NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute (US); 2002-.

PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet].
Show detailsThis PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of childhood bladder cancer. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
Editorial Boards write the PDQ cancer information summaries and keep them up to date. These Boards are made up of experts in cancer treatment and other specialties related to cancer. The summaries are reviewed regularly and changes are made when there is new information. The date on each summary ("Date Last Modified") is the date of the most recent change. The information in this patient summary was taken from the health professional version, which is reviewed regularly and updated as needed, by the PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board.
General Information about Childhood Bladder Cancer
Key Points for This Section
Bladder cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the bladder.
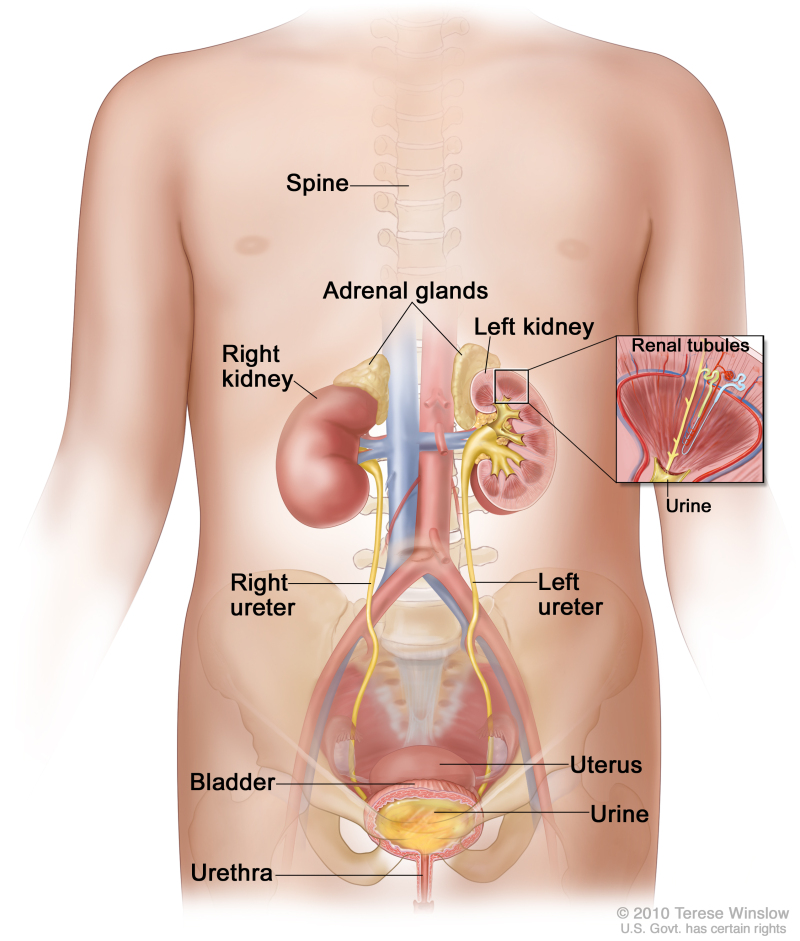
The bladder is a hollow organ in the lower part of the abdomen. It is shaped like a small balloon and has a muscle wall that allows it to get bigger or smaller. Tiny tubules in the kidneys filter and clean the blood. They take out waste products and make urine. The urine passes from each kidney through a long tube called a ureter into the bladder. The bladder holds the urine until it passes through the urethra and leaves the body.
Anatomy of the female urinary system showing the kidneys, adrenal glands, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Urine is made in the renal tubules and collects in the renal pelvis of each kidney. The urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the bladder. The urine is stored in the bladder until it leaves the body through the urethra.
The most common type of bladder cancer is transitional cell cancer. Squamous cell and other more aggressive types of bladder cancer are less common.
Chemotherapy to treat a previous cancer increases the risk of bladder cancer.
Anything that increases your chance of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn't mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your child's doctor if you think your child may be at risk for bladder cancer.
The risk of bladder cancer is increased in children who have been treated for cancer with certain anticancer drugs, called alkylating agents, which include cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, busulfan, and temozolomide.
Signs and symptoms of bladder cancer include blood in the urine and frequent urination.
These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by bladder cancer or by other conditions.
Check with your child’s doctor if your child has any of the following:
- Blood in the urine (slightly rusty to bright red in color).
- Frequent urination or feeling the need to urinate without being able to do so.
- Pain during urination.
- Abdominal or lower back pain.
Tests that examine the bladder are used to help diagnose bladder cancer.
The following tests and procedures may be used:
- Physical exam and health history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health, including checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patient’s health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
- CT scan (CAT scan): A procedure that makes a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body, such as the pelvis, taken from different angles. The pictures are made by a computer linked to an x-ray machine. This procedure is also called computed tomography, computerized tomography, or computerized axial tomography.
- Ultrasound exam: A procedure in which high-energy sound waves (ultrasound) are bounced off internal tissues or organs, such as the pelvis, and make echoes. The echoes form a picture of body tissues called a sonogram. The picture can be printed to be looked at later.
- Cystoscopy: A procedure to look inside the bladder and urethra to check for abnormal areas. A cystoscope is inserted through the urethra into the bladder. A cystoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument with a light and a lens for viewing. It may also have a tool to remove tissue samples, which are checked under a microscope for signs of cancer. If a cystoscopy is not done at diagnosis, tissue samples are removed and checked for cancer during surgery to remove all or part of the bladder.
Stages of Childhood Bladder Cancer
Key Points for This Section
There is no standard staging system for childhood bladder cancer.
The process used to find out if cancer has spread from the bladder to nearby areas or to other parts of the body is called staging. There is no standard system for staging childhood bladder cancer. The results of tests and procedures done to diagnose bladder cancer are used to help make decisions about treatment.
Sometimes childhood bladder cancer recurs (comes back) after treatment.
Treatment Option Overview
Key Points for This Section
There are different types of treatment for children and adolescents with bladder cancer.
Some treatments are standard (the currently used treatment), and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment.
Because cancer in children is rare, taking part in a clinical trial should be considered. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Children and adolescents with bladder cancer should have their treatment planned by a team of doctors who are experts in treating childhood cancer.
Treatment will be overseen by a pediatric oncologist, a doctor who specializes in treating children with cancer. The pediatric oncologist works with other pediatric health professionals who are experts in treating children with cancer and who specialize in certain areas of medicine. This may include the following specialists and others:
- Pediatric urologist.
One type of standard treatment is used for bladder cancer.
New types of treatment are being tested in clinical trials.
This summary section describes treatments that are being studied in clinical trials. It may not mention every new treatment being studied. Information about clinical trials is available from the NCI website.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy is a treatment that uses drugs or other substances to identify and attack cancer cells. Targeted therapies usually cause less harm to normal cells than chemotherapy and radiation therapy do.
Targeted therapy is being studied for the treatment of childhood bladder cancer that has recurred (come back).
Treatment for childhood bladder cancer may cause side effects.
For information about side effects that begin during treatment for cancer, see our Side Effects page.
Side effects from cancer treatment that begin after treatment and continue for months or years are called late effects. Late effects of cancer treatment may include:
- Physical problems.
- Changes in mood, feelings, thinking, learning, or memory.
- Second cancers (new types of cancer) or other conditions.
Some late effects may be treated or controlled. It is important to talk with your child's doctors about the possible late effects caused by some treatments. See the PDQ summary on Late Effects of Treatment for Childhood Cancer for more information.
Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial.
For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
Many of today's standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment.
Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward.
Patients can enter clinical trials before, during, or after starting their cancer treatment.
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring (coming back) or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCI’s clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Follow-up tests may be needed.
Some of the tests that were done to diagnose the cancer or to find out the stage of the cancer may be repeated. Some tests will be repeated in order to see how well the treatment is working. Decisions about whether to continue, change, or stop treatment may be based on the results of these tests.
Some of the tests will continue to be done from time to time after treatment has ended. The results of these tests can show if your child's condition has changed or if the cancer has recurred (come back). These tests are sometimes called follow-up tests or check-ups.
Treatment of Childhood Bladder Cancer
For more information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of newly diagnosed bladder cancer in children is usually the following:
- Surgery to remove part of the bladder. Transurethral resection (TUR) is a surgical procedure to remove tissue from the bladder using a resectoscope inserted into the bladder through the urethra. A resectoscope is a thin, tube-like instrument with a light, a lens for viewing, and a tool to remove tissue and burn away any remaining tumor cells. Tissue samples from the area where the tumor was removed are checked under a microscope for signs of cancer.
- Surgery to remove the bladder (rare).
Talk to your child’s doctor about how this type of surgery can affect urinating, sexual function, and fertility.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Treatment of Recurrent Childhood Bladder Cancer
For more information about the treatment listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of recurrent bladder cancer in children may include the following:
- A clinical trial that checks a sample of the patient's tumor for certain gene changes. The type of targeted therapy that will be given to the patient depends on the type of gene change.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
To Learn More About Childhood Bladder Cancer
For more information from the National Cancer Institute about bladder cancer, see the following:
For more childhood cancer information and other general cancer resources, see the following:
About This PDQ Summary
About PDQ
Physician Data Query (PDQ) is the National Cancer Institute's (NCI's) comprehensive cancer information database. The PDQ database contains summaries of the latest published information on cancer prevention, detection, genetics, treatment, supportive care, and complementary and alternative medicine. Most summaries come in two versions. The health professional versions have detailed information written in technical language. The patient versions are written in easy-to-understand, nontechnical language. Both versions have cancer information that is accurate and up to date and most versions are also available in Spanish.
PDQ is a service of the NCI. The NCI is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). NIH is the federal government’s center of biomedical research. The PDQ summaries are based on an independent review of the medical literature. They are not policy statements of the NCI or the NIH.
Purpose of This Summary
This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of childhood bladder cancer. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
Reviewers and Updates
Editorial Boards write the PDQ cancer information summaries and keep them up to date. These Boards are made up of experts in cancer treatment and other specialties related to cancer. The summaries are reviewed regularly and changes are made when there is new information. The date on each summary ("Updated") is the date of the most recent change.
The information in this patient summary was taken from the health professional version, which is reviewed regularly and updated as needed, by the PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board.
Clinical Trial Information
A clinical trial is a study to answer a scientific question, such as whether one treatment is better than another. Trials are based on past studies and what has been learned in the laboratory. Each trial answers certain scientific questions in order to find new and better ways to help cancer patients. During treatment clinical trials, information is collected about the effects of a new treatment and how well it works. If a clinical trial shows that a new treatment is better than one currently being used, the new treatment may become "standard." Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Clinical trials can be found online at NCI's website. For more information, call the Cancer Information Service (CIS), NCI's contact center, at 1-800-4-CANCER (1-800-422-6237).
Permission to Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as “NCI’s PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: [include excerpt from the summary].”
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Childhood Bladder Cancer Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated <MM/DD/YYYY>. Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/types/bladder/patient/child-bladder-treatment-pdq. Accessed <MM/DD/YYYY>.
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author(s), artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 3,000 scientific images.
Disclaimer
The information in these summaries should not be used to make decisions about insurance reimbursement. More information on insurance coverage is available on Cancer.gov on the Managing Cancer Care page.
Contact Us
More information about contacting us or receiving help with the Cancer.gov website can be found on our Contact Us for Help page. Questions can also be submitted to Cancer.gov through the website’s E-mail Us.
- Review Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.[PDQ Cancer Information Summari...]Review Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries. 2002
- Review Childhood Heart Tumors (PDQ®): Patient Version.[PDQ Cancer Information Summari...]Review Childhood Heart Tumors (PDQ®): Patient Version.PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries. 2002
- Review Childhood Melanoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.[PDQ Cancer Information Summari...]Review Childhood Melanoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries. 2002
- Review Childhood Chordoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.[PDQ Cancer Information Summari...]Review Childhood Chordoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries. 2002
- Review Childhood Mesothelioma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.[PDQ Cancer Information Summari...]Review Childhood Mesothelioma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries. 2002
- Childhood Bladder Cancer Treatment (PDQ®) - PDQ Cancer Information SummariesChildhood Bladder Cancer Treatment (PDQ®) - PDQ Cancer Information Summaries
- Prostate Cancer Treatment (PDQ®) - PDQ Cancer Information SummariesProstate Cancer Treatment (PDQ®) - PDQ Cancer Information Summaries
- Childhood Colorectal Cancer Treatment (PDQ®) - PDQ Cancer Information SummariesChildhood Colorectal Cancer Treatment (PDQ®) - PDQ Cancer Information Summaries
- Esophageal Cancer Prevention (PDQ®) - PDQ Cancer Information SummariesEsophageal Cancer Prevention (PDQ®) - PDQ Cancer Information Summaries
- yu77g06.s1 Soares fetal liver spleen 1NFLS Homo sapiens cDNA clone IMAGE:239866 ...yu77g06.s1 Soares fetal liver spleen 1NFLS Homo sapiens cDNA clone IMAGE:239866 3', mRNA sequencegi|1058728|gnl|dbEST|382938|gb|H806Nucleotide
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...