NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Butler M, Urosevic S, Desai P, et al. Treatment for Bipolar Disorder in Adults: A Systematic Review [Internet]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2018 Aug. (Comparative Effectiveness Review, No. 208.)
Section 1. Allopurinol
Appendix Table G1Characteristics of eligible studies: allopurinol for acute mania
| Study, Year Design Location Funder Risk of Bias PMID | # Randomized Age (mean) Sex (% Female) Race (% White) Diagnosis (% BP I, II, NOS) Setting | Inclusions Key Exclusions | Intervention Dosage | Comparison Dosage | Follow-up Duration | Outcomes Reported Withdrawal (%) at endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jahangard, 20141 RCT Singlesite Iran Nonprofit RoB Low 24953766 | N = 60 Mean Age NR Female NR Race NR BP I 100% Inpatient | Manic; YMRS ≥ 28 Schizoaffective Substance Abuse Other Mental Health Pregnant/Nursing | Allopurinol 600 mg/day + sodium valproate (15–20 mg/kg) and benzodiazepines | Placebo + sodium valproate (15–20 mg/kg) and benzodiazepines | 4 weeks | YMRS Remission (YMRS≤7) CGI Withdrawal 18% |
| Weiser, 20142 RCT Multisite Romania Nonprofit RoB High 24712840 | N = 180 Mean Age 47 Female 66% White 100% BP I 100% Inpatient or Outpatient | Manic; Clinical Interview in DSM-IV treated with mood stabilizer or neuroleptics for between 3 days and 2 weeks. None Specified | Allopurinol 300 mg/day + mood stabilizer and/or antipsychotic | Placebo+ mood stabilizer and/or antipsychotic | 6 weeks | Response (YMRS≥50% improvement) YMRS CGI-BP PANSS AEs Withdrawal 17% |
| Fan, 20123 RCT Singlesite United States Nonprofit RoB Medium 22420596 | N = 27 Mean Age 43 Female 50% White 63% BP I 100% Outpatient | Manic; YMRS≥14 partial response to lithium, valproate, carbamazepine, or atypical antipsychotics Substance Abuse Other Mental Health Pregnant/Nursing Labs/Other Conditions | Allopurinol 600 mg/day (300 mg/day first week) Current psychiatric medications | Placebo + current psychiatric medications | 6 weeks | YMRS HAM-D CGI SDS Q-LES-Q Withdrawal 15% |
| Machado-Vieira, 20084 RCT Brazil Non-Profit RoB Moderate 18681754 | N = 180 Mean Age 29.3 Female 59% White NR BP I 100% Not Disclosed | Manic; YMRS≥22 Schizoaffective Substance abuse Other mental health Taking other meds Labs/other conditions | T1: Allopurinol 60 mg/day T2: Dipyridamole 200 mg/day Lithium 600–900 mg/day serum level 0.6–1.2 mmol/L (mean 0.99 mmol/L) | Placebo Lithium 600–900 mg/day serum level 0.6–1.2 mmol/L (mean 0.95 mmol/L) | 4 weeks | CGI-S Remission (YMRS≤7) (YMRS≤12) Response (50% improved YMRS) Adverse Events Lab Values Withdrawal 20% |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Effects; BP=bipolar disorder; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP=Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; DSM-IV= Diagnostic and statistical manual, 4th edition; EPS=Extrapyramidal Symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Depression Rating Scale; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; NOS=not otherwise specified; NR= not reported; Q-LES-Q=Quality of Life Enjoyment and Satisfaction Questionnaire; PANSS=Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT= Randomized Controlled Trial; RoB=risk of bias; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SDS=Sheehan Disability Scale; T=Trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G2Summary risk of bias assessments: allopurinol for mania
| Drug | Study Funding Source PMID | Overall Risk of Bias Assessment | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allopurinol | Jahangard, 20141 No external funding 24953766 | Low | No sources of bias identified. |
| Weiser, 20142 Non-Profit 24712840 | High | Randomization and blinding not described. The original study design allows for any prescribed adjunctive medication so the medication effects cannot be localized to one drug. These treatments are not measured as part of the baseline or endpoint characteristics to ensure comparison group is similar to treatment group. | |
| Fan, 20123 Not reported 22420596 | Moderate | Randomization and blinding procedures not described. | |
| Machado-Vieira, 20084 Non-Profit 18681754 | Moderate | 22% (39/180) of patients randomized not included in results (censored due to discontinuance), unclear how this group compares to general population. Dropout rates appear similar. |
Abbreviations: PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial;
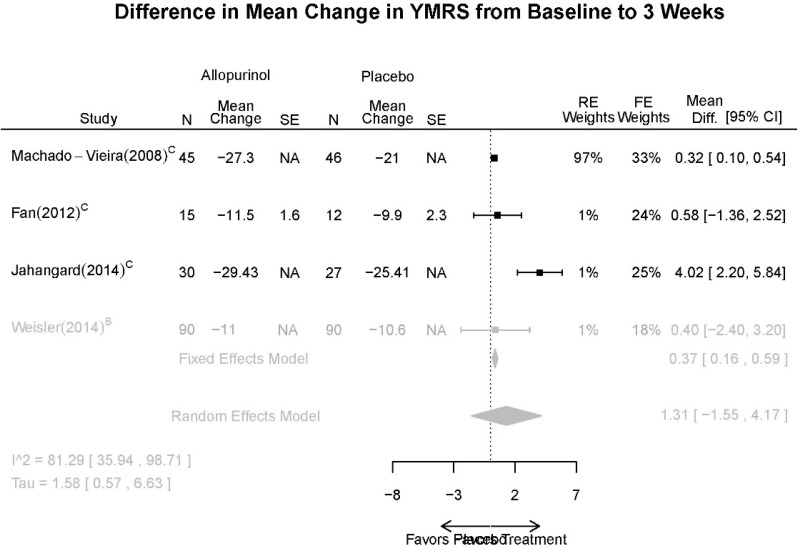
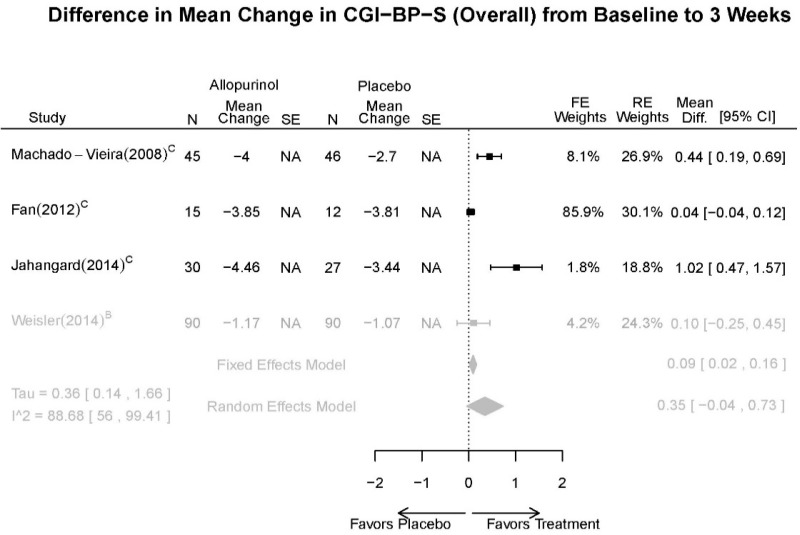
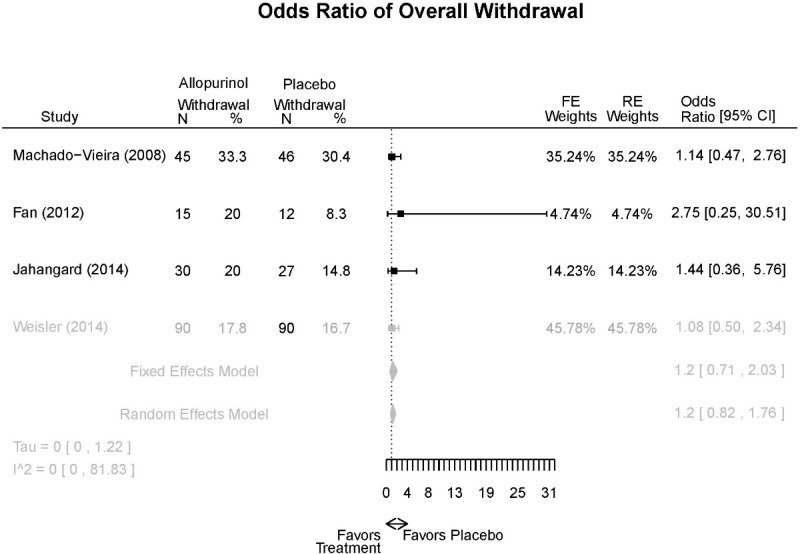
Allopurinol Forest Plots
Outcomes in studies assessed as having a high risk of bias, or low to moderate risk of bias but at least 40 percent attrition, are presented in grey tones. Both fixed-effect models and random-effects models are presented. We calculated fixed-effect models to provide a charitable estimate of the average effect among completed trials. However, we base our main conclusions on the random-effects models.
Appendix Table G3Outcomes summary: allopurinol for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Study ROB PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allopurinol + mood stabilizers vs. placebo + mood stabilizers | Jahangard, 20141 Low 24953766 | Remission (YMRS≤7) 4 weeks Allopurinol: 24/30 Placebo: 1/27 OR: 9.46 (1.19,81.57) | See forest plot G1 above | See forest plot G2 above | See forest plot G3 above Withdrawal Overall: 17% Efficacy: NR AEs: NR | No reported SAE |
| Weiser, 20142 High 24712840 | Response (YMRS≥50% decrease) 4 weeks Allopurinol: 34/90 Placebo: 35/90 NS OR 0.95 (0.52,1.74) | See forest plot G1 above | See forest plot G2 above | See forest plot G3 above Withdrawal Overall: 17% Efficacy: NR AEs: NR | No reported SAE | |
| Fan, 20123 Moderate 22420596 | NR | See forest plot G1 above | See forest plot G2 above | See forest plot G3 above Withdrawal Overall: 15% Efficacy: NR AEs: NR | NR | |
| Machado-Vieira, 20084 Moderate 18681754 | Remission (YMRS≤7) 4 weeks Allopurinol: 32/45 Placebo: 15/46 OR: 5.09 (2.09,12.41) Response (YMRS≥50% decrease) 4 weeks Allopurinol: 36/45 Placebo: 29/56 NS 2.34 (0.91, 6.03) | See forest plot G1 above | See forest plot G2 above Linear mixed model showed drug main effect was significant (p=0.004), and mixed effects with time were significant (p≤0.001) | NR Withdrawal Overall: 22% Efficacy: 5.6% AEs: 5.56 | No reported SAE |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; BMI=Body Mass Index; CI=Confidence Interval; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S= Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; EPS=extrapyramidal symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS=Global Assessment Scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; OR=Odds Ratio; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SD=standard deviation; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G4Strength of evidence assessment: allopurinol for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allopurinol + lithium vs. placebo + lithium | Remission 4 wks | 2 RCT (n=96) | See table above | Moderate | Inconsistent | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
| Response 4 wks | 2 RCT (n=96) | See table above | High | Consistent | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient | |
| YMRS 4 wks CGI 4 wks Overall Withdrawal | 4 RCT (n=355) | NS | Moderate | Consistent | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; IPD=Individual Patient Data; NS=not significant; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Appendix Table G5Outcomes summary: allopurinol for mania vs. active control
| Drug | Study Comparison PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allopurinol + lithium vs. Dipyridamole + lithium | Machado-Vieira, 20084 Moderate 18681754 | Remission (YMRS≤7) Favors Allopurinol p=0.03 Response (YMRS≥50% decrease) NS | YMRS 4 weeks Mean change Favors Allopurinol p<0.01 | CGI-S 4 weeks Linear mixed model Favors Allopurinol d=0.29 (0.09, 0.49) | NR Overall Withdrawal Allopurinol=15/60 Dipyridamole=10/60 NS Withdrawal lack of effect Allopurinol=3/60 Dipyridamole=5/60 NS Withdrawal adverse events Allopurinol=0/60 Dipyridamole=1/60 NS | SAE 1 dipyridmol patient severe skin rash |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; BMI=Body Mass Index; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CI=Confidence Interval; EPS=extrapyramidal symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RR=Risk Ratio; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SD=standard deviation; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G6Strength of evidence assessment: allopurinol for mania vs. active control
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allopurinol + lithium vs. Dipyridamole + lithium | Remission 4 wks Response 4 wks YMRS 4 wks CGI 4 wks Withdrawals | 1 RCT (n=120) | See table above | Moderate | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CI=Confidence Interval; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; IPD=Individual Patient Data; NS=not significant; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Section 2. Dipyridamole
Appendix Table G7Characteristics of eligible studies: dipyridamole for acute mania
| Study, Year Design Location Funder Risk of Bias PMID | # Randomized Age (mean) Sex (% Female) Race (% White) Diagnosis (% BP I, II, NOS) Setting | Inclusions Key Exclusions | Intervention Dosage | Comparison Dosage | Follow-up Duration | Outcomes Reported Withdrawal (%) at endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Machado-Vieira, 20084 RCT Brazil Non-Profit RoB Moderate 18681754 | N = 180 Mean Age 29.3 Female 59% White NR BP I 100% Not Disclosed | Manic; YMRS≥22 Schizoaffective Substance abuse Other mental health Taking other meds Labs/other conditions | T1: Allopurinol 60 mg/day T2: Dipyridamole 200 mg/day Lithium 600–900 mg/day serum level 0.6–1.2 mmol/L (mean 0.99 mmol/L) | Placebo Lithium 600–900 mg/day serum level 0.6–1.2 mmol/L (mean 0.95 mmol/L) | 4 weeks | CGI-S Remission (YMRS≤7) (YMRS≤12) Response (50% improved YMRS) Adverse Events Lab Values Withdrawal 20% |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Effects; BP=bipolar disorder; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP=Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; DSM-IV= Diagnostic and statistical manual, 4th edition; EPS=Extrapyramidal Symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Depression Rating Scale; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; NOS=not otherwise specified; NR= not reported; Q-LES-Q=Quality of Life Enjoyment and Satisfaction Questionnaire; PANSS=Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT= Randomized Controlled Trial; RoB=risk of bias; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SDS=Sheehan Disability Scale; T=Trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G8Summary risk of bias assessments: dipyridamole for mania
| Drug | Study Funding Source PMID | Overall Risk of Bias Assessment | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dipyridamole | Machado-Vieira, 20084 Non-Profit 18681754 | Moderate | 22% (39/180) of patients randomized not included in results (censored due to discontinuance), unclear how this group compares to general population. Dropout rates appear similar. |
Abbreviations: PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial
Appendix Table G9Outcomes summary: dipyridamole for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Study ROB PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dipyridamole + lithium vs. placebo + lithium | Machado-Vieira, 20084 Moderate 18681754 | Remission (YMRS≤7) NR Response (YMRS≥50% decrease) NR | YMRS 4 weeks NS NR Linear mixed model showed drug main effect was not significant (p=0.11) | CGI-S 4 weeks NS p=0.13 Linear mixed model showed drug main effect was significant (p=0.004), and mixed effects with time were significant (p≤0.001) | NR Overall Withdrawal Dipyridamole=10/60 Placebo=14/60 NS Withdrawal lack of efficacy Dipyridamole=5/60 Placebo=7/60 NS Withdrawal adverse events Dipyridamole=1/60 Placebo=0/60 NS | 1 dipyridamole participant with severe edverse event skin rash |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; BMI=Body Mass Index; CI=Confidence Interval; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S= Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; EPS=extrapyramidal symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS=Global Assessment Scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; OR=Odds Ratio; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SD=standard deviation; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G10Strength of evidence assessment: dipyridamole for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dipyridamole + lithium vs. placebo + lithium | YMRS 4 wks CGI-S 4 wks Withdrawals | 1 RCT (n=120) | See table above | Moderate | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; IPD=Individual Patient Data; NS=not significant; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Section 3. Celecoxib
Appendix Table G11Characteristics of eligible studies: celecoxib for acute mania
| Study, Year Design Location Funder Risk of Bias PMID | # Randomized Age (mean) Sex (% Female) Race (% White) Diagnosis (% BP I, II, NOS) Setting | Inclusions Key Exclusions | Intervention Dosage | Comparison Dosage | Follow-up Duration | Outcomes Reported Withdrawal (%) at endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabzadeh, 20155 RCT Iran University RoB Low 26291962 | N = 48 Mean Age 31.4 Female 35% White NR BP I 100% Inpatient | Manic; YMRS≥20 Schizoaffective Substance abuse Other mental health Taking other meds Labs/other conditions | Celecoxib 400 mg/day | Placebo | 6 weeks | YMRS HAM-D Remission (YMRS≤7) Time to Remission Response (YMRS≥50% decrease) Adverse Events Withdrawal 4% |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Effects; BP=bipolar disorder; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP=Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; DSM-IV= Diagnostic and statistical manual, 4th edition; EPS=Extrapyramidal Symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Depression Rating Scale; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; NOS=not otherwise specified; NR= not reported; Q-LES-Q=Quality of Life Enjoyment and Satisfaction Questionnaire; PANSS=Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT= Randomized Controlled Trial; RoB=risk of bias; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SDS=Sheehan Disability Scale; T=Trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G12Summary risk of bias assessments: celecoxib for mania
| Drug | Study Funding Source PMID | Overall Risk of Bias Assessment | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Celecoxib | Arabzadeh, 20155 University 26291962 | Low | No sources of bias identified |
Abbreviations: PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial;
Appendix Table G13Outcomes summary: celecoxib for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Study ROB PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celecoxib vs. placebo | Arabzadeh, 20155 Low 26291962 | Response (YMRS≥50% decrease) 3 weeks NS (p=0.08) 6 weeks NS p=0.11 Remission (YMRS≤7) 3 weeks NS p=0.15 6 weeks Favors celecoxib p=0.002 | YMRS 3 weeks Favors celecoxib Mean difference −5.17 (−9.61, −0.74) p=0.006 6 weeks Favors celecoxib p<0.001 | NR | NR Withdrawal Celecoxib=1/24 Placebo=1/24 NS | Serious Adverse Events 6 weeks 0 in both arms Deaths 6 weeks 0 in both arms EPS NR |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; BMI=Body Mass Index; CI=Confidence Interval; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S= Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; EPS=extrapyramidal symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS=Global Assessment Scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; OR=Odds Ratio; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SD=standard deviation; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G14Strength of evidence assessment: celecoxib for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celecoxib vs. placebo | Remission 3 wks Response 3 wks YMRS 3 wks Withdrawals | 1 RCT (n=44) | See table above | Low | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; IPD=Individual Patient Data; NS=not significant; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Section 4. Donepezil
Appendix Table G15Characteristics of eligible studies: donepezil for acute mania
| Study, Year Design Location Funder Risk of Bias PMID | # Randomized Age (mean) Sex (% Female) Race (% White) Diagnosis (% BP I, II, NOS) Setting | Inclusions Key Exclusions | Intervention Dosage | Comparison Dosage | Follow-up Duration | Outcomes Reported Withdrawal (%) at endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen, 20136 RCT China Non-profit RoB Moderate 23807849 | N = 30 Mean Age 34.1 Female 40% White (%) NR BP I 100% Inpatient | Manic; YMRS>20 Schizoaffective Substance abuse Other mental health Taking other meds Pregnant/nursing Labs/other conditions | Donepezil 10 mg/day Lithium 600–900 mg/day serum level 0.8–1.2 mmol/L (mean 0.83 mmol/L) | Placebo Lithium 600–900 mg/day serum level 0.8–1.2 mmol/L (mean 0.82 mmol/L) | 4 weeks | BPRS YMRS Response (YMRS decrease ≥50%) Remission (YMRS≤12) Adverse Events Withdrawal 0% |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Effects; BP=bipolar disorder; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP=Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; DSM-IV= Diagnostic and statistical manual, 4th edition; EPS=Extrapyramidal Symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Depression Rating Scale; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; NOS=not otherwise specified; NR= not reported; Q-LES-Q=Quality of Life Enjoyment and Satisfaction Questionnaire; PANSS=Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT= Randomized Controlled Trial; RoB=risk of bias; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SDS=Sheehan Disability Scale; T=Trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G16Summary risk of bias assessments: donepezil for mania
| Drug | Study Funding Source PMID | Overall Risk of Bias Assessment | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Donepezil | Chen, 20136 Nonprofit 23807849 | Moderate | Randomization and blinding procedures not described. |
Abbreviations: PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial
Appendix Table G17Outcomes summary: donepezil for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Study ROB PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donepezil + lithium vs. placebo + lithium | Chen, 20136 Moderate 23807849 | Remission (YMRS≤12) 4 weeks NS p=0.27 Response (YMRS≥50% decrease) 4 weeks NS p=1.0 | YMRS Decrease 4 weeks NS p=0.16 | NR | No withdrawals | Reported no serious adverse events |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; BMI=Body Mass Index; CI=Confidence Interval; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S= Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; EPS=extrapyramidal symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS=Global Assessment Scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; OR=Odds Ratio; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SD=standard deviation; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G18Strength of evidence assessment: donepezil for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Donepezil + lithium vs. placebo + lithium | Response 4 wks Remission 4 wks YMRS 4 wks | 1 RCT (n=30) | See table above | Moderate | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; IPD=Individual Patient Data; NS=not significant; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Section 5. Endoxifen
Appendix Table G19Characteristics of eligible studies: endoxifen for acute mania
| Study, Year Design Location Funder Risk of Bias PMID | # Randomized Age (mean) Sex (% Female) Race (% White) Diagnosis (% BP I, II, NOS) Setting | Inclusions Key Exclusions | Intervention Dosage | Comparison Dosage | Follow-up Duration | Outcomes Reported Withdrawal (%) at endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ahmad, 20168 RCT India Industry ROB Low 27346789 | N=66 Mean Age 33 Female 52% Race NR BP I 100% Inpatient | Manic/Mixed; YMRS ≥ 20 and CGI-S ≥ 4 New diagnosis Labs/other conditions Pregnant/nursing | Endoxifen oral enteric coated tablets at two fixed doses T1: 4 mg/day T2: 8 mg/day) | Divalproex 1000 mg/day | 3 weeks | Response (YMRS decrease ≥50%) CGI-S YMRS MADRS Withdrawal 7% |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Effects; BP=bipolar disorder; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP=Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; DSM-IV= Diagnostic and statistical manual, 4th edition; EPS=Extrapyramidal Symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Depression Rating Scale; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; NOS=not otherwise specified; NR= not reported; Q-LES-Q=Quality of Life Enjoyment and Satisfaction Questionnaire; PANSS=Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT= Randomized Controlled Trial; RoB=risk of bias; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SDS=Sheehan Disability Scale; T=Trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G20Summary risk of bias assessments: endoxifen for mania
| Drug | Study Funding Source PMID | Overall Risk of Bias Assessment | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endoxifen | Ahmad, 20168 Industry 27346789 | Low | Well-disclosed and reported study. |
Abbreviations: PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial;
Appendix Table G21Outcomes summary table: endoxifen for mania vs. active control
| Drug | Study Comparison PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endoxifen vs. divalproex | Ahmad, 20168 Low 27346789 | Response (YMRS≥50% decrease) 3 weeks NS Endoxifen 4 mg: 44% Endoxifen 8 mg: 64% Divalproex:: 72% | YMRS 3 weeks NS Mean change Endoxifen 4 mg:−12.65 Endoxifen 8 mg: −16.21 Divalproex:: −16.38 | CGI-S 3 week Reported NS (details not reported) | 2 patients withdrew due to adverse events 4 mg arm | Serious Adverse Events 3 weeks 2 4 mg arm (delusions) No deaths |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; BMI=Body Mass Index; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CI=Confidence Interval; EPS=extrapyramidal symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RR=Risk Ratio; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SD=standard deviation; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G22Strength of evidence assessment: endoxifen for mania vs. active control
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endoxifen vs. divalproex | Remission 3 wks YMRS 3 weeks CGI-S 3 weeks | 1 RCT (4 mg: n=42 (8 mg: n=42) | See table above | Low | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CI=Confidence Interval; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; IPD=Individual Patient Data; NS=not significant; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Section 6. Gabapentin
Appendix Table G23Characteristics of eligible studies: gabapentin for acute mania
| Study, Year Design Location Funder Risk of Bias PMID | # Randomized Age (mean) Sex (% Female) Race (% White) Diagnosis (% BP I, II, NOS) Setting | Inclusions Key Exclusions | Intervention Dosage | Comparison Dosage | Follow-up Duration | Outcomes Reported Withdrawal (%) at endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Astaneh, 20127 RCT Single-site Iran University RoB High 22978083 | N = 60 Mean Age NR Female about 50% White NR BP I NR Inpatient | Mania; Not Defined Substance abuse | Gabapentin 900 mg/day Lithium NR | Placebo Lithium NR | 6 week | YMRS Withdrawal 0 |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Effects; BP=bipolar disorder; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP=Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; DSM-IV= Diagnostic and statistical manual, 4th edition; EPS=Extrapyramidal Symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Depression Rating Scale; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; NOS=not otherwise specified; NR= not reported; Q-LES-Q=Quality of Life Enjoyment and Satisfaction Questionnaire; PANSS=Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT= Randomized Controlled Trial; RoB=risk of bias; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SDS=Sheehan Disability Scale; T=Trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G24Summary risk of bias assessments: gabapentin for mania
| Drug | Study Funding Source PMID | Overall Risk of Bias Assessment | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gabapentin | Astaneh, 20127 University 22978083 | High | Clinical and demographic traits at baseline not reported or compared for similarity. Blinding of staff and patients not addressed. Reporting is insufficient and may be misleading (e.g. missing values in graphs, missing error bars in graphs, raw data not provided/only sum of squares, asserts statistically meaningful improvement when improvement not shown statistically). |
Abbreviations: PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial
Appendix Table G25Outcomes summary: gabapentin for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Study ROB PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gabapentin + lithium vs. placebo + lithium | Astaneh, 20127 High 22978083 | NR | YMRS Reported favors gabapentin. However, baseline YMRS gabapentin = ~50 while control = ~13. | NR | NR | NR |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; BMI=Body Mass Index; CI=Confidence Interval; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S= Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; EPS=extrapyramidal symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS=Global Assessment Scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; OR=Odds Ratio; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SD=standard deviation; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G26Strength of evidence assessment: gabapentin for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gabapentin + lithium vs. placebo + lithium | YMRS 6 wks | 1 RCT (n=60) | See table above | High | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; IPD=Individual Patient Data; NS=not significant; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Section 7. Paliperidone
Appendix Table G27Characteristics of eligible studies: paliperidone for acute mania
| Study, Year Design Location Funder Risk of Bias PMID | # Randomized Age (mean) Sex (% Female) Race (% White) Diagnosis (% BP I, II, NOS) Setting | Inclusions Key Exclusions | Intervention Dosage | Comparison Dosage | Follow-up Duration | Outcomes Reported Withdrawal (%) at endpoint | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Berwaerts, 2012a9 RCT 3 Continents Industry ROB Moderate 20624657 | N = 469 Mean Age 40 Female 47% White 50% BP I 100% Inpatient (at least 1 week) Outpatient (weeks 2–3) | Manic/Mixed; YMRS ≥ 20 with 1 manic or mixed episode in past three years Schizoaffective; Substance abuse; Other Mental Health Condition; Taking other medications; Pregnant/Nursing | Paliperdone extended release (separate 3,6,12 mg/day arms) | Placebo | 3 weeks | CGI-BP-S GAF MADRS PANSS Scale for Suicide Ideation (SSI) YMRS SAE EPS Withdrawal 39% | |
| Berwaerts, 201110 RCT 3 Continents Industry ROB Moderate 20947174 | n = 300 Mean Age 40 Female 46% White 77% BP I 100% Inpatient (at least 1 week) Outpatient (weeks 2–7) | Manic/Mixed; YMRS ≥ 20 First Manic Episode; Schizoaffective; Substance Abuse; Other Mental Health Conditions; Neurological Disorders; Taking other medications; Pregnant/Nursing | Paliperidone extended release 3–12 mg/day (mean 8.1 mg/day) Lithium 0.6–1.2 mEq/L (mean NR) Or Valproate 50–125 mcg/mL (mean NR) | Placebo NA Lithium 0.6–1.2 mEq/L (mean NR) Or Valproate 50–125 mcg/mL (mean NR) | 7 weeks | CGI-BP-S GAF PANSS YMRS Response (YMRS decrease ≥50%) Remission (YMRS≤12) MADRS Adverse Events Withdrawal 37% | |
| Vieta, 201011 RCT 3 weeks Multisite 4 Continents Industry RoB Moderate 20565430 | N = 493 Mean Age 39 Female 42% White 68% BP I 100% Inpatient (at least 1 week) Outpatient (weeks 2–3) | Manic/Mixed; YMRS≥20; At least one episode within three years prior First Manic Episode Schizoaffective Substance abuse Other mental health Neurological disorders Labs/other conditions | Paliperidone extended release 3–12 mg/day (median/mode dosage 9 mg) | C1: Placebo C2: Quetiapine 400–800 mg/day | 3 week (12 week excluded for attrition) | YMRS GAF PANSS CGI-BP-S Response (YMRS decrease ≥50%) Remission (YMRS≤12) Withdrawal 21% at 3 weeks | |
| Berwaerts, 201212 RCT Multisite 5 Continents Industry RoB Moderate 22377512 | N = 766 Mean Age 40 Female 52% White 62% BP I 100% Outpatient | Manic/Mixed; YMRS≥20; 2 previous mood episodes (1 of which manic/mixed) within past 3 years; First manic episode; Schizoaffective; Other mental health; Neurological disorders; Taking other meds; Pregnant/nursing; Labs/Other conditions | Paliperidone extended release 3–12 mg/day | Olanzapine 5–20 mg/day | 15 weeks | Response (≥50% reduction in YMRS) Remission (YMRS and MADRS≤12) Withdrawal 49% | |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Effects; BP=bipolar disorder; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP=Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; DSM-IV= Diagnostic and statistical manual, 4th edition; EPS=Extrapyramidal Symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Depression Rating Scale; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; NOS=not otherwise specified; NR= not reported; Q-LES-Q=Quality of Life Enjoyment and Satisfaction Questionnaire; PANSS=Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT= Randomized Controlled Trial; RoB=risk of bias; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SDS=Sheehan Disability Scale; T=Trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G28Summary risk of bias assessments: paliperidone for mania
| Drug | Study Funding Source PMID | Overall Risk of Bias Assessment | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Paliperidone extended release | Berwaerts, 201212 Industry 22377512 | High | Very large dropout rate among all study arms, across all time periods |
| Berwaerts, 2012a9 Industry 20624657 | Moderate | Large dropout rate among all study arms; attrition 39% | |
| Vieta, 201011 Industry 20565430 | Moderate (3 week only) | Moderate dropout rate among all study arms, across all time periods; raters may not be blinded | |
| Berwaerts, 201110 Industry 20947174 | Moderate | Large dropout rate among all study arms; attrition 37% |
Abbreviations: PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial
Appendix Table G29Outcomes summary: paliperidone for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Study ROB PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paliperidone vs. placebo | Vieta, 201011 Moderate 20565430 | Responders (YMRS decrease ≥50%) 3 weeks Favors Paliperidone Paliperidone=106/190 Placebo=36/104 p<0.001 Remission (YMRS≤12) 3 weeks Favors Paliperidone Paliperidone=99/190 Placebo=30/104 p<0.001 | YMRS Change 3 weeks Favors treatment Least square mean difference between groups −5.5 (95% CI −7.57, −3.35) p<0.001 | CGI-BP-S 3 week Paliperidone −2.0 (95%CI −4, 2) Placebo −0.5 (95%CI −4, 2) Favors Paliperidone p<0.001 GAF 3 weeks Favors treatment Mean difference treatment: 11.6 Placebo: 12.2 p<0.001 | Overall Withdrawal Paliperidone=40/195 Placebo=41/105 Favors Paliperidone Withdrawal lack of effect Paliperidone=6/195 Placebo=19/105 Favors Paliperidone Withdrawal adverse events Paliperidone=9/195 Placebo=5/105 NS | Serious AE NR EPS No serious events in any treatment arm |
| Berwaerts, 2012a9 Moderate 20624657 | Responders (YMRS decrease ≥50%) 3 weeks NS Remission (YMRS≤12) 3 weeks NS | YRMS Change 3 weeks Least square mean difference Paliperidone 12 mg: −13.5 (9.17) n=109 Placebo: −10.1 (10.21) Difference between groups 3.4 n=115 p=0.025 Favors Paliperidone 12 mg (dose dependent) | CGI-BP-S 3 week NS GAF 3 weeks NS | Overall Withdrawal Paliperidone=132/347 Placebo=50/122 NS Withdrawal lackof effect Paliperidone=31/347 Placebo=24/122 Favors Paliperidone Withdrawal adverse events Paliperidone=25/347 Placebo=6/122 NS | Serious AE 1 death Paliperidone 6 mg (deemed not related) EPS Statistically significantly more in 12 mg paliperidon for akathisia and dystonia Treatment emergent depression: NS >7% weight gain NS | |
| Paliperidone + mood stabilizers vs. placebo + mood stabilizers | Berwaerts, 201110 Moderate 20947174 | Remission (YMRS≤12) 6 weeks NS Paliperidone 60% Placebo 57% p=0.12 Response (YMRS≥50% decrease) 6 weeks NS Paliperidone 62% Placebo 56% p=0.24 | YMRS 6 weeks Least squares mean difference NS p=0.16 | CGI-BP-S 6 weeks NS p=0.26 GAF 6 weeks NS p=0.71 | Suicide Ideation 1 in each group Overall Withdrawal Paliperidon=60/150 Placebo=51/150 NS Withdrawal lack of effect Paliperidone=12/150 Placebo=18/150 NS Withdrawal adverse events Paliperidone=12/150 Placebo=2/150 Favors Placebo | SAE 7 in each group; psychiatric disorders most common Treament emergent depression: 1% in each group Akathesia 8% vs. 1% Favored placebo. Weight increase≥7%: Paliperidone 15% Placebo 5% |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; BMI=Body Mass Index; CI=Confidence Interval; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S= Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; EPS=extrapyramidal symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS=Global Assessment Scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; OR=Odds Ratio; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SD=standard deviation; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G30Strength of evidence assessment: paliperidone for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paliperidone vs. placebo | Remission 3 wks Response 3 wks CGI Withdrawal – overall | 2 RCT (n=763) | See table above | Moderate | Inconsistent | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
| Withdrawal – adverse events | 2 RCT (n=763) | NS | Moderate | Consistent | Direct | Imprecise | Low | |
| YMRS 3 wks Withdrawal lack of efficacy | 2 RCT (n=763) | Favors Paliperidone possible dose response: NS at 3 and 6 mg, benefit at 12 mg or median dosage of 9 mg | Moderate | Consistent | Direct | Imprecise | Low | |
| Paliperidone + mood stabilizers vs. placebo + mood stabilizers | Remission 6 wks Response 6 wks YMRS 6 wks CGI-S 6 wks Withdrawals | 1 RCT (n=299) | See table above | Moderate | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; IPD=Individual Patient Data; NS=not significant; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Appendix Table G31Outcomes summary: paliperidone for mania vs. active control
| Drug | Study Comparison PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paliperidone extended release vs. olanzapine | Berwaerts, 201212 Moderate 22377512 | Response (YMRS decrease ≥50%) 15 weeks NS >70% responded overall Remission (YMRS≤12) 15 weeks NS >60% achieved remission | YMRS Least square mean difference 15 weeks NS −0.3 (−2.12, 1.57) | NR | Overall Withdrawal 15 weeks Paliperidone: 09/617 Olanzapine: 63/149 NS Withdrawal lack of effect Paliperidone:30/617 Olanzapine:5/149 NS Withdrawal adverse events Paliperidone:63/617 Olanzapine:13/149 NS | SAE Paliperidone: 42/614 Olanzapine: 10/148 NS |
| Paliperidone extended release vs. quetiapine | Vieta, 201011 Moderate 20565430 | Response (YMRS decrease ≥50%) 3 week Paliperidone 55.8% Quetiapine 49% NS RR 1.1 (95% CI 0.94, 1.38) Remission (YMRS≤12) 3 week Paliperidone 52.1% Quetiapine 47.4% NS RR 1.1 (95% CI 0.90, 1.35) | YMRS Change 3 week LSM difference (Quet-Pali) 1.5 (95% CI −0.28, 3.22) NS p=0.099 | GAF Change1 3 week Paliperidone 12.2 (sd 11.17) Quetiapine 11.6 (sd 11.96) NS p=NR CGI-BP-S 3 week Paliperidone −2.0 (95%CI −4, 2) Quetiapine −1.0 (95%CI −4, 2) NS p=NR | Switching 3 week Paliperidone 4.3% Quetiapine 2.7% NS p=NR Overall Withdrawal Paliperidone=40/195 Quetiapine=41/193 NS Withdrawal lack of effect Paliperidone=6/195 Quetiapine=15/105 Favors Paliperidone Withdrawal adverse events Paliperidone=9/195 Quetiapine=4/193 NS | SAE NR EPS No serious events in any treatment arm |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; BMI=Body Mass Index; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CI=Confidence Interval; EPS=extrapyramidal symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RR=Risk Ratio; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SD=standard deviation; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G32Strength of evidence assessment: paliperidone for mania vs. active control
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paliperidone extended release vs. olanzapine | Remission 15 wks Response 15 wks YMRS 15 wks Withdrawals | 1 RCT (n=766) | See table above | High | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
| Paliperidone extended release vs. quetiapine | Remission 3 wks Response 3 wks YMRS 3 wks CGI 3 wks GAF 3 wks Withdrawals | 1 RCT (n=388) | See table above | High | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CI=Confidence Interval; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; IPD=Individual Patient Data; NS=not significant; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Section 8. Tamoxifen
Appendix Table G33Characteristics of eligible studies: tamoxifen for acute mania
| Study, Year Design Location Funder Risk of Bias PMID | # Randomized Age (mean) Sex (% Female) Race (% White) Diagnosis (% BP I, II, NOS) Setting | Inclusions Key Exclusions | Intervention Dosage | Comparison Dosage | Follow-up Duration | Outcomes Reported Withdrawal (%) at endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yildiz, 200813 RCT Single-site Turkey Non-Profit RoB Moderate 18316672 | N = 66 Mean Age 33 Female 52% Race NR BP I 100% Outpatient | Mania; YMRS≥20 Schizoaffective Substance abuse Other mental health Neurological disorders Taking other meds Pregnant/nursing | Tamoxifen 20–80 mg/twice daily | Placebo | 3 week | CGI-BP-S HAM-D MADRS PANSS YMRS Response (YMRS decrease ≥50%) Withdrawal 24% |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Effects; BP=bipolar disorder; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP=Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; DSM-IV= Diagnostic and statistical manual, 4th edition; EPS=Extrapyramidal Symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Depression Rating Scale; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; NOS=not otherwise specified; NR= not reported; Q-LES-Q=Quality of Life Enjoyment and Satisfaction Questionnaire; PANSS=Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT= Randomized Controlled Trial; RoB=risk of bias; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SDS=Sheehan Disability Scale; T=Trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G34Summary risk of bias assessments: tamoxifen for mania
| Drug | Study Funding Source PMID | Overall Risk of Bias Assessment | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tamoxifen | Yildiz, 200813 Non-Profit 18316672 | Moderate | Blinding of patients, staff, raters not described; minor differences at baseline regarding pretreatment drugs may create residual confounding |
Abbreviations: PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial;
Appendix Table G35Outcomes summary: tamoxifen for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Study ROB PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tamoxifen vs. placebo | Yildiz, 200813 Moderate 18316672 | Response (YMRS decrease ≥50%) 3 weeks Favors tamoxifen Tamoxifen=14/29 Placebo=1/21 p=0.003 Remission (YMRS≤12) 3 weeks Favors tamoxifen Tamoxifen=8/29 Placebo=0/21 p=0.03 | YMRS Decrease Rate Over 3 weeks Favors tamoxifen Linear mixed model p<0.001 YMRS (Mean SD) Week 0 Tamoxifen 38.6 (5.0) Placebo 37.2 (6.6) Week 3 Tamoxifen 20.3 (11.2) Placebo 40.1 (10.4) | NR | NR Withdrawal Tamoxifen=6/35 Placebo=10/31 NS | Serious Adverse Events 1 Tamoxifen – Suicide Attempt 1 Placebo – Suicide Attempt |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; BMI=Body Mass Index; CI=Confidence Interval; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S= Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; EPS=extrapyramidal symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS=Global Assessment Scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; OR=Odds Ratio; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SD=standard deviation; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G36Strength of evidence assessment: tamoxifen for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tamoxifen vs. placebo | Remission 3 wks Response 3 wks YMRS 3 wks Withdrawals | 1 RCT (n=50) | See table above | Low | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; IPD=Individual Patient Data; NS=not significant; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Section 9. Topiramate
Appendix Table G37Characteristics of eligible studies: topiramate for acute mania
| Study, Year Design Location Funder Risk of Bias PMID | # Randomized Age (mean) Sex (% Female) Race (% White) Diagnosis (% BP I, II, NOS) Setting | Inclusions Key Exclusions | Intervention Dosage | Comparison Dosage | Follow-up Duration | Outcomes Reported Withdrawal (%) at endpoint |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bahk, 200514 Open-label RCT Multisite South Korea Industry ROB High 15610953 | N=74 Mean Age 37 Female 51% Race Asian BP-I 100% Outpatient | Mania YMRS≥20 Other mental health Pregnant/nursing Labs/other conditions Taking other meds | Topiramate average 220.6 mg/day + Risperidone average 3.4 mg/day | Divalproex average 908.3 mg/day Risperidone average 3.3 mg/day | 3 week | YMRS CGI Adverse Events Withdrawal 18% |
| Chengappa, 200615 RCT Multisite US Low Industry RoB Low 17196048 | N = 287 Mean Age 40 Female 56% White 84% BP I 100% Outpatient | Manic/Mixed; YMRS≥18 Recevied lithium or valproate at least 6 weeks, including stable dose 2 weeks prior to screening within specified serum levels Substance abuse Other mental health Neurological disorders Taking other meds Pregnant/nursing Labs/other conditions | T1: Topiramate 50–400mg/day (mean 6.2 mcg/mL day 42, 7.8 mcg/ml day 84) Lithium mean 0.7 mEq/L Valproate mean 69.8 mcg/ml | Placebo Lithium mean 0.7 mEq/L Valproate mean 71.0 mcg/ml | 12 week | YMRS CGI-S BPRS MADRS GAS Weight Response (≥50% improvement in YRMS) Withdrawal 38% |
| Kushner, 200616 Pooled Analysis of 4 RCTs (3 week data) Multisite 6 Continents Industry RoB Low 16411977 | N = 876 (includes only 400 mg/day topiramte arms and placebo arms Mean Age 41 Female 51% White 75% BP I 100% Inpatient (at least 4 days, as clinically warranted) | Manic/Mixed; YMRS≥20 First Manic Episode Schizoaffective Substance abuse Other mental health Taking other meds Pregnant/nursing Labs/other conditions | Topiramate 400mg/day (mean 313mg/day) (only 400 mg/day arms were common across pooled studies) | C1: Placebo C2: Lithium 300–1800 mg/day (0.8–1.2mEq/L) | 3 week | Weight YMRS Withdrawal 27% |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Effects; BP=bipolar disorder; BPRS=Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP=Clinical Global Impressions Scale for Bipolar Disorder; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; DSM-IV= Diagnostic and statistical manual, 4th edition; EPS=Extrapyramidal Symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS= Global Assessment Scale; HAM-D=Hamilton Depression Rating Scale; MADRS=Montgomery-Asberg Depression Rating Scale; NOS=not otherwise specified; NR= not reported; Q-LES-Q=Quality of Life Enjoyment and Satisfaction Questionnaire; PANSS=Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT= Randomized Controlled Trial; RoB=risk of bias; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SDS=Sheehan Disability Scale; T=Trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G38Summary risk of bias assessments: topimarate for mania
| Drug | Study Funding Source PMID | Overall Risk of Bias Assessment | Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topiramate | Bahk, 200514 Industry 15610953 | High | Randomization and allocation concealment not specified, open label dosing |
| Kushner, 200616 Industry 16411977 | Low | Well-disclosed and reported study (RCTs unique to this publication.) | |
| Chengappa, 200615 Industry 17196048 | Low | Well-disclosed and reported study |
Abbreviations: PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial
Appendix Table G39Outcomes summary: topiramate for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Study ROB PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topiramate vs. placebo | Kushner, 200616 Low 16411977 | NR | YMRS Change 3 weeks NS Mean difference (top-plac) 0.60 (95% CI −0.85, 2.0) p=0.418 n=434 I, n=317 C | NR | Overall Withdrawal Topiramte=123/331 Placebo=85/317 Favors Placebo Withdrawal lack of effect Topiramate=52/331 Placebo=39/317 NS Withdrawal adverse events Topiramate=20/331 Placebo=9/317 Favors Placebo | SAE Topiramate 3% Placebo 2% Suicide Attempt 3 weeks Topiramate 2/656 Placebo 0/429 (reported over 4 pooled RCTs, not 3 monotherapy tests) |
| Topiramate+mood stabilizer vs. placebo+mood stabilizer | Chengappa, 200615 Low 17196048 | Response (YMRS≥50% decrease) 12 weeks NS Topiramate 39% Placebo 38% p=0.914 | YMRS Change 12 weeks NS Topiramate −10.1±8.7 Placebo −9.6±8.2 p=0.797 | CGI-S Change 12 weeks NS Topiramate −0.9±1.1 Placebo −0.9±1.1 p=0.698 GAS Change 12 weeks NS Topiramate 7.2±9.9 Placebo 7.1±11.5 p=0.838 | BMI Change 12 weeks Favors Topiramate Topiramate −0.84±1.2 kg/m2 Placebo 0.07±1.1 kg/m2 p<0.001 Suicide Ideation Topiramate 1 patient Placebo 2 patients Overall Withdrawal Topiramate=57/143 Placebo=53/144 NS Withdrawal lack of effect Topiramate=6/143 Placebo=4/144 NS Withdrawal adverse events Topiramate=20/143 Placebo=10/144 Favors Placebo | NR |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; BMI=Body Mass Index; CI=Confidence Interval; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CGI-S= Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; EPS=extrapyramidal symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; GAS=Global Assessment Scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; OR=Odds Ratio; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RCT=randomized controlled trial; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SD=standard deviation; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G40Strength of evidence assessment: topiramate for mania vs. inactive control
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topiramate vs. placebo | YMRS 3 wks Withdrawal – lack of effect | 4 RCT (1 IPD) (n=876) | NS | Low | Consistent | Direct | Imprecise | Low |
| Withdrawals – overall | 4 RCT (1 IPD) (n=876) | Favors Placebo 37.2% vs. 26.8%, p=0.005 | Low | Consistent | Direct | Imprecise | Low | |
| Withdrawals – adverse events | 4 RCT (1 IPD) (n=876) | Favors Placebo 6.04% vs. 2.84%, p=0.049 | Low | Consistent | Direct | Imprecise | Low | |
| Topiramate +mood stabilizer vs. placebo+mood stabilizer | Response 12 wks YMRS 12 wks CGI-S 12 wks Withdrawals | 1 RCT (n=287) | See table above | Low | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Severity Scale; IPD=Individual Patient Data; NS=not significant; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
Appendix Table G41Outcomes summary: topiramate for mania vs. active control
| Drug | Study Comparison PMID | Responder/Remitter | Symptom | Function | Other | AE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topiramate vs. lithium | Kushner, 200616 Low 16411977 | NR | YMRS Change 3 week Mean difference (top-lith) 6.14 (95% CI 3.94, 8.34) Favors Lithium p<0.001 | NR | Weight 3 week Mean difference (top-lith) −1.82% (95% CI −2.90%, −0.74%) Favors Topiramate p<0.001 Overall Withdrawal Topiramte=47/226 Lithium=51/227 NS Withdrawal lack of effect Topiramate=23/226 Lithium=19/227 NS Withdrawal adverse events Topiramate=6/226 Lithium=17/227 Favors Topiramate p=.019 | SAE Topiramate 3% Lithium 1.5% |
| Topiramate + risperidone vs. divalproex + risperidone | Bahk, 200514 High 15610953 | Response (YMRS decrease ≥50%) 15 weeks NS >70% responded overall Remission (YMRS≤12) 15 weeks NS >60% achieved remission | YMRS 6 weeks NS (Both groups improved statistically significantly) | CGI 6 weeks NS (Both groups improved statistically significantly) | BMI Divalproex 73% patients increase Topiramate 25% patients decreased Overall Withdrawal NS Withdrawals reasons not reported by group | Reported no SAEs EPS NS between groups (“about 1/3 of patients in both groups”) |
Abbreviations: AE=Adverse Events; BMI=Body Mass Index; CGI=Clinical Global Impressions; CGI-BP-S=Clinical Global Impressions, Bipolar, Severity Scale; CI=Confidence Interval; EPS=extrapyramidal symptoms; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; NR=not reported; NS=not significant; PMID=PubMed Identification Number; RR=Risk Ratio; SAE=Serious Adverse Events; SD=standard deviation; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Appendix Table G42Strength of evidence assessment: topiramate for mania vs. active control
| Comparison | Outcome | # Studies/Design (n analyzed) | Finding or Summary Statistic | Study Limitations | Consistency | Directness | Precision | Overall Grade/Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Topiramate vs. Lithium | YMRS 3 wks | 2 RCTs (1 IPD) (n=453) | Favors Lithium Mean difference 6.14 (95% CI 3.94, 8.34) | Low | Consistent | Direct | Imprecise | Low |
| Withdraw – overall, lack of effect | 2 RCTs (1 IPD) (n=453) | NS | Low | Consistent | Direct | Imprecise | Low | |
| Withdraw – adverse events | 2 RCTs (1 IPD) (n=453) | Favors Topiramate 2.65% vs. 7.49%, p=0.019 | Low | Consistent | Direct | Imprecise | Low | |
| Topiramate + risperidone vs. divalproex + risperidone | Remission 6 wks Response 6 wks YMRS 6 wks CGI 6 wks Withdrawals | 1 RCT (n=74) | See table above | High | Unknown | Direct | Imprecise | Insufficient |
Abbreviations: CGI= Clinical Global Impressions; CI=Confidence Interval; GAF=General Assessment of Functioning Scale; IPD=Individual Patient Data; NS=not significant; RCT=randomized controlled trial; YMRS = Young Mania Rating Scale
Notes:
- 1
Publication bias for antipsychotics, antidepressants, and behavioral interventions for depressive disorders is suspected.
- 2
Data were generally imprecise due to missing data from high attrition rates, which was commonly dealt with by Last Observation Carried Forward (LOCF). LOCF requires an assumption that the health status of patients who dropped out of the trial would not have changed had future observations been recorded, a strong assumption in the context of bipolar disorder research.
References for Appendix G
- 1.
- Jahangard L, Soroush S, Haghighi M, et al In a double-blind, randomized and placebo-controlled trial, adjuvant allopurinol improved symptoms of mania in in-patients suffering from bipolar disorder. European Neuropsychopharmacology. Jun. 2014 2, 2014(Pagination)doi: http://dx
.doi.org/10 .1016/j.euroneuro.2014.05.013. PMID: 24953766. [PubMed: 24953766] - 2.
- Weiser M, Burshtein S, Gershon AA, et al Allopurinol for mania: A randomized trial of allopurinol versus placebo as add-on treatment to mood stabilizers and/or antipsychotic agents in manic patients with bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disorders. 2014 2014);16(4):441–7. doi: http://dx
.doi.org/10.1111/bdi.12202. PMID: 24712840. [PubMed: 24712840] - 3.
- Fan A, Berg A, Bresee C, et al Allopurinol augmentation in the outpatient treatment of bipolar mania: a pilot study. Bipolar Disorders. 2012 Mar;14(2):206–10. doi: http://dx
.doi.org/10 .1111/j.1399-5618.2012.01001.x. PMID: 22420596. [PubMed: 22420596] - 4.
- Machado-Vieira R, Soares JC, Lara DR, et al A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled 4-week study on the efficacy and safety of the purinergic agents allopurinol and dipyridamole adjunctive to lithium in acute bipolar mania. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2008 Aug;69(8):1237–45. PMID: 18681754. [PMC free article: PMC2727594] [PubMed: 18681754]
- 5.
- Arabzadeh S, Ameli N, Zeinoddini A, et al Celecoxib adjunctive therapy for acute bipolar mania: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Bipolar Disorders. 2015 01 Sep;17(6):606–14. doi: http://dx
.doi.org/10.1111/bdi.12324. PMID: 26291962 (pubmed) 2015329826 (embase). [PubMed: 26291962] - 6.
- Chen J, Lu Z, Zhang M, et al A randomized, 4-week double-blind placebo control study on the efficacy of donepezil augmentation of lithium for treatment of acute mania. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment. 2013 17, 2013;9:839–45. PMID: 23807849. [PMC free article: PMC3688436] [PubMed: 23807849]
- 7.
- Astaneh AN, Rezaei O. Adjunctive treatment with gabapentin in bipolar patients during acute mania. International Journal of Psychiatry in Medicine. 2012;43(3):261–71. PMID: 22978083. [PubMed: 22978083]
- 8.
- Ahmad A, Sheikh S, Shah T, et al Endoxifen, a New Treatment Option for Mania: A Double-Blind, Active-Controlled Trial Demonstrates the Antimanic Efficacy of Endoxifen. Clinical and Translational Science. 2016 01 Oct;9(5):252–9. doi: http://dx
.doi.org/10.1111/cts.12407. PMID: 27346789 PMID/611114504 Embase. [PMC free article: PMC5350997] [PubMed: 27346789] - 9.
- Berwaerts J, Xu H, Nuamah I, et al Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of paliperidone extended-release in the treatment of acute mania: a randomized, double-blind, dose-response study. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2012 Jan;136(1–2):e51–60. doi: http://dx
.doi.org/10 .1016/j.jad.2010.06.030. PMID: 20624657. [PubMed: 20624657] - 10.
- Berwaerts J, Lane R, Nuamah IF, et al Paliperidone extended-release as adjunctive therapy to lithium or valproate in the treatment of acute mania: a randomized, placebo-controlled study. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2011 Mar;129(1–3):252–60. doi: http://dx
.doi.org/10 .1016/j.jad.2010.09.011. PMID: 20947174. [PubMed: 20947174] - 11.
- Vieta E, Nuamah IF, Lim P, et al A randomized, placebo- and active-controlled study of paliperidone extended release for the treatment of acute manic and mixed episodes of bipolar I disorder. Bipolar Disorders. 2010 May;12(3):230–43. doi: http://dx
.doi.org/10 .1111/j.1399-5618.2010.00815.x. PMID: 20565430. [PubMed: 20565430] - 12.
- Berwaerts J, Melkote R, Nuamah I, et al A randomized, placebo- and active-controlled study of paliperidone extended-release as maintenance treatment in patients with bipolar I disorder after an acute manic or mixed episode. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2012 May;138(3):247–58. doi: http://dx
.doi.org/10 .1016/j.jad.2012.01.047. PMID: 22377512. [PubMed: 22377512] - 13.
- Yildiz A, Guleryuz S, Ankerst DP, et al Protein kinase C inhibition in the treatment of mania: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of tamoxifen. Archives of General Psychiatry. 2008 Mar;65(3):255–63. doi: http://dx
.doi.org/10 .1001/archgenpsychiatry.2007.43. PMID: 18316672. [PubMed: 18316672] - 14.
- Bahk WM, Shin YC, Woo JM, et al Topiramate and divalproex in combination with risperidone for acute mania: a randomized open-label study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2005 Jan;29(1):115–21. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2004.10.013. PMID: 15610953. [PubMed: 15610953] [CrossRef]
- 15.
- Chengappa RKN, Schwarzman LK, Hulihan JF, et al Adjunctive topiramate therapy in patients receiving a mood stabilizer for bipolar I disorder: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2006 Nov;67(11):1698–706. PMID: 17196048. [PubMed: 17196048]
- 16.
- Kushner SF, Khan A, Lane R, et al Topiramate monotherapy in the management of acute mania: results of four double-blind placebo-controlled trials. Bipolar Disorders. 2006 Feb;8(1):15–27. PMID: 16411977. [PubMed: 16411977]
- Other Drugs for Acute Mania - Treatment for Bipolar Disorder in Adults: A System...Other Drugs for Acute Mania - Treatment for Bipolar Disorder in Adults: A Systematic Review
- Preface - Treatment for Restless Legs SyndromePreface - Treatment for Restless Legs Syndrome
- Results - Safety of Vaccines Used for Routine Immunization in the United States:...Results - Safety of Vaccines Used for Routine Immunization in the United States: An Update
- Applicability Tables - Treatments for Ankyloglossia and Ankyloglossia With Conco...Applicability Tables - Treatments for Ankyloglossia and Ankyloglossia With Concomitant Lip-Tie
- Drug Treatments for Depression - Treatment for Bipolar Disorder in Adults: A Sys...Drug Treatments for Depression - Treatment for Bipolar Disorder in Adults: A Systematic Review
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...