NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Butler M, Urosevic S, Desai P, et al. Treatment for Bipolar Disorder in Adults: A Systematic Review [Internet]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018 Aug. (Comparative Effectiveness Review, No. 208.)
Section 1. Carbamazepine
Appendix Table F1Characteristics of eligible studies: carbamazepine for acute mania
| Study, Year Design Location Funder Risk of Bias PMID | # Randomized Age (mean) Sex (% Female) Race (% White) Diagnosis (% BP I, II, NOS) Setting | Inclusions Key Exclusions | Intervention Dosage | Comparison Dosage | Follow-up Duration | Outcomes Reported Withdrawal (%) at endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weisler, 20061 2 pooled RCTs Multisite 2 Continents Industry RoB High 16529527 (pooled 15766298 and 15119909) | N = 443 Mean Age 38 Female 38% White 59% BP I 100% Inpatient or Outpatient | Manic/Mixed; YMRS ≥ 20 Taking Other Meds | Carbamazepine ER 200–1600 mg/day (642.6 mg/day average) | Placebo | 3 weeks | YMRS CGI-S CGI-I HAM-D Withdrawal 46% |
| Vasudev, 20002 RCT Singlesite India Industry RoB Moderate 10867972 | N = 30 Age NR Sex NR Race NR BP I 100% Outpatient | Mania; DSM-III criteria for BP diagnosis Substance Abuse Neurological Disorders Taking other meds Pregnant/Nursing | Carbamazepine 800–1600 mg/day (22.05 mg/kg/day) | Valproate 800–2200 mg/day (22.9 mg/kg/day) | 4 weeks | Response (50% decrease in YMRS) YMRS Withdrawal 20% |
| Small, 19913 RCT Singlesite US Government RoB High 1929761 | N = 48 Mean Age 39 Female 38% White 59% BP I 100% Inpatient | Manic/Mixed; YMRS ≥ 20 First Manic Episode Substance Abuse Other Mental Health | Carbamazepine 700 mg/day-1052 mg/day (high and low weekly mean dose) (950.8 mg/day mean weekly dose) | Lithium 1035–1278 mg/day (high and low mean dose) (1207.5 mean weekly dose) | 8 weeks | SDMS-D SDMS-M YMRS GAS CGI-I BCL Withdrawal 42% |
| Lerer, 19874 RCT Singlesite US Industry RoB High 3546274 | N = 34 Mean Age 41 Female 54% Race NR BP I 100% Inpatient | Manic Neurological Disorders | Carbamazepine 600–2600 mg/day (1250 mg/day mean of the reported weekly median) | Lithium 900–3900 mg/day (1650 mg/day mean of the reported weekly median) | 4 weeks | Response (CGI change 2+) CGI Withdrawal 18% |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; AIMS=Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale; BAS=Behavioral Approach System; BCL= Shopsin-Gershon Social Behavior Checklist; BIS-11=Barratt Impulsiveness Scale; BP=bipolar disorder; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; C=Comparision; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions Scale; CGI-BP =Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-I= Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; DSM=Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; DSM-IV= Diagnostic and statistical manual, 4th edition; DSS=Depressive Syndrome Scale; ER=extended release; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Scale for Depression; LIFE-RIFT= Range of Impaired Functioning Tool; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; MSS=Manic Syndrome Scale; NOS=not otherwise specified; NR=not reported; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; ROB=risk of bias; SADS-C=Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia Change Version; SAS=Simpson Angus Scale; SDMS=Symptoms of Depression and Mania Scale; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table F2Summary risk of bias assessments: carbamazepine for acute mania
| Drug | Study Funding Source PMID | Overall Risk of Bias Assessment | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbamazepine | Weisler, 20061 Industry 16529527 | High | Large dropout rates (46%) with randomization and blinding not described. |
| Vasudev, 20002 Industry 10867972 | Moderate | Protection of allocation not described, but blinding and randomization are well addressed as are other aspects of the paper. Withdrawal 20%. | |
| Small, 19913 Government 1929761 | High | Randomization procedure and allocation masking not described. 42% dropout. | |
| Lerer, 19874 Industry 3546274 | High | The researcher only included in the analysis those who completed the study. This is likely to bias the results of the Lithium group who lost roughly 1/4 of the study population during the four weeks. Randomization procedure and allocation masking not described. 18% dropout. |
Abbreviations: PMID=PubMed Identification Number
Appendix Table F3Outcomes summary: carbamezepine versus placebo for acute mania
| Drug | Study PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbamazepine vs. placebo | Weisler, 20061 16529527 2 pooled RCTs (15766298 and 15119909) High | Responders (>50% decrease YMRS) 3 weeks Favors carbamazepine Carbamazepine 52% Placebo 26% p<0.0001 | YMRS decrease 3 weeks Favors carbamazepine Carbamazepine 12.3 Placebo 6.2 p<0.0001 HAM-D decrease 3 weeks Favors carbamazepine Carbamazepine 2.9 Placebo 1.3 p=0.01 | CGI-S increase 3 weeks Favors carbamazepine Carbamazepine 1.2 Placebo 0.5 p<0.0001 CGI-I improvement 3 weeks Favors carbamazepine Carbamazepine 55.6% Placebo 28.4% p<0.0001 | Overall Withdrawal Carbamazepine 93/223 Placebo 110/220 NS Withdrawal lack of effect Carbamazepine 22/223 Placebo 49/220 Favors Carbamazepine Withdrawal adverse events Carbamazepine 24/223 Placebo 12/220 NR (EPC calculated favors carbamazepine) BMI Change Favors placebo ≥7% gain Carbamazepine 5.3% Placebo 1% p=0.011 | SAE (from original studies) Carbamazepine: 8 patients Placebo: 10 patients Severe Rash: 11 carbamazepine patient 1 placebo patient attempted suicide |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Effects; BMI=Body Mass Index; CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP =Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-I= Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement; CGI-S=CGI-Severity; CI= Confidence Interval; EPS=Extrapyramidal Side Effects; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Scale for Depression; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; OPT=Optimalized Personalized Treatment; OR=Odds Ratio; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; SAE= Serious Adverse Events; SD=Standard Deviation; SE=Standard Error; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table F4Strength of evidence assessment: carbamezepine versus placebo for acute mania
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbamazepine vs. placebo | Response YMRS CGI Withdrawals | 1 RCT + 1 IPD (n=443) | See table above | High | Consistent (based on original RCTs) | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CI=Confidence Interval; IPD=Individual patient data; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; MD=Mean Difference; NS=Not Significant; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Appendix Table F5Outcomes summary: carbamezapine versus active comparator for acute mania
| Drug | Study PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbamazepine vs. lithium | Small, 19913 1929761 High | NR | YMRS 8 weeks Carbamazepine −8.5 Lithium −9.7 4% difference between groups HAM-D 8 weeks Carbamazepine −2.5 Lithium 0.5 10% difference between groups SDMS-D 8 weeks Carbamazepine 0 Lithium 0.6 18% difference between groups SDMS-M 8 weeks Carbamazepine −3.4 Lithium −3.3 1% difference between groups | CGI-I 8 weeks Carbamazepine −0.9 Lithium 1.0 1% difference between groups GAS 8 weeks Carbamazepine 11.7 Lithium 11.8 3% difference between groups | Overall Withdrawal Carbamazepine 16/24 Lithium 16/24 NS | SAE None |
| Lerer, 19874 3546274 High | Response (CGI change 2+) 4 weeks Favors lithium Carbamazepine 4/14 Lithium 11/14 p<0.05 | NR | CGI Carbamazepine Baseline 5.6 (8.2) 4 weeks 4.1 (1.51) Lithium Baseline 5.7(0.88) 4 weeks 3.1(1.5) ANOVA group effect NS | Overall Withdrawal Carbamazepine 1/15 Lithium 4/19 NR Withdrawal adverse events Carbamazepine 1/15 Lithium 2/19 NR | SAE Carbamazepine 4/15 Lithium 1/19 | |
| Carbamazepine vs. valproate | Vasudev, 20002 10867972 Moderate | Response (50% decrease in YMRS) 4 weeks Carbamazepine 8/15 Valproic acid 11/15 NS | NR | NR | Overall Withdrawal Carbamazepine 3/15 Valproic acid 3/15 NS | All AEs Carbamazepine 67% Valproic acid 17% Tremors Carbamazepine 25% Valproic acid 8% |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Effects; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; CGI= Clinical Global Impressions Scale; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-I=Clinical Global Impressions Scale-Improvement; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS=Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Scale for Depression; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Syndrome Scale; MRS=mania rating scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; SAE= Serious Adverse Events; SD=standard deviation; SDMS-D=Symptoms of Depression and Mania Scale-Depression; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table F6Strength of evidence assessment: carbamezapine versus active comparator for acute mania
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbamazepine vs. lithium | Response YMRS CGI Withdrawals – overall Withdrawal – AEs | 2 RCTs (n=82) | See table above | High | Consistent | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
| Carbamazepine vs. valproate | Response Withdrawals – overall | 1 RCT (n=30) | See table above | Moderate | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Event; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions Scale; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; n=number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Section 2. Divalproex/Valproate
Appendix Table F7Characteristics of eligible studies: divalproex for acute mania
| Study, Year Design Location Funder Risk of Bias PMID | # Randomized Age (mean) Sex (% Female) Race (% White) Diagnosis (% BP I, II, NOS) Setting | Inclusions Key Exclusions | Intervention Dosage | Comparison Dosage | Follow-up Duration | Outcomes Reported Withdrawal (%) at endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tohen, 2008b5 RCT Multisite 3 Continents Industry RoB Low 19014751 | N = 521 Mean Age 40 Female 49% Race NR Diagnosis NR Setting NR | Manic or Mixed Episode; YMRS 20–30 CGI-BP mania 3–4 Schizoaffective Other Mental Health Conditions Pregnant/Nursing | Divalproex 500–2500 mg/day | C1: Placebo C2: Olanzapine 5–20 mg/day | 3 weeks | Response (YMRS reduction ≥ 50%) Time to response (days from baseline to ≥ 50% YMRS reduction) Remission (YMRS ≤ 12) Efficacy YMRS CGI (multiple subscales) MADRS Adverse events Extrapyramidal symptoms SAS BAS AIMS Withdrawal 26% |
| Bowden, 20066 RCT Multisite US Industry RoB High 17107240 | N = 364 Mean Age 38 Female 43% White 74% BP I 100% Inpatient (0–15 days) Outpatient (>15–21 days, subject to clinical criteria) | Mania; Mania Rating Scale (derived from SADS-C interview) ≥ 18 with at least 4 item scores >1. First Manic Episode; Schizoaffective; Substance Abuse; Other Mental Health Conditions; Taking other Medications; | Divalproex 85–125 microgram/ml (2961 mg/day average) | Placebo | 3 weeks | Remission (YMRS ≤ 12) Response (50% decrease in YMRS) YMRS BIS MSS GAS DSS AEs Weight gain Withdrawal 45% |
| Xu, 20157 RCT Single-site China Government RoB Low 26060401 | N = 120 Mean Age 31 Female 52% Race NR BP 1 100% Setting NR | First manic; YMRS ≥17 | Olanzapine 10 mg/day + Valproate 600 mg/day | C1: Olanzapine 10 mg/day Flexible dosing 5–20 mg/day C2: Valproate 600 mg/day alone | 4 weeks | Efficacy YMRS CGI-BP Adverse events Extrapyramidal symptoms SAS Withdrawal 5% |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; AIMS=Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale; BAS=Behavioral Approach System; BCL= Shopsin-Gershon Social Behavior Checklist; BIS-11=Barratt Impulsiveness Scale; BP=bipolar disorder; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; C=Comparision; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions Scale; CGI-BP =Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-I= Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; DSM=Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; DSM-IV= Diagnostic and statistical manual, 4th edition; DSS=Depressive Syndrome Scale; ER=extended release; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Scale for Depression; LIFE-RIFT= Range of Impaired Functioning Tool; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; MSS=Manic Syndrome Scale; NOS=not otherwise specified; NR=not reported; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; ROB=risk of bias; SADS-C=Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia Change Version; SAS=Simpson Angus Scale; SDMS=Symptoms of Depression and Mania Scale; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table F8Summary risk of bias assessments: dival/valproate for acute mania
| Drug | Study Funding Source PMID | Overall Risk of Bias Assessment | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Divalproex/Valproate | Tohen, 20085 Industry 19014751 | Low | No sources of bias identified. 26% dropout at 3 weeks. |
| Bowden, 20066 Industry 17107240 | High | Randomization and allocation procedures not described. Author notes, “We plan to report in a separate article a detailed exploration of the site-related differences and the implications for study design and execution” This statement infers that there is a difference caused by site that is not addressed or controlled for in the paper. 45% dropout. | |
| Xu, 20157 Government 26060401 | Low | Well-constructed, described, and reported study. 5% dropout. |
Abbreviations: PMID=PubMed Identification Number
Appendix Table F9Outcomes summary: divalproex/valproate versus placebo for acute mania
| Drug | Study PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Divalproex vs. placebo | Bowden, 20066 17107240 High | Response 3 weeks Favors divalproex Divalproex 48% Placebo 34% p=0.012 Remission 3 weeks Favors divalproex Divalproex 48% Placebo 35% p=0.015 | MRS Change 3 weeks Favors divalproex Divalproex −11.5 Placebo −9.0 p=0.013 | GAS 3 weeks NS | Overall Withdrawal Divalproex 108/187 Placebo 92/177 NS Withdrawal lack of effect Divalproes 24/187 Placebo 46/177 Favors Divalproex p=0.001 Withdrawal adverse events Divalproex 19/187 Placebo 5/177 Favors Placebo p=0.003 | Serious Adverse Events 3 weeks 1 in divalproex 0 in placebo Deaths 3 weeks 0 in both arms |
| Tohen, 20085 19014751 Low | Response 3 weeks Divalproex 40.3% Placebo 31.3% NS Remission 3 weeks Divalproex 40.3% Placebo 35.4% NS | YMRS Change 3 weeks Divalproex −8.2 (SE 0.62) Placebo −7.4 (SE 0.80) NS | CGI Overall Change 3 weeks Divalproex −0.6 (SE 0.08) Placebo −0.5 (SE 0.10) NS CGI Mania Change 3 weeks Divalproex −0.8 (SE 0.08) Placebo −0.7 (SE 0.11) NS CGI Depression Change 3 weeks Divalproex −0.2 (SE 0.07) Placebo −0.1 (SE 0.09) NS | Withdrawal 3 weeks Overall: 25.5% Efficacy: 2.0% AEs: 2.3% | Serious Adverse Events 3 weeks 1 in divalproex 1 in placebo | |
| Valproate adjunctive vs. placebo or no placebo | Xu, 20157 26060401 Low | NR | YMRS 3 weeks Favors Valproate % Reduction (SD) Olanzapine+Valporate= 86.5% (8.9%) Olanzapine= 75.2% (15.1%) P<0.01 CGI-BP 3 weeks Favors Valproate p<0.01 | NR | Overall Withdrawal 3 weeks NS Olanzapine + Valporate = 2/40 Olanzapine=1/40 Withdrawal due to AEs 3 weeks NS Olanzapine+Valporate=2/40 Olanzapine=1/40 Withdrawal, Lack of Efficacy 3 weeks NS Olanzapine+Valporate=0/40 Olanzapine=0/40 | Severe Harms 3 weeks NS Olanzapine+Valporate=1/38 Olanzapine=0/39 Normalized Weight Change 3 weeks Olanzapine+Valporate=31/38 Olanzapine=29/39 Emergent Mood Episodes 3 weeks NS Olanzapine+Valporate=0/38 Olanzapine=0/39 |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Effects; BMI=Body Mass Index; CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP =Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-I= Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement; CGI-S=CGI-Severity; CI= Confidence Interval; EPS=Extrapyramidal Side Effects; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Scale for Depression; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; OPT=Optimalized Personalized Treatment; OR=Odds Ratio; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; SAE= Serious Adverse Events; SD=Standard Deviation; SE=Standard Error; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table F10Strength of evidence assessment: divalproex/valproate versus placebo for acute mania
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Divalproex vs. placebo | Relapse Remission YMRS CGI Withdrawals | 2 RCTs (n=670) | See table above | Moderate | Inconsistent | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
| Valproate vs. no placebo | YMRS CGI Withdrawals | 1 RCT (n=79) | See table above | Low | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CI=Confidence Interval; IPD=Individual patient data; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; MD=Mean Difference; NS=Not Significant; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Section 3. Lamotrigine
Appendix Table F11Characteristics of eligible studies: lamotrigine for acute mania
| Study, Year Design Location Funder Risk of Bias PMID | # Randomized Age (mean) Sex (% Female) Race (% White) Diagnosis (% BP I, II, NOS) Setting | Inclusions Key Exclusions | Intervention Dosage | Comparison Dosage | Follow-up Duration | Outcomes Reported Withdrawal (%) at endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ichim, 20008 RCT Singlesite South Africa Industry RoB Moderate 10798820 | N=30 Mean Age 33 Female 47% Race NR BP I 100% Inpatient | Mania Substance Abuse Taking Other Meds Pregnant/Nursing Labs/Other Conditions | Lamotrigine Week 1 25mg/day, Week 2 50mg/day, Week 3 100mg/day | Lithium 400mg twice/daily | 4 weeks | YMRS BPRS CGI GAF Withdrawal 17% |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; AIMS=Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale; BAS=Behavioral Approach System; BCL= Shopsin-Gershon Social Behavior Checklist; BIS-11=Barratt Impulsiveness Scale; BP=bipolar disorder; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; C=Comparision; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions Scale; CGI-BP =Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-I= Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; DSM=Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; DSM-IV= Diagnostic and statistical manual, 4th edition; DSS=Depressive Syndrome Scale; ER=extended release; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Scale for Depression; LIFE-RIFT= Range of Impaired Functioning Tool; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; MSS=Manic Syndrome Scale; NOS=not otherwise specified; NR=not reported; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; ROB=risk of bias; SADS-C=Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia Change Version; SAS=Simpson Angus Scale; SDMS=Symptoms of Depression and Mania Scale; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table F12Summary risk of bias assessments: lamotrigine for acute mania
| Drug | Study Funding Source PMID | Overall Risk of Bias Assessment | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lamotrigine | Ichim, 20008 Industry 10798820 | Moderate | Randomization and blinding procedures not described. Initial difference between the two groups identified on duration since index episode before hospitalization. |
Abbreviations: PMID=PubMed Identification Number
Appendix Table F13Outcomes summary: lamotrigine versus active comparator for acute mania
| Drug | Study PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lamotrigine vs. Lithium | Ichim, 20008 Moderate 10798820 | Response 4 weeks NS Lamotrigine=8/15 Lithium=9/15 | YMRS 4 weeks NS Lamotrigine=14.3 Lithium=13.2 BPRS 4 weeks NS Lamotrigine=30.2 Lithium=28.2 | CGI-Severity 4 weeks NS Lamotrigine=2.77 Lithium=2.87 CGI-Improvement 4 weeks NS GAF 4 weeks NS Lamotrigine=55.7 Lithium=56.2 | Overall Withdrawal 4 weeks NS 17% Lamotrigine=2/15 Lithium=3/15 | Serious AEs 4 weeks No serious AEs reported in either group and no rashes were reported in the lamotrigine group. |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Effects; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; CGI= Clinical Global Impressions Scale; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-I=Clinical Global Impressions Scale-Improvement; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS=Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Scale for Depression; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Syndrome Scale; MRS=mania rating scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; SAE= Serious Adverse Events; SD=standard deviation; SDMS-D=Symptoms of Depression and Mania Scale-Depression; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table F14Strength of evidence assessment: lamotrigine versus active comparator for acute mania
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lamotrigine vs. lithium | Response Withdrawals – overall | 1 RCT (n=30) | See table above | Moderate | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Event; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions Scale; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; n=number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Section 4. Lithium
Appendix Table F15Characteristics of eligible studies: lithium for acute mania
| Study, Year Design Location Funder Risk of Bias PMID | # Randomized Age (mean) Sex (% Female) Race (% White) Diagnosis (% BP I, II, NOS) Setting | Inclusions Key Exclusions | Intervention Dosage | Comparison Dosage | Follow-up Duration | Outcomes Reported Withdrawal (%) at endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kushner, 20069 RCT Multisite 4 Continents Industry RoB Low 16411977 | N = 876 (includes only 400 mg/day topiramte arms and placebo arms Mean Age 41 Female (%) 51 White (%) 75 BP I (%) 100 Inpatient (at least 4 days, as clinically warranted) | Mania; YMRS ≥ 20 Schizoaffective; Substance Abuse; Other Mental Health Conditions; Taking Other Medications; | Topiramate 400mg/day (mean 313mg/day) (only 400 mg/day arms were common across pooled studies) | C1: Placebo n=427 C2: Lithium 300–1800 mg/day (0.8–1.2mEq/L) n=227 | 3 weeks | YMRS Weight BPRS CGI-S GAS Withdrawal 26% |
| Bowden, 200510 RCT Multisite 2 Continents Industry RoB High 15669897 | N=302 Mean Age 39 Female 42% Race NR BP I 100% Inpatient (week 1) Outpatient (weeks 2–12, subject to inspector discretion) | Mania; YMRS ≥ 20 including score of at least 4 on 2 of the 4 double-weighted items (irritability, speech, content, and disruptive/aggressive behavior), CGI ≥ 4 First manic episode; Substance Use; Taking other medications; Pregnant/Nursing; Labs/Other Conditions | Lithium 0.6–1.4 mEq/L (mean 0.80 mEq/L) | C1:Placebo C2: Quetiapine 100–800mg/day | 12 weeks | CGI-BP-S GAS Remission YMRS ≤12) Response (≥50% YMRS decrease) Withdrawal 43% |
| Segal, 199811 RCT Singlesite South Africa Industry/University RoB Moderate 9617509 | N=45 Mean Age 34 Female 78% Race NR BP I 100% Inpatient | Mania; DSM-IV criteria for Bipolar Manic Phase Substance Abuse; Taking other Medications; Pregnant/Nursing; Abnormal Lab Results | Lithium 0.6–1.2 mmol/L (Mean 0.72 mmol/L) | C1: Placebo C2: Haloperidol 10 mg/day | 4 weeks | BPRS CGI Unknown Scale - Not reported whether global improvement or severity scale is being reported GAF MRS Seclusion – Hours Seclusion - Proportion of patients needing SAS Withdrawal 13% |
| Bowden, 201012 RCT Multisite 2 Continents Industry RoB Moderate 20101186 | N = 270 Mean Age 39 Female 59% Race NR BP I 100% Inpatient and Outpatient | Mania; YMRS ≥ 18 First Manic Episode Substand Abuse Pregnant/Nursing Labs/Other Conditions Other Mental Health | Lithium 0.6–1.2 mmol/L (mean 969 mg/day) | Valproate 70–125 mcg/ml (mean 1394 mg/day) | 12 weeks | CGI-BP-S Remission (YMRS ≤12 and decrease in CGI-BP ≥ 2) Remission (YMRS ≤ 12 and no increase in MADRS total score OR YMRS ≤ 12 and CGI ≤ 2 points) Response (improvement in YMRS ≥30%) YMRS Withdrawal 28% |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; AIMS=Abnormal Involuntary Movement Scale; BAS=Behavioral Approach System; BCL= Shopsin-Gershon Social Behavior Checklist; BIS-11=Barratt Impulsiveness Scale; BP=bipolar disorder; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; C=Comparision; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions Scale; CGI-BP =Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-I= Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; DSM=Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders; DSM-IV= Diagnostic and statistical manual, 4th edition; DSS=Depressive Syndrome Scale; ER=extended release; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Scale for Depression; LIFE-RIFT= Range of Impaired Functioning Tool; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; MSS=Manic Syndrome Scale; NOS=not otherwise specified; NR=not reported; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; ROB=risk of bias; SADS-C=Schedule for Affective Disorders and Schizophrenia Change Version; SAS=Simpson Angus Scale; SDMS=Symptoms of Depression and Mania Scale; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table F16Summary risk of bias assessments: lithium for acute mania
| Drug | Study Funding Source PMID | Overall Risk of Bias Assessment | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium | Bowden, 201012 Industry 20101186 | Moderate | Randomization procedure not described, patients and raters may not be blinded. 28% dropout. |
| Kushner, 20069 Industry 16411977 | Low | No sources of bias identified | |
| Bowden, 200510 Industry 15669897 | High | Randomization and blinding not described. Overall dropout of 43%. | |
| Segal, 199811 Industry/University 9617509 | Moderate | Noted ‘randomly and assigned consecutively to treatment with…” which is a pseudorandom assignment technique. Blinding not described. |
Abbreviations: PMID=PubMed Identification Number
Mood Stabilizer Forest Plots
Outcomes in studies assessed as having a high risk of bias, or low to moderate risk of bias but at least 40 percent attrition, are presented in grey tones. Both fixed-effect models and random-effects models are presented. We calculated fixed-effect models to provide a charitable estimate of the average effect among completed trials. However, we base our main conclusions on the random-effects models.
Appendix Table F17Outcomes summary: lithium versus placebo for acute mania
| Drug | Study PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
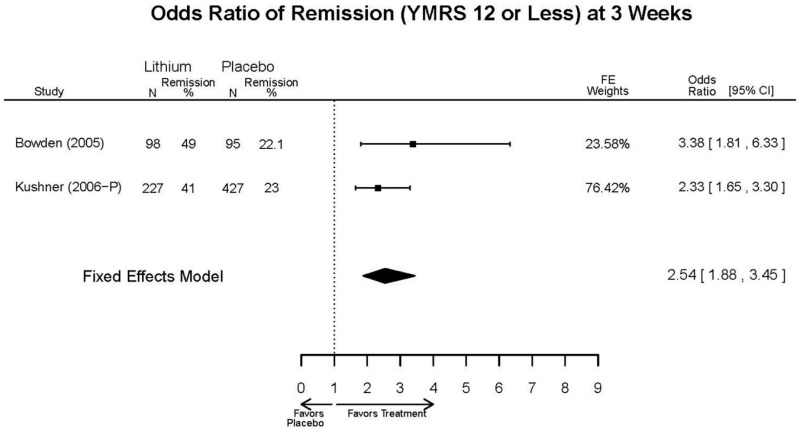
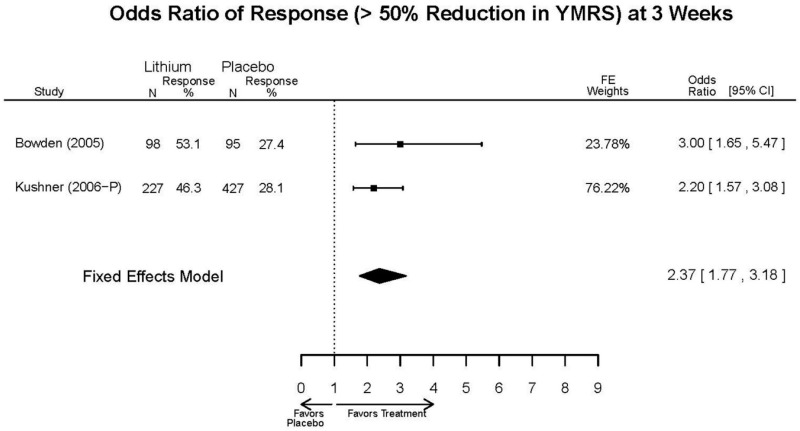
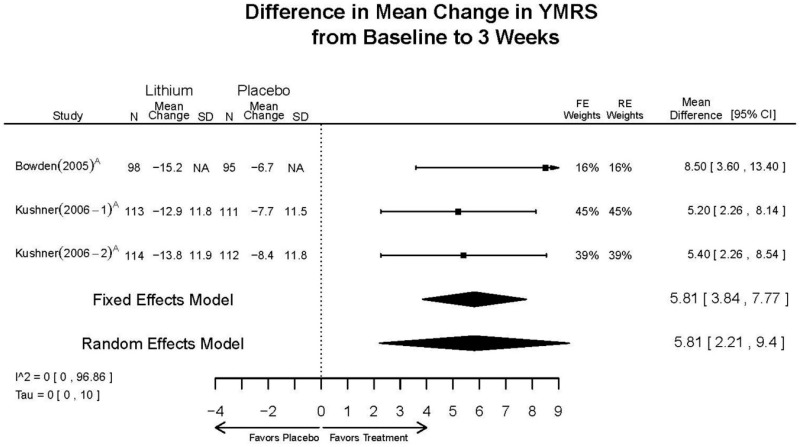
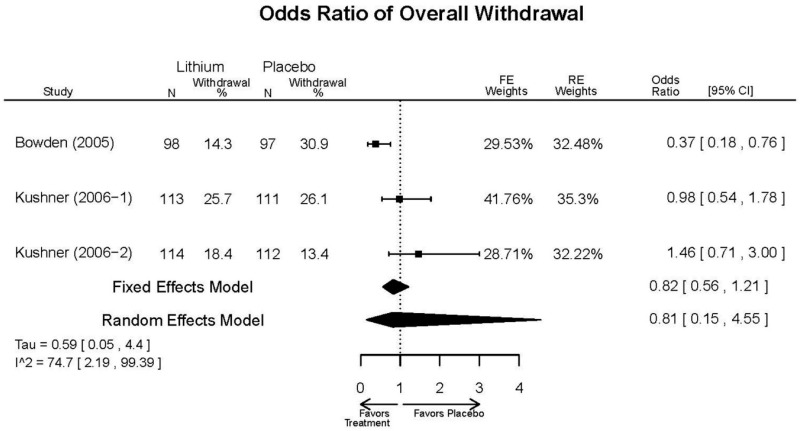
| Lithium vs. placebo | Bowden, 200510 15669897 Moderate | Response See forest plot F1 above Remission See forest plot F2 above | YMRS See forest plot F3 above | CGI-BP 12 weeks Favors Lithium Lithium= −2.2 Placebo=−0.9 Difference in Difference (SD)= 1.3 (0.38) p<0.001 | Overall Withdrawal See forest plot F4 above Withdrawal due to Lack of Efficacy 12 weeks Favors Lithium Lithium= 12/98 Placebo=38/97 OR=0.22 (95% CI 0.10, 0.45) p<0.0001 Withdrawal due to AEs 12 weeks NS Lithium= 6/98 Placebo=4/97 OR=1.49 (95% CI 0.40, 6.26) p=0.75 | EPS 12 weeks Lithium= 21/98* Placebo=35/97 *May be more cases, exact number NR Emergent Depression 12 weeks Lithium= 8/95 Placebo=3/97 Akathisia 12 weeks Lithium= 3/98 Placebo=6/97 |
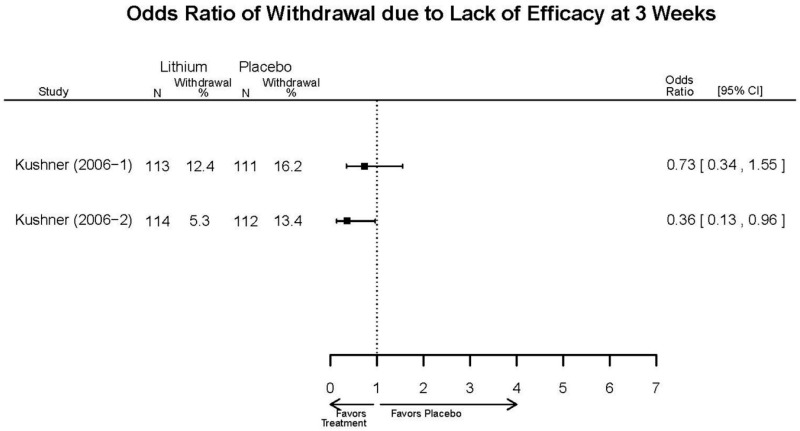
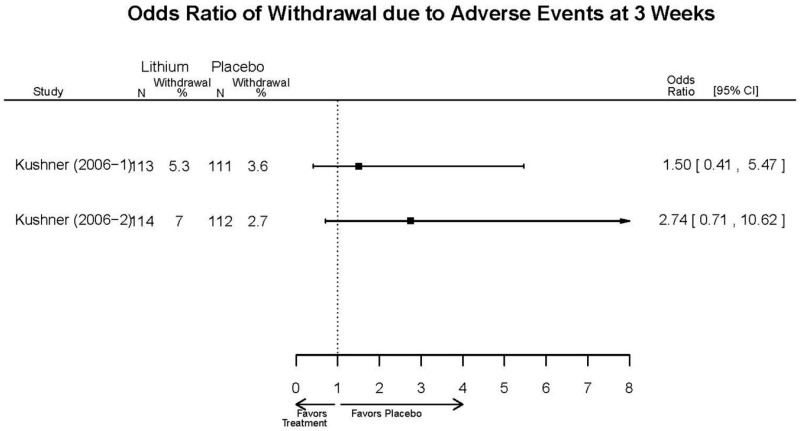
| Kushner, 20069 16411977 Low | Response See forest plot F1 above Remission See forest plot F2 above | YMRS See forest plot F3 above | NR | Overall Withdrawal See forest plot F4 above Withdrawal Lack of Efficacy See forest plot F5 above Withdrawal due to AEs See forest plot F6 above | Severe AEs 3 weeks (Placebo) 12 weeks (Lithium) Lithium= 4/227 Placebo=9/427 Emergent Depression 3 weeks (Placebo) 12 weeks (Lithium) Lithium= 16/227 Placebo=51/427 Emergent Depression 12 weeks (Lithium) 3 weeks (Placebo) 3 cases of suicidal ideation in placebo group. |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Effects; BMI=Body Mass Index; CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP =Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-I= Clinical Global Impressions-Improvement; CGI-S=CGI-Severity; CI= Confidence Interval; EPS=Extrapyramidal Side Effects; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Scale for Depression; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; OPT=Optimalized Personalized Treatment; OR=Odds Ratio; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; SAE= Serious Adverse Events; SD=Standard Deviation; SE=Standard Error; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table F18Strength of evidence assessment: lithium versus placebo for acute mania
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium vs. placebo | Remission 3 wks Response 3 wks | 1 RCT + 1 IPD (n=325) | Favors Lithium | Moderate | Consistent | Direct | Imprecise | Low |
| YMRS 3 wks | 3 RCTs (n=325) | Favors Lithium MD 5.81 (95% CI 2.21, 9.4) | Moderate | Consistent | Direct | Imprecise | Low | |
| Withdrawal – Overall 3 wks | 3 RCTs (n=325) | NS | Moderate | Consistent | Direct | Imprecise | Low | |
| Withdrawal – Lack of Efficacy, AE | 1 IPD (n=450) | NS | Moderate | Consistent | Direct | Imprecise | Low | |
| CGI | 1 RCT (n=193) | See table above | Moderate | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CI=Confidence Interval; IPD=Individual patient data; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; MD=Mean Difference; NS=Not Significant; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Appendix Table F19Outcomes summary: lithium active comparator for acute mania
| Drug | Study PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium vs. haloperidol | Segal, 199811 9617509 Moderate | NR | MRS 4 weeks NS Lithium= −19.3 Haloperidol=−19.9 | CGI-BP 4 weeks NS No additional data reported | Overall Withdrawal 4 weeks NS Lithium= 1/15 Haloperidol=3/15 p=0.06 | NR |
| Lithium vs. valproate | Bowden, 201012 20101186 Moderate | Response 12 weeks Valproate 79.5% Lithium 72.6% NS Remission (YMRS/MADRS) 12 weeks Valproate 71.3% Lithium 65.9% NS Remission (YMRS/CGI) 12 weeks Favors valproate Valproate 71.9% Lithium 58.5% p=0.025 | YMRS Change (90% CI) 12 weeks Valproate −17.3 (9.4) Lithium −15.8 (5.3) NS | CGI-BP-S Change 12 weeks Valproate −2.1 (1.4) Lithium −2.3 (1.3) NS | Overall Withdrawal Lithium 38/135 Valproate 34/122 Withdrawal Lack of efficacy Lithium 13/135 Valproate 13/122 Withdrawal AE Lithium 9/138 Valproate 8/122 | Serious Adverse Events 12 weeks 10 in valproate 5 in lithium Weight gain >7% Lithium 9% Valproate 7% |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Effects; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; CGI= Clinical Global Impressions Scale; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-I=Clinical Global Impressions Scale-Improvement; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS=Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Scale for Depression; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Syndrome Scale; MRS=mania rating scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; SAE= Serious Adverse Events; SD=standard deviation; SDMS-D=Symptoms of Depression and Mania Scale-Depression; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table F20Strength of evidence assessment: lithium versus active comparator for acute mania
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium vs. haloperidol | YMRS CGI | 1 RCT (n=30) | See table above | Moderate | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
| Lithium vs. divalproex | Response Remission YMRS CGI-BP-S Withdrawals | 1 RCT (n=270) | See table above | Moderate | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Event; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions Scale; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; n=number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
References for Appendix F
- 1.
- Weisler RH, Hirschfeld R, Cutler AJ, et al Extended-release carbamazepine capsules as monotherapy in bipolar disorder : pooled results from two randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. CNS Drugs. 2006;20(3):219–31. PMID: 16529527. [PubMed: 16529527]
- 2.
- Vasudev K, Goswami U, Kohli K. Carbamazepine and valproate monotherapy: feasibility, relative safety and efficacy, and therapeutic drug monitoring in manic disorder. Psychopharmacology. 2000 May;150(1):15–23. PMID: 10867972. [PubMed: 10867972]
- 3.
- Small JG, Klapper MH, Milstein V, et al Carbamazepine compared with lithium in the treatment of mania. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1991 Oct;48(10):915–21. PMID: 1929761. [PubMed: 1929761]
- 4.
- Lerer B, Moore N, Meyendorff E, et al Carbamazepine versus lithium in mania: a double-blind study. J Clin Psychiatry. 1987 Mar;48(3):89–93. PMID: 3546274. [PubMed: 3546274]
- 5.
- Tohen M, Vieta E, Goodwin GM, et al Olanzapine versus divalproex versus placebo in the treatment of mild to moderate mania: a randomized, 12-week, double-blind study. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2008 Nov;69(11):1776–89. PMID: 19014751. [PubMed: 19014751]
- 6.
- Bowden CL, Swann AC, Calabrese JR, et al A randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter study of divalproex sodium extended release in the treatment of acute mania. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2006 Oct;67(10):1501–10. PMID: 17107240. [PubMed: 17107240]
- 7.
- Xu L, Lu Y, Yang Y, et al Olanzapine-valproate combination versus olanzapine or valproate monotherapy in the treatment of bipolar imania: A randomized controlled study in a chinese population group. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment. 2015 25 May;11:1265–71. doi: http://dx
.doi.org/10.2147/NDT.S81146. PMID: 26060401 (pubmed) 2015078440 (embase). [PMC free article: PMC4450656] [PubMed: 26060401] - 8.
- Ichim L, Berk M, Brook S. Lamotrigine compared with lithium in mania: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry. 2000 Mar;12(1):5–10. PMID: 10798820. [PubMed: 10798820]
- 9.
- Kushner SF, Khan A, Lane R, et al Topiramate monotherapy in the management of acute mania: results of four double-blind placebo-controlled trials. Bipolar Disorders. 2006 Feb;8(1):15–27. PMID: 16411977. [PubMed: 16411977]
- 10.
- Bowden CL, Grunze H, Mullen J, et al A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled efficacy and safety study of quetiapine or lithium as monotherapy for mania in bipolar disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2005 Jan;66(1):111–21. PMID: 15669897. [PubMed: 15669897]
- 11.
- Segal J, Berk M, Brook S. Risperidone compared with both lithium and haloperidol in mania: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Clinical Neuropharmacology. 1998 May–Jun;21(3):176–80. PMID: 9617509. [PubMed: 9617509]
- 12.
- Bowden CL, Mosolov S, Hranov L, et al Efficacy of valproate versus lithium in mania or mixed mania: a randomized, open 12-week trial. International Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2010 Mar;25(2):60–7. doi: http://dx
.doi.org/10 .1097/YIC.0b013e328333ac1b. PMID: 20101186. [PubMed: 20101186]
- Mood Stabilizers for Mania - Treatment for Bipolar Disorder in Adults: A Systema...Mood Stabilizers for Mania - Treatment for Bipolar Disorder in Adults: A Systematic Review
- Preface - Outpatient Case Management for Adults With Medical Illness and Complex...Preface - Outpatient Case Management for Adults With Medical Illness and Complex Care Needs
- Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 35 [Caenorhabditis elegans]Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 35 [Caenorhabditis elegans]gi|115533921|ref|NP_495180.2|Protein
- Exact Search Strings - Outpatient Case Management for Adults With Medical Illnes...Exact Search Strings - Outpatient Case Management for Adults With Medical Illness and Complex Care Needs
- Strength of Evidence - Outpatient Case Management for Adults With Medical Illnes...Strength of Evidence - Outpatient Case Management for Adults With Medical Illness and Complex Care Needs
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...