NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute (US); 2002-.

PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet].
Show detailsThis PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of childhood Hodgkin lymphoma. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
Editorial Boards write the PDQ cancer information summaries and keep them up to date. These Boards are made up of experts in cancer treatment and other specialties related to cancer. The summaries are reviewed regularly and changes are made when there is new information. The date on each summary ("Date Last Modified") is the date of the most recent change. The information in this patient summary was taken from the health professional version, which is reviewed regularly and updated as needed, by the PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board.
General Information About Childhood Hodgkin Lymphoma
Key Points for This Section
Childhood Hodgkin lymphoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lymph system.
Childhood Hodgkin lymphoma is a type of cancer that develops in the lymph system, which is part of the body's immune system. The immune system protects the body from foreign substances, infection, and diseases. The lymph system is made up of the following:
- Lymph: Colorless, watery fluid that carries white blood cells called lymphocytes through the lymph system. Lymphocytes protect the body against infections and the growth of tumors.
- Lymph vessels: A network of thin tubes that collect lymph from different parts of the body and return it to the bloodstream.
- Lymph nodes: Small, bean-shaped structures that filter lymph and store white blood cells that help fight infection and disease. Lymph nodes are located along the network of lymph vessels found throughout the body. Clusters of lymph nodes are found in the neck, underarm, abdomen, pelvis, and groin.
- Thymus: An organ in which lymphocytes grow and multiply. The thymus is in the chest behind the breastbone.
- Bone marrow: The soft, spongy tissue in the center of large bones. Bone marrow makes white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets.
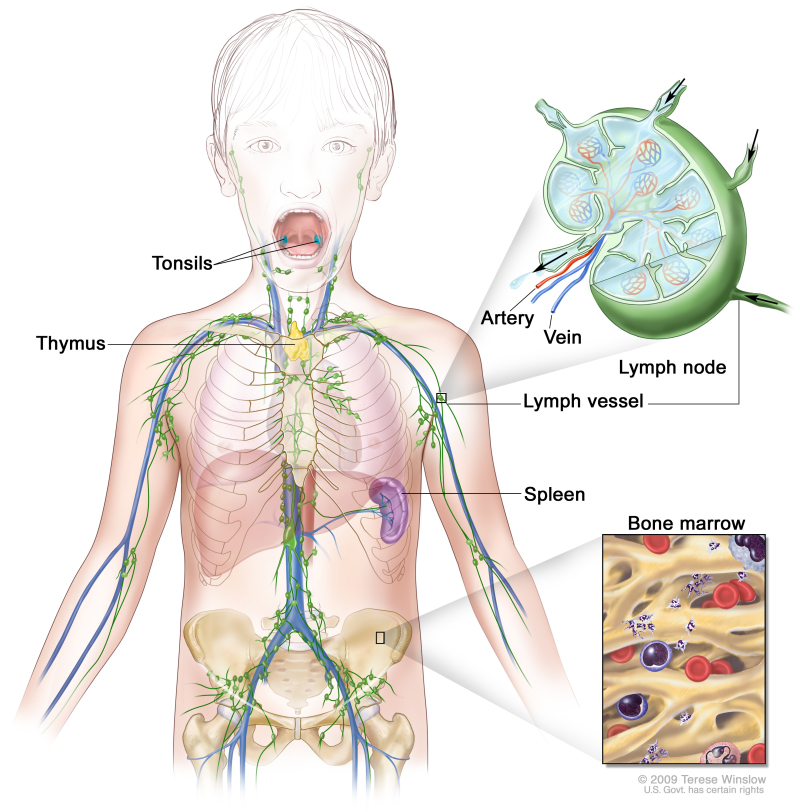
Anatomy of the lymph system, showing the lymph vessels and lymph organs including lymph nodes, tonsils, thymus, spleen, and bone marrow. Lymph (clear fluid) and lymphocytes travel through the lymph vessels and into the lymph nodes where the lymphocytes destroy harmful substances. The lymph enters the blood through a large vein near the heart.
Lymph tissue is also found in other parts of the body such as the stomach, thyroid gland, brain, and skin.
There are two general types of lymphoma: Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. (See the PDQ summary on Childhood Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment for more information.)
Hodgkin lymphoma often occurs in adolescents 15 to 19 years of age. The treatment for children and adolescents is different than treatment for adults. (See the PDQ summary on Adult Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment for more information.)
There are two types of childhood Hodgkin lymphoma.
The two types of childhood Hodgkin lymphoma are:
Classical Hodgkin lymphoma is divided into four subtypes, based on how the cancer cells look under a microscope:
- Lymphocyte-rich classical Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Nodular sclerosis Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Mixed cellularity Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Lymphocyte-depleted Hodgkin lymphoma.
Epstein-Barr virus infection increases the risk of childhood Hodgkin lymphoma.
Anything that increases your risk of getting a disease is called a risk factor. Having a risk factor does not mean that you will get cancer; not having risk factors doesn’t mean that you will not get cancer. Talk with your child’s doctor if you think your child may be at risk.
Risk factors for childhood Hodgkin lymphoma include the following:
- Being infected with the Epstein-Barr virus.
- Being infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
- Having certain diseases of the immune system.
- Having a personal history of mononucleosis ("mono").
- Having a parent or sibling with a personal history of Hodgkin lymphoma.
Being exposed to common infections in early childhood may decrease the risk of Hodgkin lymphoma in children because of the effect it has on the immune system.
Signs of childhood Hodgkin lymphoma include swollen lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, and weight loss.
These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by childhood Hodgkin lymphoma or by other conditions. Check with your child's doctor if your child has any of the following:
- Painless, swollen lymph nodes near the collarbone or in the neck, chest, underarm, or groin.
- Fever for no known reason.
- Weight loss for no known reason.
- Night sweats.
- Itchy skin.
- Pain in the lymph nodes after drinking alcohol.
Fever, weight loss, and night sweats are called B symptoms.
Tests that examine the lymph system are used to detect (find) and diagnose childhood Hodgkin lymphoma.
The following tests and procedures may be used:
- Physical exam and history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health, including checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patient's health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
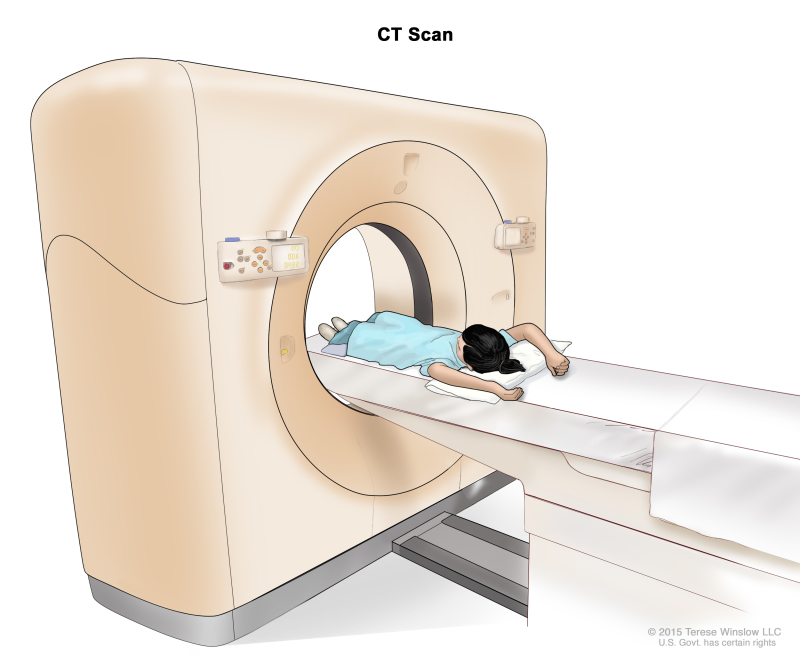
- CT scan (CAT scan): A procedure that makes a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body, such as the neck, chest, abdomen, or pelvis, taken from different angles. The pictures are made by a computer linked to an x-ray machine. A dye may be injected into a vein or swallowed to help the organs or tissues show up more clearly. This procedure is also called computed tomography, computerized tomography, or computerized axial tomography.
- PET scan (positron emission tomography scan): A procedure to find malignant tumor cells in the body. A small amount of radioactive glucose (sugar) is injected into a vein. The PET scanner rotates around the body and makes a picture of where glucose is being used in the body. Malignant tumor cells show up brighter in the picture because they are more active and take up more glucose than normal cells do. Sometimes a PET scan and a CT scan are done at the same time. If there is any cancer, this increases the chance that it will be found.
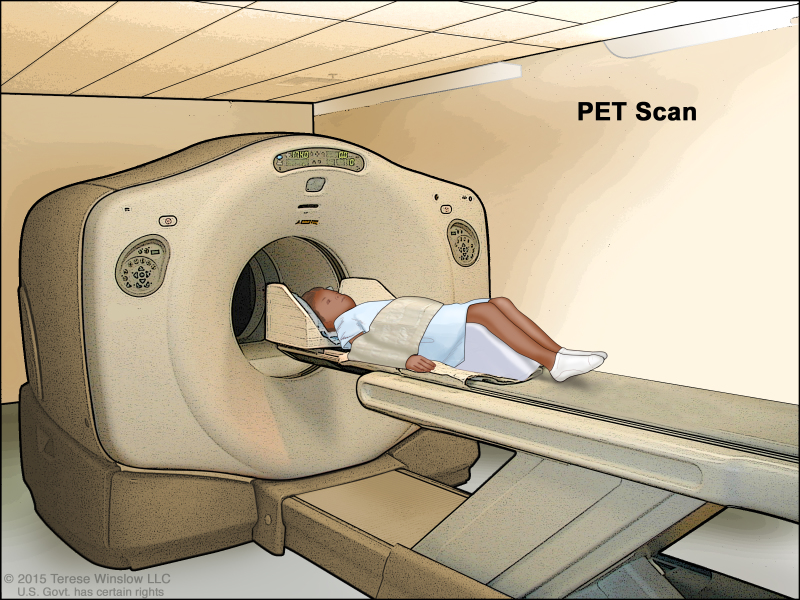
Positron emission tomography (PET) scan. The child lies on a table that slides through the PET scanner. The head rest and white strap help the child lie still. A small amount of radioactive glucose (sugar) is injected into the child's vein, and a scanner makes a picture of where the glucose is being used in the body. Cancer cells show up brighter in the picture because they take up more glucose than normal cells do.
- Chest x-ray: An x-ray of the organs and bones inside the chest. An x-ray is a type of energy beam that can go through the body and onto film, making a picture of areas inside the body.
- Complete blood count (CBC): A procedure in which a sample of blood is drawn and checked for the following:
- -
The number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- -
The amount of hemoglobin (the protein that carries oxygen) in the red blood cells.
- -
The portion of the blood sample made up of red blood cells.
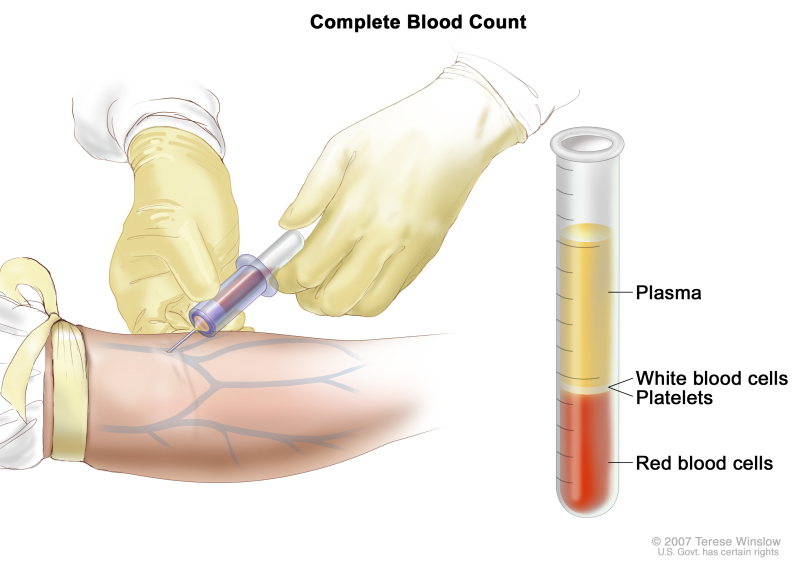
Complete blood count (CBC). Blood is collected by inserting a needle into a vein and allowing the blood to flow into a tube. The blood sample is sent to the laboratory and the red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are counted. The CBC is used to test for, diagnose, and monitor many different conditions.
- Blood chemistry studies: A procedure in which a blood sample is checked to measure the amounts of certain substances released into the blood by organs and tissues in the body. An unusual (higher or lower than normal) amount of a substance can be a sign of disease.
- Sedimentation rate: A procedure in which a sample of blood is drawn and checked for the rate at which the red blood cells settle to the bottom of the test tube. The sedimentation rate is a measure of how much inflammation is in the body. A higher than normal sedimentation rate may be a sign of lymphoma. Also called erythrocyte sedimentation rate, sed rate, or ESR.
- Lymph node biopsy: The removal of all or part of a lymph node. The lymph node may be removed during an image-guided CT scan or a thoracoscopy, mediastinoscopy, or laparoscopy. One of the following types of biopsies may be done:
- -
Excisional biopsy: The removal of an entire lymph node.
- -
Incisional biopsy: The removal of part of a lymph node.
- -
Core biopsy: The removal of tissue from a lymph node using a wide needle.
- -
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy: The removal of tissue from a lymph node using a thin needle.
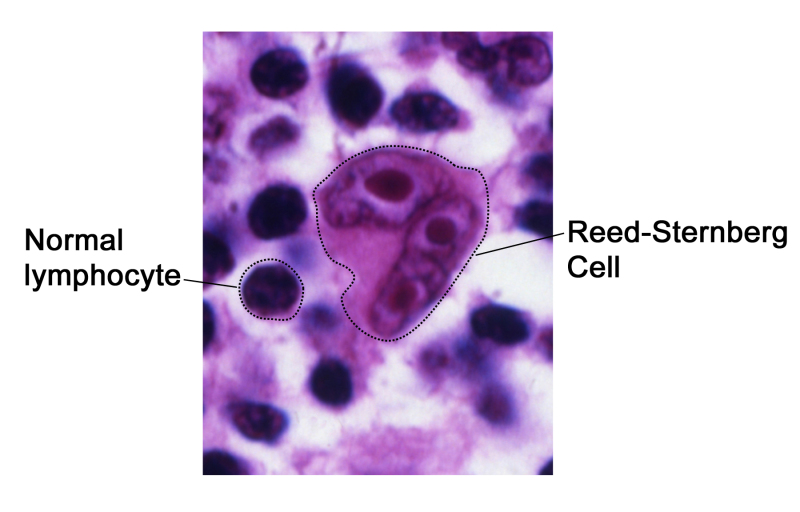
A pathologist views the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells, especially Reed-Sternberg cells. Reed-Sternberg cells are common in classical Hodgkin lymphoma.The following test may be done on tissue that was removed:- Immunophenotyping: A laboratory test used to identify cells, based on the types of antigens or markers on the surface of the cell. This test is used to diagnose the specific type of lymphoma by comparing the cancer cells to normal cells of the immune system.
Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
The prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options depend on the following:
- The stage of the cancer.
- The size of the tumor.
- Whether there are B symptoms at diagnosis.
- The type of Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Certain features of the cancer cells.
- Whether there are too many white blood cells or too few red blood cells at the time of diagnosis.
- How well the tumor responds to initial treatment with chemotherapy.
- Whether the cancer is newly diagnosed or has recurred (come back).
The treatment options also depend on:
- The child's age and sex.
- The risk of long-term side effects.
Most children and adolescents with newly diagnosed Hodgkin lymphoma can be cured.
Stages of Childhood Hodgkin Lymphoma
Key Points for This Section
After childhood Hodgkin lymphoma has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if cancer cells have spread within the lymph system or to other parts of the body.
The process used to find out if cancer has spread within the lymph system or to other parts of the body is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process determines the stage of the disease. Treatment is based on the stage and other factors that affect prognosis.
The following tests and procedures may be used in the staging process:
- CT scan (CAT scan): A procedure that makes a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body, such as the neck, chest, abdomen, or pelvis, taken from different angles. The pictures are made by a computer linked to an x-ray machine. A dye may be injected into a vein or swallowed to help the organs or tissues show up more clearly. This procedure is also called computed tomography, computerized tomography, or computerized axial tomography.
- PET scan (positron emission tomography scan): A procedure to find malignant tumor cells in the body. A small amount of radioactive glucose (sugar) is injected into a vein. The PET scanner rotates around the body and makes a picture of where glucose is being used in the body. Malignant tumor cells show up brighter in the picture because they are more active and take up more glucose than normal cells do. Sometimes a PET scan and a CT scan are done at the same time. If there is any cancer, this increases the chance that it will be found.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging): A procedure that uses a magnet, radio waves, and a computer to make a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body. This procedure is also called nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMRI). An MRI of the abdomen and pelvis may be done.
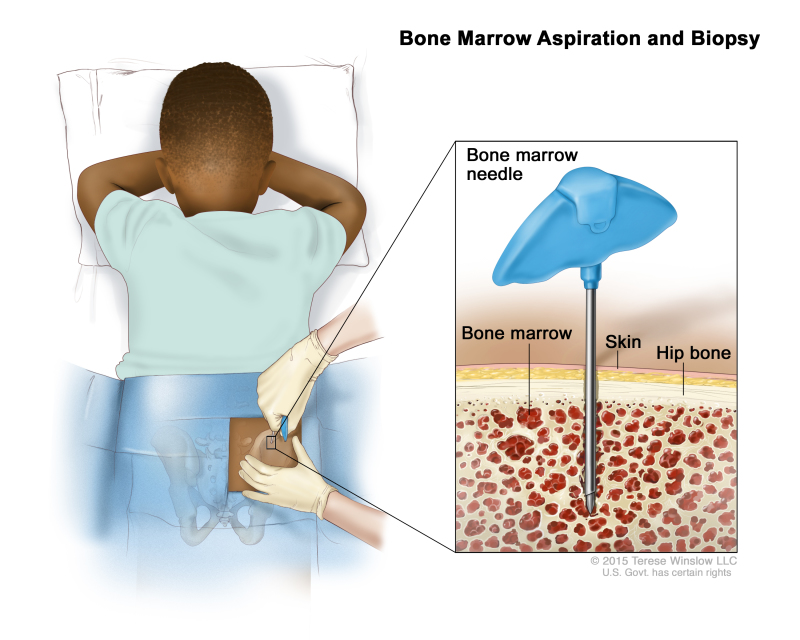
- Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy: The removal of bone marrow and a small piece of bone by inserting a hollow needle into the hipbone or breastbone. A pathologist views the bone marrow and bone under a microscope to look for abnormal cells.
There are three ways that cancer spreads in the body.
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Stages of childhood Hodgkin lymphoma may include A, B, E, and S.
Childhood Hodgkin lymphoma may be described as follows:
The following stages are used for childhood Hodgkin lymphoma:
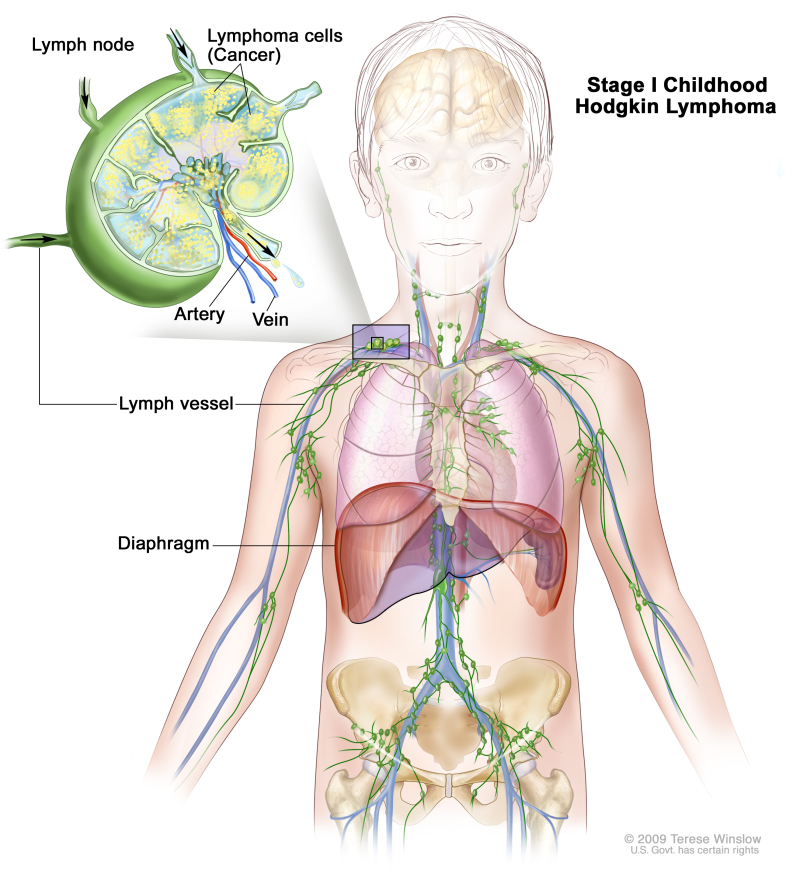
Stage I
Stage I childhood Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer is found in one or more lymph nodes in one lymph node group. In stage IE (not shown), cancer is found outside the lymph nodes in one organ or area.
Stage I is divided into stage I and stage IE.
- Stage I: Cancer is found in one of the following places in the lymph system:
- One or more lymph nodes in one lymph node group.
- Waldeyer's ring.
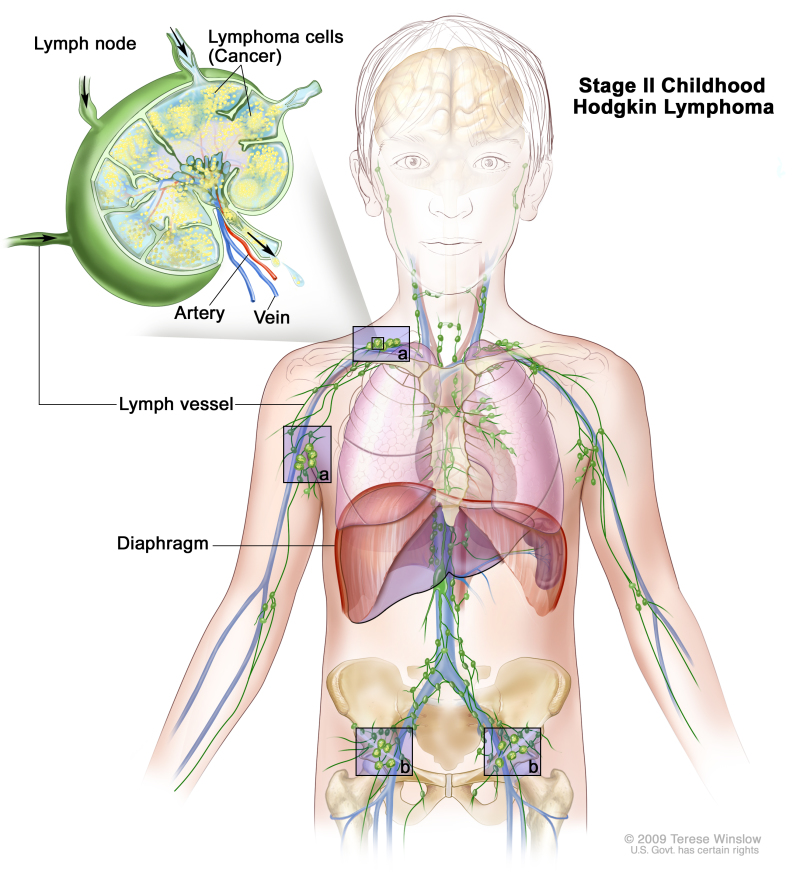
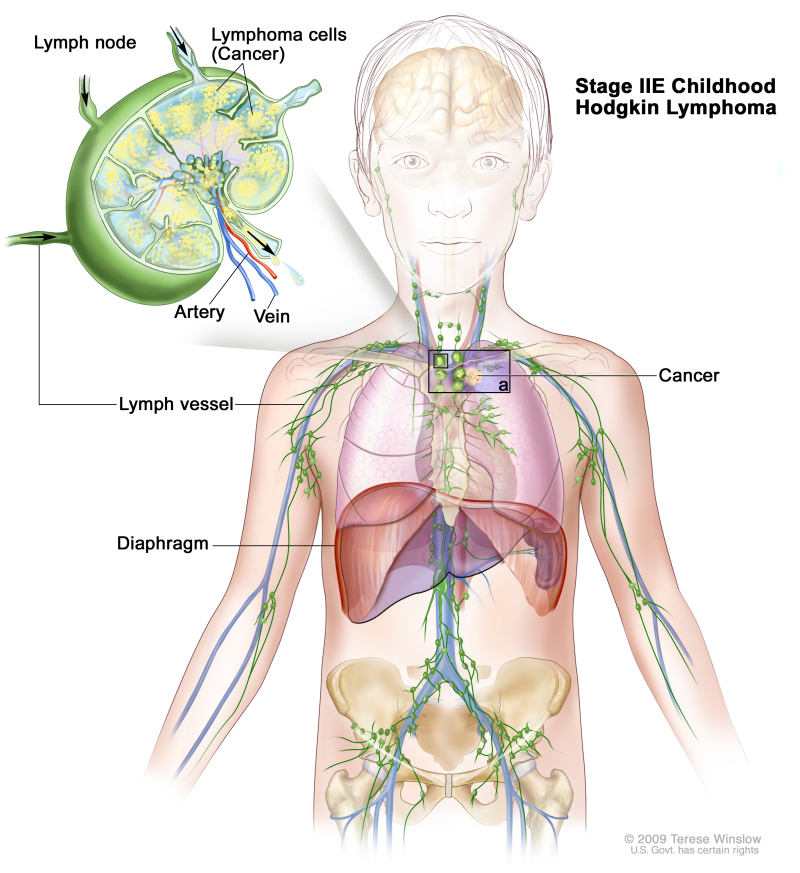
Stage II
Stage II is divided into stage II and stage IIE.
- Stage IIE: Cancer is found in one or more lymph node groups either above or below the diaphragm and outside the lymph nodes in a nearby organ or area.
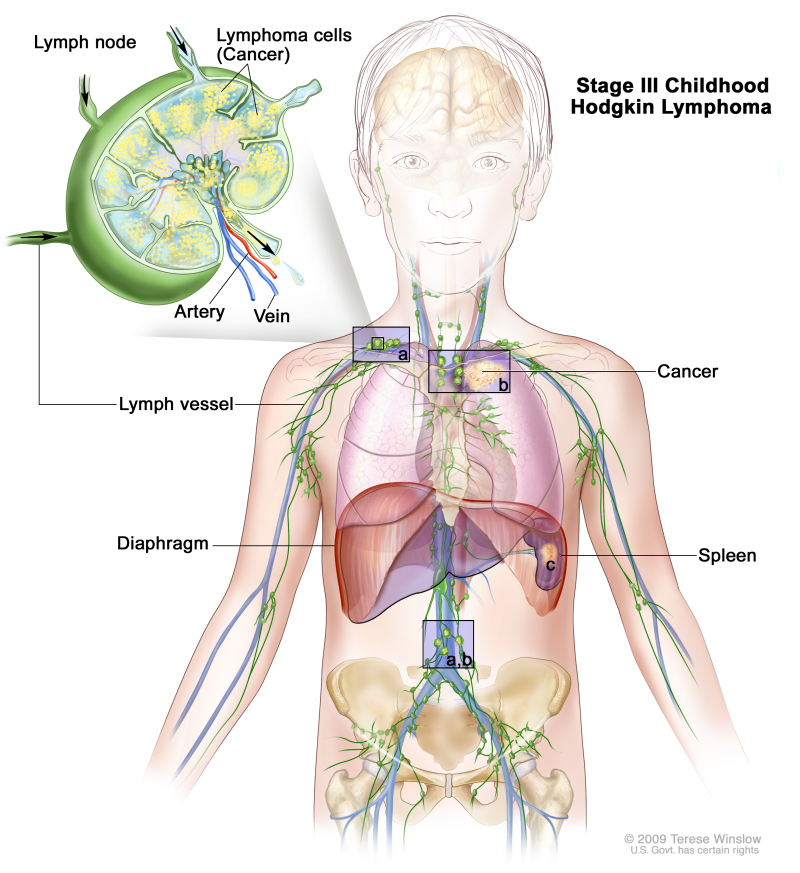
Stage III
Stage III childhood Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer is found in one or more lymph node groups above and below the diaphragm (a). In stage IIIE, cancer is found in lymph node groups above and below the diaphragm and outside the lymph nodes in a nearby organ or area (b). In stage IIIS, cancer is found in lymph node groups above and below the diaphragm (a) and in the spleen (c). In stage IIIS plus E, cancer is found in lymph node groups above and below the diaphragm, outside the lymph nodes in a nearby organ or area (b), and in the spleen (c).
Stage III is divided into stage III, stage IIIE, stage IIIS, and stage IIIE,S.
- Stage IIIE: Cancer is found in lymph node groups above and below the diaphragm and outside the lymph nodes in a nearby organ or area.
- Stage IIIE,S: Cancer is found in lymph node groups above and below the diaphragm, outside the lymph nodes in a nearby organ or area, and in the spleen.
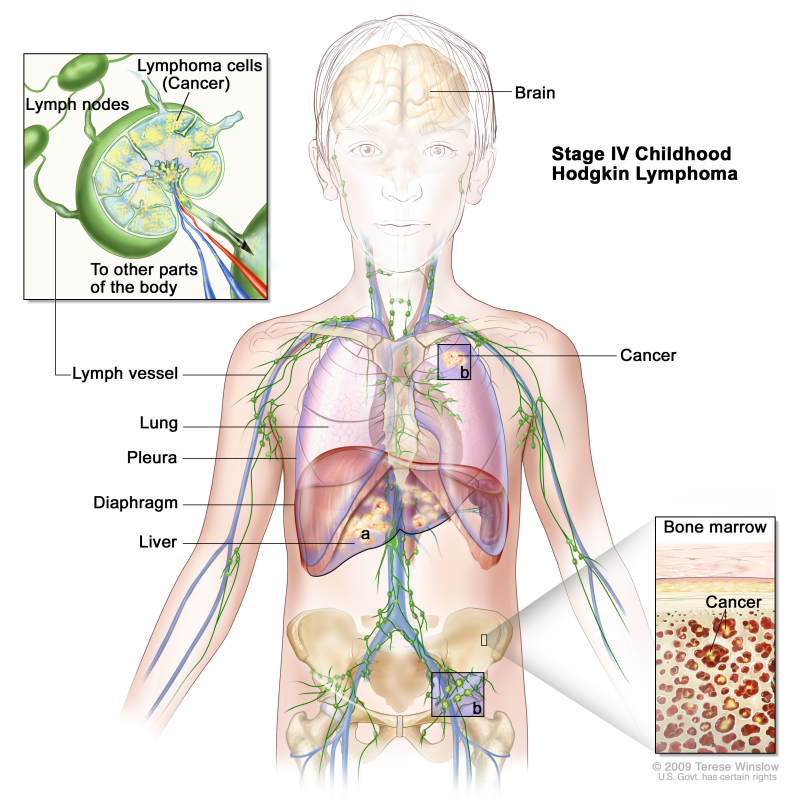
Stage IV
Stage IV childhood Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer is found outside the lymph nodes throughout one or more organs (a); or outside the lymph nodes in one organ and has spread to lymph nodes far away from that organ (b); or in the lung, liver, or bone marrow.
- is found outside the lymph nodes throughout one or more organs, and may be in lymph nodes near those organs; or
- is found outside the lymph nodes in one organ and has spread to areas far away from that organ; or
- is found in the lung, liver, bone marrow, or cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The cancer has not spread to the lung, liver, bone marrow, or CSF from nearby areas.
Untreated Hodgkin lymphoma is divided into risk groups.
Untreated childhood Hodgkin lymphoma is divided into risk groups based on the stage, size of the tumor, and whether the patient has B symptoms (fever, weight loss, or night sweats). The risk group is used to plan treatment.
Primary Refractory/Recurrent Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children and Adolescents
Primary refractory Hodgkin lymphoma is lymphoma that continues to grow or spread during treatment.
Recurrent Hodgkin lymphoma is cancer that has recurred (come back) after it has been treated. The lymphoma may come back in the lymph system or in other parts of the body, such as the lungs, liver, bones, or bone marrow.
Treatment Option Overview
Key Points for This Section
There are different types of treatment for children with Hodgkin lymphoma.
Different types of treatment are available for children with Hodgkin lymphoma. Some treatments are standard and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment.
Because cancer in children is rare, taking part in a clinical trial should be considered. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Children with Hodgkin lymphoma should have their treatment planned by a team of health care providers who are experts in treating childhood cancer.
Treatment will be overseen by a pediatric oncologist, a doctor who specializes in treating children with cancer. The pediatric oncologist works with other pediatric health care providers who are experts in treating children with Hodgkin lymphoma and who specialize in certain areas of medicine. These may include the following specialists:
The treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma in adolescents and young adults may be different than the treatment for children. Some adolescents and young adults are treated with an adult treatment regimen.
Treatment for childhood Hodgkin lymphoma may cause side effects.
For information about side effects that begin during treatment for cancer, see our Side Effects page.
Side effects from cancer treatment that begin after treatment and continue for months or years are called late effects. Because late effects affect health and development, regular follow-up exams are important.
Late effects of cancer treatment may include the following:
- Physical problems that affect the following:
- -
Development of sex and reproductive organs.
- -
Fertility (ability to have children).
- -
Bone and muscle growth and development.
- -
- -
Teeth, gums, and salivary gland function.
- -
- Changes in mood, feelings, thinking, learning, or memory.
- Second cancers (new types of cancer).
For female survivors of Hodgkin lymphoma, there is an increased risk of breast cancer. This risk depends on the amount of radiation therapy they received to the breast during treatment and the chemotherapy regimen used. The risk of breast cancer is decreased if these female survivors also received radiation therapy to the ovaries.
It is suggested that female survivors who received radiation therapy to the breast have a mammogram once a year starting 8 years after treatment or at age 25 years, whichever is later. Female survivors of childhood Hodgkin lymphoma who have breast cancer have an increased risk of dying from the disease compared to patients with no history of Hodgkin lymphoma who have breast cancer.
Some late effects may be treated or controlled. It is important to talk with your child's doctors about the possible late effects caused by some treatments. (See the PDQ summary on Late Effects of Treatment for Childhood Cancer for more information).
Five types of standard treatment are used:
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body (systemic chemotherapy). When chemotherapy is placed directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, an organ, or a body cavity such as the abdomen, the drugs mainly affect cancer cells in those areas (regional chemotherapy). Combination chemotherapy is treatment using more than one anticancer drug.
The way the chemotherapy is given depends on the risk group. For example, children with low-risk Hodgkin lymphoma receive fewer cycles of treatment, fewer anticancer drugs, and lower doses of anticancer drugs than children with high-risk lymphoma.
See Drugs Approved for Hodgkin Lymphoma for more information.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. There are two types of radiation therapy:
- External radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the cancer. Certain ways of giving radiation therapy can help keep radiation from damaging nearby healthy tissue. These types of external radiation therapy include the following:
- -
Conformal radiation therapy: Conformal radiation therapy is a type of external radiation therapy that uses a computer to make a 3-dimensional (3-D) picture of the tumor and shapes the radiation beams to fit the tumor.
- -
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT): IMRT is a type of 3-dimensional (3-D) radiation therapy that uses a computer to make pictures of the size and shape of the tumor. Thin beams of radiation of different intensities (strengths) are aimed at the tumor from many angles.
- Internal radiation therapy uses a radioactive substance sealed in needles, seeds, wires, or catheters that are placed directly into or near the cancer.
Radiation therapy may be given, based on the child’s risk group and chemotherapy regimen. External radiation therapy is used to treat childhood Hodgkin lymphoma. The radiation is given only to the lymph nodes or other areas with cancer. Internal radiation therapy is not used to treat Hodgkin lymphoma.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs or other substances to identify and attack specific cancer cells without harming normal cells. Monoclonal antibody therapy and proteasome inhibitor therapy are being used in the treatment of childhood Hodgkin lymphoma.
Monoclonal antibody therapy is a cancer treatment that uses antibodies made in the laboratory from a single type of immune system cell. These antibodies can identify substances on cancer cells or normal substances that may help cancer cells grow. The antibodies attach to the substances and kill the cancer cells, block their growth, or keep them from spreading. Monoclonal antibodies are given by infusion. They may be used alone or to carry drugs, toxins, or radioactive material directly to cancer cells.
In children, rituximab may be used to treat refractory or recurrent Hodgkin lymphoma. Brentuximab, nivolumab, pembrolizumab, and atezolizumab are monoclonal antibodies being studied to treat children.
Proteasome inhibitor therapy is a type of targeted therapy that blocks the action of proteasomes in cancer cells. Proteasomes remove proteins no longer needed by the cell. When the proteasomes are blocked, the proteins build up in the cell and may cause the cancer cell to die. Bortezomib is a proteasome inhibitor used to treat refractory or recurrent childhood Hodgkin lymphoma.
Surgery
Surgery may be done to remove as much of the tumor as possible for localized nodular lymphocyte-predominant childhood Hodgkin lymphoma.
High-dose chemotherapy with stem cell transplant
High-dose chemotherapy with stem cell transplant is a way of giving high doses of chemotherapy and replacing blood-forming cells destroyed by the cancer treatment. Stem cells (immature blood cells) are removed from the blood or bone marrow of the patient or a donor and are frozen and stored. After the chemotherapy is completed, the stored stem cells are thawed and given back to the patient through an infusion. These reinfused stem cells grow into (and restore) the body's blood cells.
See Drugs Approved for Hodgkin Lymphoma for more information.
New types of treatment are being tested in clinical trials.
This summary section describes treatments that are being studied in clinical trials. It may not mention every new treatment being studied. Information about clinical trials is available from the NCI website.
Proton beam radiation therapy
Proton-beam therapy is a type of high-energy, external radiation therapy that uses streams of protons (small, positively-charged particles of matter) to make radiation. This type of radiation therapy may help lessen the damage to healthy tissue near the tumor.
Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial.
For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
Many of today's standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment.
Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward.
Patients can enter clinical trials before, during, or after starting their cancer treatment.
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring (coming back) or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. Information about clinical trials supported by NCI can be found on NCI’s clinical trials search webpage. Clinical trials supported by other organizations can be found on the ClinicalTrials.gov website.
Follow-up tests may be needed.
Some of the tests that were done to diagnose the cancer or to find out the stage of the cancer may be repeated. Some tests will be repeated in order to see how well the treatment is working. Decisions about whether to continue, change, or stop treatment may be based on the results of these tests.
Some of the tests will continue to be done from time to time after treatment has ended. The results of these tests can show if your child's condition has changed or if the cancer has recurred (come back). These tests are sometimes called follow-up tests or check-ups.
For patients who receive chemotherapy alone, a PET scan may be done 3 weeks or more after treatment ends. For patients who receive radiation therapy last, a PET scan should not be done until 8 to 12 weeks after treatment.
Treatment Options for Children and Adolescents with Hodgkin Lymphoma
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Low-Risk Classical Childhood Hodgkin Lymphoma
Treatment of low-risk classical childhood Hodgkin lymphoma may include the following:
- Radiation therapy may also be given to the areas with cancer.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Intermediate-Risk Classical Childhood Hodgkin Lymphoma
Treatment of intermediate-risk classical childhood Hodgkin lymphoma may include the following:
- Radiation therapy may also be given to the areas with cancer.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
High-Risk Classical Childhood Hodgkin Lymphoma
Treatment of high-risk classical childhood Hodgkin lymphoma may include the following:
- Higher dose combination chemotherapy.
- Radiation therapy may also be given to the areas with cancer.
- A clinical trial of targeted therapy and combination chemotherapy. Radiation therapy may also be given to the areas with cancer.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Nodular Lymphocyte-Predominant Childhood Hodgkin Lymphoma
Treatment of nodular lymphocyte-predominant childhood Hodgkin lymphoma may include the following:
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
Treatment Options for Primary Refractory/Recurrent Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children and Adolescents
For information about the treatments listed below, see the Treatment Option Overview section.
Treatment of primary refractory or recurrent childhood Hodgkin lymphoma may include the following:
- High-dose chemotherapy with stem cell transplant using the patient's own stem cells. Low-dose radiation therapy or monoclonal antibody therapy (brentuximab) may be given after the transplant.
- High-dose chemotherapy with stem cell transplant using a donor's stem cells.
- Monoclonal antibody therapy (brentuximab) in patients whose disease recurred after a stem cell transplant using the patient's own stem cells.
Use our clinical trial search to find NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are accepting patients. You can search for trials based on the type of cancer, the age of the patient, and where the trials are being done. General information about clinical trials is also available.
To Learn More About Childhood Hodgkin Lymphoma
For more information from the National Cancer Institute about childhood Hodgkin lymphoma, see the following:
For more childhood cancer information and other general cancer resources, see the following:
About This PDQ Summary
About PDQ
Physician Data Query (PDQ) is the National Cancer Institute's (NCI's) comprehensive cancer information database. The PDQ database contains summaries of the latest published information on cancer prevention, detection, genetics, treatment, supportive care, and complementary and alternative medicine. Most summaries come in two versions. The health professional versions have detailed information written in technical language. The patient versions are written in easy-to-understand, nontechnical language. Both versions have cancer information that is accurate and up to date and most versions are also available in Spanish.
PDQ is a service of the NCI. The NCI is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). NIH is the federal government’s center of biomedical research. The PDQ summaries are based on an independent review of the medical literature. They are not policy statements of the NCI or the NIH.
Purpose of This Summary
This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of childhood Hodgkin lymphoma. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
Reviewers and Updates
Editorial Boards write the PDQ cancer information summaries and keep them up to date. These Boards are made up of experts in cancer treatment and other specialties related to cancer. The summaries are reviewed regularly and changes are made when there is new information. The date on each summary ("Updated") is the date of the most recent change.
The information in this patient summary was taken from the health professional version, which is reviewed regularly and updated as needed, by the PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board.
Clinical Trial Information
A clinical trial is a study to answer a scientific question, such as whether one treatment is better than another. Trials are based on past studies and what has been learned in the laboratory. Each trial answers certain scientific questions in order to find new and better ways to help cancer patients. During treatment clinical trials, information is collected about the effects of a new treatment and how well it works. If a clinical trial shows that a new treatment is better than one currently being used, the new treatment may become "standard." Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Clinical trials are listed in PDQ and can be found online at NCI's website. For more information, call the Cancer Information Service 1-800-4-CANCER (1-800-422-6237).
Permission to Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as “NCI’s PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: [include excerpt from the summary].”
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
PDQ® Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Childhood Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Updated <MM/DD/YYYY>. Available at: https://www.cancer.gov/types/lymphoma/patient/child-hodgkin-treatment-pdq. Accessed <MM/DD/YYYY>. [PMID: 26389224]
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author(s), artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 2,000 scientific images.
Disclaimer
The information in these summaries should not be used to make decisions about insurance reimbursement. More information on insurance coverage is available on Cancer.gov on the Managing Cancer Care page.
Contact Us
More information about contacting us or receiving help with the Cancer.gov website can be found on our Contact Us for Help page. Questions can also be submitted to Cancer.gov through the website’s E-mail Us.
- General Information About Childhood Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Stages of Childhood Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Primary Refractory/Recurrent Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children and Adolescents
- Treatment Option Overview
- Treatment Options for Children and Adolescents with Hodgkin Lymphoma
- Treatment Options for Primary Refractory/Recurrent Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children and Adolescents
- To Learn More About Childhood Hodgkin Lymphoma
- About This PDQ Summary
- Review Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.[PDQ Cancer Information Summari...]Review Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries. 2002
- Review Childhood Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.[PDQ Cancer Information Summari...]Review Childhood Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries. 2002
- Review Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.[PDQ Cancer Information Summari...]Review Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries. 2002
- Review Primary CNS Lymphoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.[PDQ Cancer Information Summari...]Review Primary CNS Lymphoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries. 2002
- Review Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.[PDQ Cancer Information Summari...]Review Childhood Rhabdomyosarcoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version.PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries. 2002
- Childhood Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment (PDQ®) - PDQ Cancer Information SummariesChildhood Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment (PDQ®) - PDQ Cancer Information Summaries
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...