in Asth...Figures - The Clinical Utility of Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide (FeNO) in Asthma Management
- Peer Reviewers - ADHD Diagnosis and Treatment in Children and AdolescentsPeer Reviewers - ADHD Diagnosis and Treatment in Children and Adolescents
- Acknowledgments - Local Therapies for Unresectable Primary Hepatocellular Carcin...Acknowledgments - Local Therapies for Unresectable Primary Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Preface - Treatments for Fecal IncontinencePreface - Treatments for Fecal Incontinence
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...