NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Liedtke WB, Heller S, editors. TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2007.

TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades.
Show detailsPutting together this volume has been greatly enjoyable! First, our heartfelt gratitude goes to all contributors for making room in their busy professional lives to generate excellent chapters. It takes considerable energy and effort to deliver a complete chapter, which generates no immediate quid pro quo benefit for the chapter author. We are all too aware that this energy and effort could have been invested in the fight-to-survive effort mandatory in 2006, amid narrowing research budgets and increasing workloads with teaching, review commitments, and administrative dead-beat jobs such as animal or internal review board protocols, which stretch our workload toward 14- to 16-hour days. In view of this, again, thank you for contributing highly relevant work. After all, it must be the fascination with TRP channels that drives us—it’s the TRP, stupid! This is highlighted by the number of publications—primary papers and review articles—over time (see Figure P.1), which has currently reached a hyperexponential phase. Where will it go?
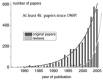
FIGURE P.1
Number of TRP papers. (Courtesy of Bernd Nilius, Leuven, Belgium.)
This fascination has led to a crowding of our field, which, in turn, has brought with it some unfortunate consequences. These imply at times undesirable side effects, not unlike those seen in the animal world, when a limited supply is available to a hypermotivated cohort consisting of so many individuals that not all of them are able to satisfy their needs. In a recent example, we learned that an author experienced, after submitting an invited review paper on a TRP-related subject to a scientific journal (a decent journal, neither a top-tier journal nor an obscure one), a harrowing review process, which consisted of two rounds of ‘‘bean counting’’ with a total of more than 90 points of criticism. Needless to say it was difficult to recognize a significant improvement by these modifications, and the primary submission had received input from several curious and critical readers and had been submitted in technically flawless shape. This leaves room for worry about where our field is heading. Is the stress of having to secure an existence as a scientist so overbearing that this leads to a dog-eat-dog attitude? Or is this merely an egregious example of narcissism and allodynic territoriality, which can happen in a rapidly moving field, and will remain, hopefully, an exception?
This volume has been edited carefully, yet one major editorial principle has been to let authors have their say without the constraints imposed by detail-obsessed reviewers. Because the field of TRP channels is new and rapidly moving, this also means that some “hot topic” areas have been covered by more than one author, and the viewpoints of these authors have not been edited for mutual alignment. Time will show where we will be taken.
This volume does not claim to represent an all-comprehensive view of the field of TRP channel biology (for this, the interested reader is referred to numerous excellent review papers referenced in the individual chapters; the latest wave of them is in an extra section of Annual Review of Physiology, vol. 68, pp. 619–736, 2006). This book, however, does shed light on selected topics of outstanding interest in the TRP arena, and the spotlight is cast by individuals who did earn their mettle.
A book on a hyper-rapidly moving topic such as TRP channels does raise the question of how such a topic can be dealt with in the publishing world. Web-based follow-up editions represent one hypothetical tool in response to this challenge, which we deem an attractive possibility.
- Preface - TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signalin...Preface - TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades
- Activation Mechanisms and Functional Roles of TRPP2 Cation Channels - TRP Ion Ch...Activation Mechanisms and Functional Roles of TRPP2 Cation Channels - TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades
- Genetics Can Be Painless: Molecular Genetic Analysis of Nociception in Drosophil...Genetics Can Be Painless: Molecular Genetic Analysis of Nociception in Drosophila - TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades
- The Ca2+-Activated TRP Channels: TRPM4 and TRPM5 - TRP Ion Channel Function in S...The Ca2+-Activated TRP Channels: TRPM4 and TRPM5 - TRP Ion Channel Function in Sensory Transduction and Cellular Signaling Cascades
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...