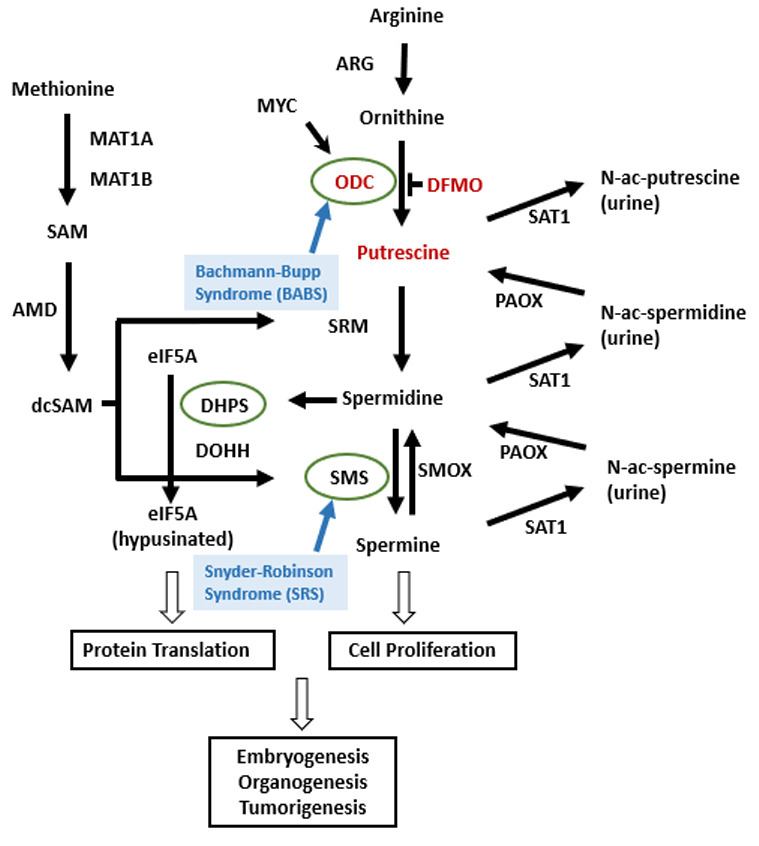
From: Bachmann-Bupp Syndrome
GeneReviews® chapters are owned by the University of Washington. Permission is hereby granted to reproduce, distribute, and translate copies of content materials for noncommercial research purposes only, provided that (i) credit for source (http://www.genereviews.org/) and copyright (© 1993-2024 University of Washington) are included with each copy; (ii) a link to the original material is provided whenever the material is published elsewhere on the Web; and (iii) reproducers, distributors, and/or translators comply with the GeneReviews® Copyright Notice and Usage Disclaimer. No further modifications are allowed. For clarity, excerpts of GeneReviews chapters for use in lab reports and clinic notes are a permitted use.
For more information, see the GeneReviews® Copyright Notice and Usage Disclaimer.
For questions regarding permissions or whether a specified use is allowed, contact: ude.wu@tssamda.