From: Role of SMG-1-mediated Phosphorylation of Upf1 in NMD

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
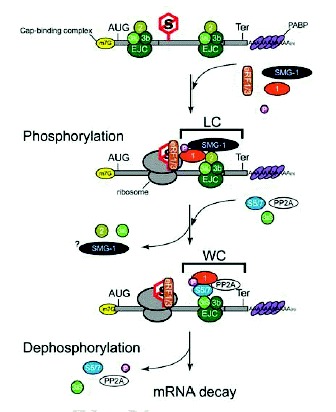
Hypothetical model showing the roles of Upf1 phosphorylation and dephosphorylation during mRNA surveillance in metazoans. A fraction of nonphosphorylated Upf1 associates with SMG-1 to form an initial SMG-1-Upf1 complex (IC). The ribosome that recognizes a termination codon recruits IC to mRNA. If IC can associate with the Upf2 component of the cytoplasmic EJC to form the large complex (LC), then SMG-1 phosphorylates Upf1. Upf1 phosphorylation triggers remodeling of the LC to form the wee complex (WC) and causes dephosphorylation of Upf1 by PP2A. Dephosphorylation is followed by degradation of the corresponding mRNA. See text for details. NMD components are shown as color-coded circles. Abbreviations: P, Phosphate group; U1, Upf1; U2, Upf2; 3b, Upf3b; 3aL, Upf3a long; 3aS, Upf3a short; S5/7, SMG-5-SMG-7 complex; eRF1/3, eRF1-eRF3 complex. AUG, start codon; Ter, termination codon; S, stop codon that triggers NMD.
From: Role of SMG-1-mediated Phosphorylation of Upf1 in NMD

NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.