NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Gartlehner G, Hansen RA, Thieda P, et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Second-Generation Antidepressants in the Pharmacologic Treatment of Adult Depression [Internet]. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2007 Jan. (Comparative Effectiveness Reviews, No. 7.)
This publication is provided for historical reference only and the information may be out of date.

Comparative Effectiveness of Second-Generation Antidepressants in the Pharmacologic Treatment of Adult Depression [Internet].
Show detailsDiscontinuation Rates
Background
Presented in this appendix are relative risk meta-analyses that compare selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) with individual drugs with respect to discontinuation. The specific comparisons with SSRIs are shown below: bupropion, duloxetine, mirtazapine; nefazodone; trazodone, and venlafaxine The first six figures are for overall discontinuation. The two sets of figures following those are for discontinuation specifically for adverse events and then for discontinuation for lack of efficacy. All are random effects models.
Relative Risk of Overall Discontinuation
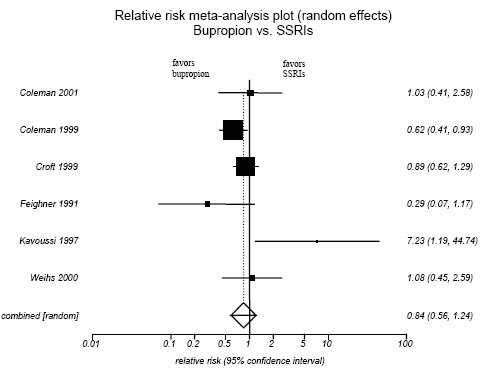
Figure H-1. Bupripion vs. SSRIs
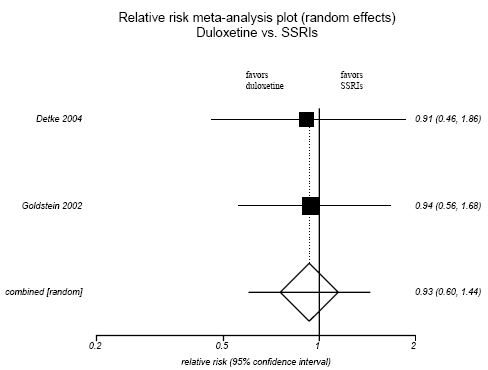
Figure H-2. Duloxetine vs. SSRIs
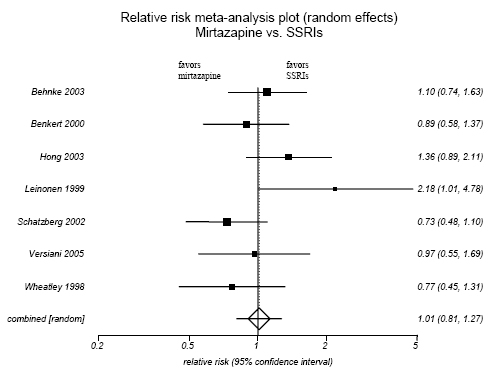
Figure H-3. Mirtazapine vs. SSRIs
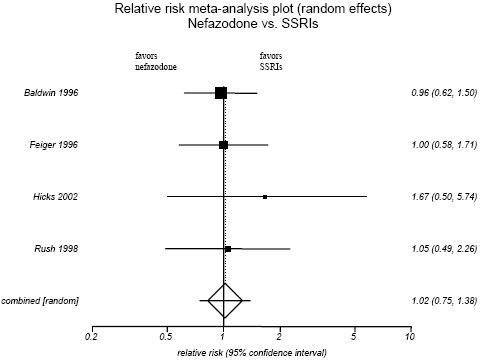
Figure H-4. Nefazodone vs. SSRIs
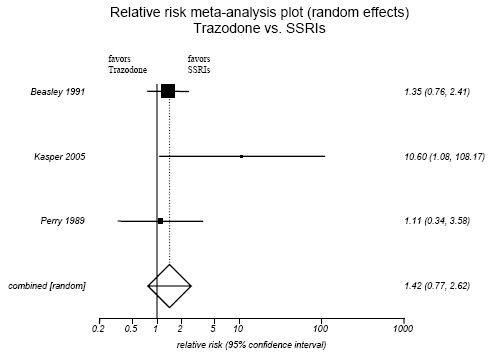
Figure H-5. Trazadone vs. SSRIs
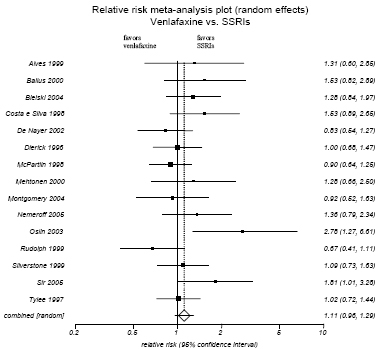
Figure H-6. Venlafaxine vs. SSRIs
Relative Risk of Discontinuation because of Adverse Events
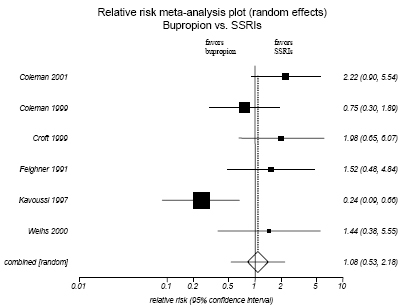
Figure H-7. Bupropion vs. SSRIs: Adverse Events

Figure H-8. Duloxetine vs. SSRIs: Adverse Events Only
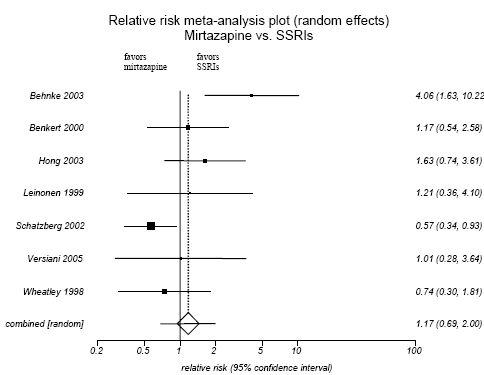
Figure H-9. Mirtzapine vs SSRIs: Adverse Events Only
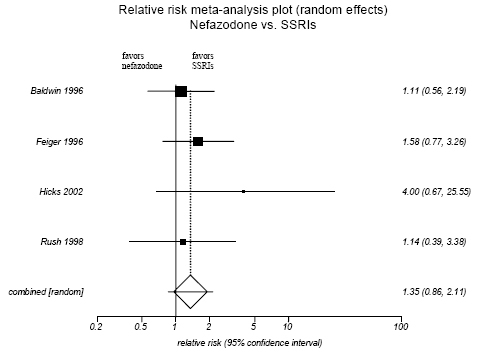
Figure H-10. Nefazodone vs SSRIs: Adverse Events Only
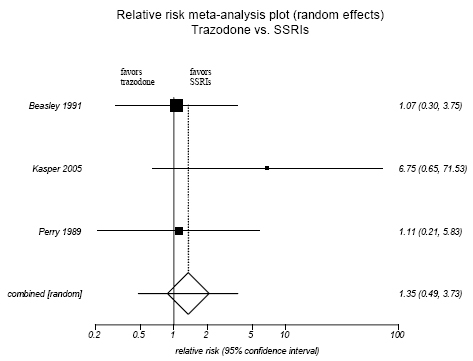
Figure H-11. Trazodone vs SSRIs: Adverse Events Only
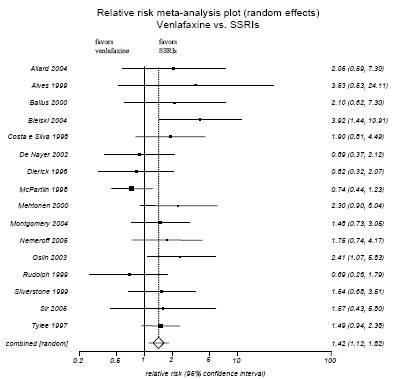
Figure H-12. Venlafaxine vs SSRIs: Adverse Events Only
Relative Risk of Discontinuation because of Lack of Efficacy
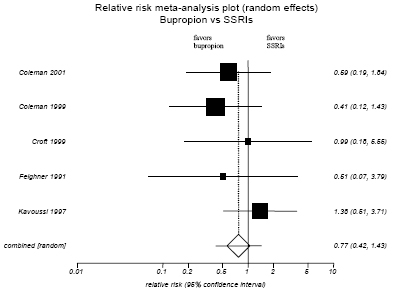
Figure H-13. Bupropion vs. SSRIs: Lack of Efficacy
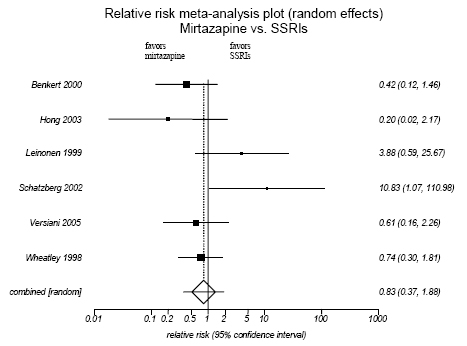
Figure H-14. Mirtzazpine vs. SSRIs: Lack of Efficacy
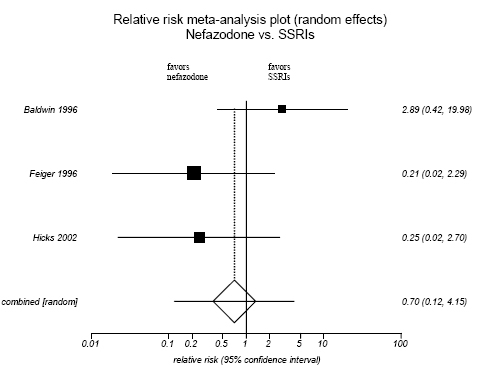
Figure H-15. Nefazodone vs SSRIs: Lack of Efficacy
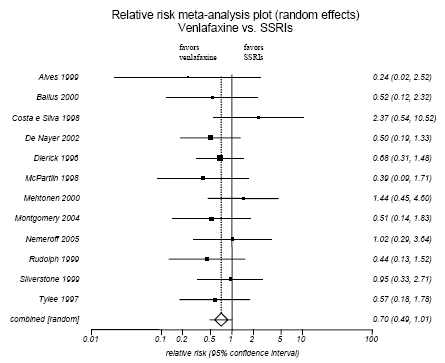
Figure H-16. Venlaxafine vs SSRIs: Lack of Efficacy
- Meta-analyses of Discontinuation Rates - Comparative Effectiveness of Second-Gen...Meta-analyses of Discontinuation Rates - Comparative Effectiveness of Second-Generation Antidepressants in the Pharmacologic Treatment of Adult Depression
- Key Informants - Treatment for Glaucoma: Comparative EffectivenessKey Informants - Treatment for Glaucoma: Comparative Effectiveness
- Peer Reviewers - Comparative Effectiveness of Second-Generation Antidepressants ...Peer Reviewers - Comparative Effectiveness of Second-Generation Antidepressants in the Pharmacologic Treatment of Adult Depression
- Results - Diagnostic Errors in the Emergency Department: A Systematic ReviewResults - Diagnostic Errors in the Emergency Department: A Systematic Review
- Evidence Summary - Interventional Treatments for Acute and Chronic Pain: Systema...Evidence Summary - Interventional Treatments for Acute and Chronic Pain: Systematic Review
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...
