NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
NCBI News [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 1991-2012.
Featured Resource: New Discovery-oriented PubMed and NCBI Homepage
A new and improved interface to the PubMed search and retrieval system is now in service at the NCBI site.
Accompanying the new PubMed is a completely re-designed NCBI Homepage.
Both pages feature a standard search bar with menus to access all NCBI resources, a list of instructions for completing common tasks (“How to…”), and a universal NCBI footer, soon to be on all NCBI pages, that provides quick links to NCBI resources.
The new PubMed is more streamlined than before with the more popular options easier to find along with access to related resources presented in a more obvious way. All previous functionality is still present for advanced searching, with options combined in a more unified and logical way bringing related tasks together and separating those that are different. The new NCBI Homepage is designed to serve as a Site Guide with a listing of all NCBI resources classified by topic and directions for common tasks readily accessible.
The NCBI Site Guide
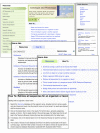
The NCBI Homepage is now the NCBI Site Guide as shown in Figure 1. This page is designed to provide rapid access to major areas of the NCBI Web site and to provide help and guidance for selecting the most appropriate databases, tools, and other resources for the task at hand. The central section of the Site Guide provides a list of 15 categories of associated NCBI resources: Literature, DNA & RNA, Proteins, Sequence Analysis, Genes & Expression, Genomes, Maps & Markers, Domains & Structures, Genetics & Medicine, Taxonomy, Data & Software, Training & Tutorials, Homology, Small Molecules, and Variation. Each one of these categories expands to a list of relevant databases and other features of the NCBI site grouped into Databases, Tools, Downloads and Submissions. For example, the DNA & RNA group expands when clicked to an organized list of 12 databases, five analysis tools, four avenues for downloading data, and two submission pathways. Each item in the Resources list has a brief description and a main heading link that leads directly to the relevant page. NCBI resources that are particularly relevant, new, or otherwise important are highlighted in these lists. These Featured Resources are also available in a section of the new universal NCBI footer, described below. In addition to the Featured Resources, a separate section on the right-hand-side of the Site Guide lists Popular Resources. The most commonly accessed resources at the NCBI site based on usage statistics are listed in this section. These provide rapid shortcuts to databases such as PubMed and Gene and tools such as BLAST.
Common Elements on New NCBI Pages
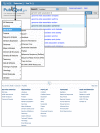
Both the new PubMed and the new Site Guide have a new search bar and footer area that will aid navigation shown in Figure 2. These two features will be standard on all NCBI pages in the near future. The search bar at the top of the page has the traditional database pull-down list providing access to all NCBI Entrez databases. This bar also has the new “Resources” and “How To” pull-down lists to aid navigation and to access to practical task-oriented help. The Resources are the 15 categories of resources from the Site Guide, described above. Items in this list expand when selected to provide rapid access to the NCBI featured resources in that category plus a link to retrieve the entire category list in the new Site Guide. The “How To” pull-down links to the practical step-by-step instructions for common tasks. These are the same “How To” directions available from the Site Guide.
The new footer provides rapid navigation to all major areas of the NCBI site. At the top of the footer is a chain of links indicating the current page and its location in the Resource categories and providing “breadcrumbs” leading up the hierarchy. The four columns of links include the Resources, Featured and Popular categories from the Site Guide as wells as help documents under “Getting Started” and NCBI news, background, and contact information under “NCBI Information.”
Using the New PubMed Interface
The new PubMed interface has a more basic format without the various tabs that were present on the previous version. The functions provided by the tabs including Limits, Preview/Index, and History are now available as part of the Advanced Search page linked at the top of the search form. Popular links that were previously available on the blue-side bar in the old system are now organized into three columns below the search bar on the PubMed Homepage: Using PubMed containing help documents; PubMed Tools with the Single and Batch Citation Matchers, Clinical Queries, and Topic-Specific Queries; and More Resources with links to the Related MeSH and Journals databases, Clinical Trials, and the Entrez programming utilities (E-utilities). Table 1 provides a map of features in the old PubMed interface to their equivalents in the new interface.
Table 1
Mapping of old PubMed features to the equivalent features in the new PubMed interface.
Example: Finding genome wide association studies on late-onset Alzheimer Disease
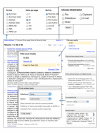
A search for genome wide association studies for late-onset Alzheimer disease is a useful demonstration of the new PubMed interface and features. Typing “genome wide association Al ...” in the PubMed search box begins the search. As the query is typed, suggested queries appear below the search (Figure 2, top panel). These auto-complete suggestions are taken from recent productive queries from PubMed visitors that match the current query. Selecting the query “genome wide association study alzheimer” retrieves the set of 60 results shown in Figure 3. Like the PubMed Homepage, this new results summary page is simpler than the previous version, lacking the numerous tabs, display options, and other devices along the top of the page. Display and save options are now incorporated into the “Display settings” and “Send to” pop-up menus. These menus are present on both the Summary, shown in Figure 3, and the Abstract displays shown in Figure 4. The “Display Settings” menu allows for selection of any standard PubMed format, for changing the number of records displayed, and altering the sort order of the records. The previous option to send to text is automatically invoked by choosing any format other than Summary or Abstract (MEDLINE, XML, PMID List, Summary(Text), Abstract(Text)). The new “Send to” menu provides various ways of saving records for later use by sending them to a local file (File), the collections in MyNCBI (Collections), the LoansomeDoc ordering system (Order), the NCBI clipboard (Clipboard), or to an e-mail account (E-mail). The File and E-mail options allow for the selection of format and sorting order before sending.
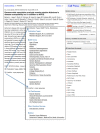
Figure 4
The new Abstract format display in PubMed. The Abstract format combines the previous Abstract Plus and Citation formats by providing expandable sections with access to Publication Types, MeSH Terms, Substances, and LinkOut items.
In addition to standard Discovery items such as Title search and the PubMed Central Ad, the right-hand Discovery Column on the summary display contains three new items that provide advanced functions: Filter links, Related data, and Search details. The Filter links provide filtered or limited results and supersedes the filter tabs in the old PubMed. Default filters show review articles or articles with free full-text. A filter may be added to the current search by clicking on the link to apply the filter, clicking the plus sign that appears to append the filter to the search, and running the search with the new terms. In the current example, applying the Free Full Text and Review Filters in succession finds one review article with full-text in PubMed Central. Custom filters may be added through a MyNCBI account by following the “Manage filters” link.
The Related Data feature links to related items in the Entrez system for the entire set of articles displayed. These relationships may be based on computed similarity as with PubMed related articles or based on known linkages as when an article reports a nucleotide or protein sequence. For instance, there are 12 Gene records that cite members of the full-text-filtered set of articles in the current example.
The Search details feature shows useful information about query translation and mapping to the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH). The query here maps to the MeSH terms “alzheimer disease” and “genome wide association study”. More precise results may be obtained by editing the query translation so that only the indexed MeSH terms are searched. The following query results in a more relevant set of 23 articles:
genome wide association study[MeSH Terms] AND alzheimer disease[MeSH Terms]
Clicking on any of the titles in the set of results displays the new Abstract view of the PubMed record shown in Figure 4. This new format combines the formerly separate Web displays of Abstract and Abstract Plus formats and replaces the Citation format by including an expandable list that contains information from the Citation format: Publication Types, MeSH Terms, and Substances. The plain-text Abstract format is still available through the Display Settings menu described above for the search summary page.
Summary
The new NCBI Site Guide and PubMed interface are designed to be more intuitive and less complicated. These improvements are part of the ongoing NCBI Discovery Initiative: making the NCBI interfaces easier to use and exposing relevant related resources. The changes in the Homepage and PubMed herald changes coming to all NCBI interfaces that will produce a more consistent, effective, and powerfully integrated set of databases and tools.
New Databases and Tools
Bookshelf
New books added to the Bookshelf include: Comparative Oncology, Preterm Birth: Causes, Consequences, and Prevention, Advancing Nuclear Medicine Through Innovation, and various Drug Class Reviews titles. To browse any of these books go to www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=Books
Microbial Genomes
Thirty-three finished microbial genomes were added to the NCBI databases between October 29 and November 24, 2009. The original sequence data files submitted to GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ are on the FTP site: ftp.ncbi.nih.gov/genbank/genomes/Bacteria/. The RefSeq provisional versions of these genomes are also available: ftp.ncbi.nih.gov/genomes/Bacteria/.
GenBank News
GenBank release 174.0 is on the NCBI Web Service and FTP site. The current release incorporates sequence data as of October 16, 2009. Release notes with detailed information are on the FTP site: ftp.ncbi.nih.gov/genbank/gbrel.txt
Updates and Enhancements
RefSeq
RefSeq Release 38 is now available through the Entrez system and can be downloaded from the FTP site (ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/refseq/release). This full release incorporates genomic, transcript, and protein data available as of November 7, 2009. It includes 13,436,447 records from 9,115 different species and strains. Changes since the last release can be found in the release notes (ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/refseq/release/release-notes/RefSeq-release38.txt). More information on the RefSeq project is available on the RefSeq Homepage: www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/RefSeq/.
Entrez Gene
New features have been added to Entrez Gene displays. A ‘Recent Activity’ display now appears in each Gene record page in addition to the summary page. The Additional Links section now includes a ‘Gene LinkOut’ subsection that displays relevant external gene links that have been submitted by external databases. To receive Gene-related announcements, sign up for the ‘gene-announce’ mailing list.
Exhibits
NCBI will have an exhibit booth at the American Society for Cell Biology annual meeting in San Diego, CA, held December 5-9, 2009.
PubMed E-Utilities
PubMed 2010 DTDs will go into effect on December 14. The 2010 DTDs are available from the Entrez DTD page: eutils.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/corehtml/query/DTD/index.shtml. Specific DTD changes are noted in the Revision Notes section near the top of each DTD. Additional information is available from the Announcement to the NLM Data Licensees 2010 DTD and XML Changes; File Distribution Schedule Changes: www.nlm.nih.gov/bsd/licensee/announce/2009.html#d09_17.
Announce Lists and RSS Feeds
Topic-specific mailing lists provide email announcements about changes and updates to NCBI resources including dbGaP, BLAST, GenBank, and Sequin. The Announcement List summary page describes the various lists and how to subscribe:
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Sitemap/Summary/email_lists.html.
The NCBI Announce mailing list sends notices on NCBI News updates and important changes at the NCBI site.
www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/About/news/announce_submit.html
Seven RSS feeds are now produced by NCBI including news on PubMed, PubMed Central, NCBI Bookshelf, LinkOut, HomoloGene, UniGene, and NCBI Announce.
Comments and questions about NCBI resources may be sent to NCBI through electronic mail, vog.hin.mln.ibcn@ofni, or by calling 301-496-2475 between the hours of 8:30 a.m. and 5:30 p.m. EST, Monday through Friday.
- NCBI News, November 2009 - NCBI NewsNCBI News, November 2009 - NCBI News
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...