From: Regulation of the Rod Photoreceptor Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated Channel

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
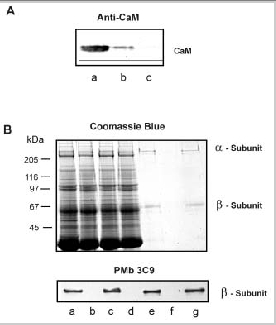
Interaction of the channel with CaM-Sepharose in the presence ROS soluble fraction with and without endogeneous CaM. A) Depletion of CaM from the ROS soluble fraction. ROS were lysed in hypotonic buffer containing EDTA and the soluble fraction containing CaM was separated from the membrane fraction by centrifugation. CaM was removed from the ROS soluble fraction on an CaM antibody-Sepharose affinity matrix. Western blots of ROS lysate (lane a), ROS lysate diluted 1:10 (lane b), ROS lysate depleted of calmodulin (lane c) were labeled with an antiCaM antibody. B) ROS membranes were washed in a hypotonic buffer containing 2 μM EDTA and solubilized in CHAPS. CaM-Sepharose was incubated with solubilized ROS in the presence of CaCl2 and containing either HEPES buffer (HEPES control); ROS soluble fraction containing endogenous CaM (+CaM); or ROS soluble fraction depleted of CaM (CaM). The unbound fraction from the CaM-Sepharose was separated from the bound, EDTA eluted fraction. SDS gels were stained with Coomassie Blue and Western blots were labeled for the β-subunit with the PMb 3C9 monoclonal antibody. Lane a: bovine ROS; lane b: unbound fraction (HEPES control); lane c: unbound fraction (+CaM); lane d: unbound fraction (CaM); lane e: bound fraction (HEPES control); lane f : bound fraction (+CaM); lane g: bound fraction (CaM). Endogenous CaM inhibited the binding of the channel to CaM-Sepharose.
From: Regulation of the Rod Photoreceptor Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated Channel

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.