NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Garsa A, Jang JK, Baxi S, et al. Radiation Therapy for Brain Metastases [Internet]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2021 Jun. (Comparative Effectiveness Review, No. 242.)
Review Approach
The methods for this evidence review follow the Methods Guide for the Evidence-based Practice Center (EPC) Program. Appendix A provides more detail on the methods. Appendix B provides the list of excluded and background studies. Appendix C provides more details on the results and Appendix D provides the evidence tables. The topic of this report was developed by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) in consultation with the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ). Initially a panel of Key Informants provided input on the Key Questions to be addressed. The Key Questions were posted on AHRQ’s Effective Health Care (EHC) website for public comment for 3 weeks in July 2019, and PCORI conducted a stakeholder call to discuss the Key Questions in August 2019. The EPC revised the questions in response to comments. A panel of Technical Experts provided high-level content and methodological expertise throughout development of the review protocol. Further details regarding expert guidance and review are provided in Appendixes E and F. The final protocol is posted on the EHC website at https://effectivehealthcare.ahrq.gov/products/radiation-brain-metastases/protocol. The PROSPERO registration is CRD42020168260.
Key Questions
The report was guided by four Key Questions, addressing initial and post-surgery treatment effects and adverse events.
- Key Question 1. What is the effectiveness of whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT), alone or in combination with stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) or systemic therapies, as initial treatment in patients with brain metastases on patient-relevant outcomes, such as overall survival and quality of life?
- How does effectiveness vary by dose fractionation schedule and technique?
- How does effectiveness differ by patient prognosis and primary tumor site?
- How does effectiveness differ by the addition of systemic therapies?
- Key Question 2. What is the effectiveness of SRS/fractionated stereotactic radiation as initial treatment in patients with brain metastases on patient-relevant outcomes, such as overall survival and quality of life?
- How does effectiveness vary by dose fractionation schedule and technique?
- How does effectiveness differ by patient prognosis and primary tumor site?
- How does effectiveness differ by the addition of systemic therapies?
- Key Question 3. What is the effectiveness (or comparative effectiveness) of postoperative SRS compared to WBRT, observation, or preoperative SRS in patients with brain metastases on patient-relevant outcomes, such as overall survival and quality of life?
- How does effectiveness vary by dose fractionation schedule?
- Key Question 4. What are the adverse effects (i.e., serious harms) of WBRT, SRS, and systemic therapies for patients with brain metastases (either alone or in combination)?
- Do adverse effects vary by important patient characteristics (i.e., age, performance status, patient prognosis, disease status, primary tumor site) or dose fractionation schedule and technique?
Analytic Framework
The analytic framework (Figure 1) outlines the patient population, the interventions, and the outcomes that are addressed in the evidence synthesis.
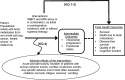
Figure 1
Analytic framework for radiation therapy for brain metastases. Abbreviations: KQ = Key Question, SRS = stereotactic radiosurgery, WBRT = whole brain radiation therapy
Study Selection
We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) evaluating radiation therapy, including WBRT and SRS alone or in combination, as initial or postoperative treatment, with or without systemic therapy (immunotherapy, chemotherapy or targeted therapy) for adults with brain metastases due to non-small cell lung cancer, breast cancer, and melanoma. Studies had to report on effects of radiation therapy in the 1990s or later, and we included studies published to July 2020. We also included large (N≥200) clinical controlled trials and cohort studies comparing two cohorts to address adverse effects of the interventions. The details of the sources, search strategies, screening procedure, and the eligibility criteria are described in detail in Appendix A.
Data Extraction and Risk of Bias Assessment
We abstracted study, patient, intervention and comparator details, and documented the results for clinical and patient-centered outcomes as well as adverse events. Publications reporting on the same patient group were consolidated. To facilitate comparisons across studies, we standardized descriptions (e.g., intervention characteristics) and converted study characteristics to proportions. Results were converted to measure-independent variables such as relative risks and standardized mean differences and effect estimates were presented together with 95-percent confidence intervals. Time to event data were analyzed as the hazard ratio.
Risk of bias assessed selection bias and risk of bias arising from the randomization process, performance bias and bias due to deviations from intended interventions, attrition bias and bias due to missing outcome data, detection bias and bias in measurement of the outcome, reporting bias and bias in selection of the reported results, and other sources of bias (lack of use of validated measures). In addition, we evaluated the data collection of adverse events and the reporting of adverse events.
The procedures are described in detail in Appendix A.
Data Synthesis and Analysis
We synthesized the effects of WBRT (Key Question [KQ] 1), SRS (KQ2), post-surgery treatment (KQ3), and any adverse events (KQ4) associated with the interventions. Where outcomes, interventions, and comparators allowed, we determined pooled effects across studies for the following outcomes: overall survival, disease-free survival, deaths due to brain metastases, intracranial progression, quality of life, functional status, cognitive effects, serious adverse events, number of adverse events, radiation necrosis, headaches, fatigue, seizure, and vomiting. We assessed statistical heterogeneity with the I-squared statistic and explored publication bias (Begg, Egger test). To address the subquestions, we conducted meta-regressions to detect effect modifiers such as the role of prognosis and the primary cancer site in indirect analyses across studies. The analytic methods are documented in detail in Appendix A.
Contacting Authors
To allow for more analyses, we contacted all RCTs’ authors and asked specifically about the 14 outcomes of interest and the effect measure we were using (e.g., time to event data to compute hazard ratios, mean and standard deviation for intervention and control group to compute mean differences between groups). We asked authors to send us the data or to submit to clinicaltrials.gov.
Grading the Strength of the Body of Evidence
We formulated evidence statements for the interventions and outcomes of interest. We then graded the strength of evidence to describe our confidence in effect estimates as high, moderate, low, and insufficient evidence. The assessment is based on our analysis of the study limitations, directness, consistency, precision, and reporting bias (see Appendix A for more details).
- Methods - Radiation Therapy for Brain MetastasesMethods - Radiation Therapy for Brain Metastases
- Abbreviations - Treatment for Bipolar Disorder in Adults: A Systematic ReviewAbbreviations - Treatment for Bipolar Disorder in Adults: A Systematic Review
- Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 [Mus musculus]Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 [Mus musculus]gi|80477474|gb|AAI08373.1|Protein
- Treatment Strategies for Women With Coronary Artery DiseaseTreatment Strategies for Women With Coronary Artery Disease
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
