All rights reserved. This material may be freely reproduced for educational and not-for-profit purposes. No reproduction by or for commercial organisations, or for commercial purposes, is allowed without the express written permission of NICE.
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
Introduction
This Evidence Update identifies new evidence that might reinforce or generate future change to the practice laid out in the following reference guidance:
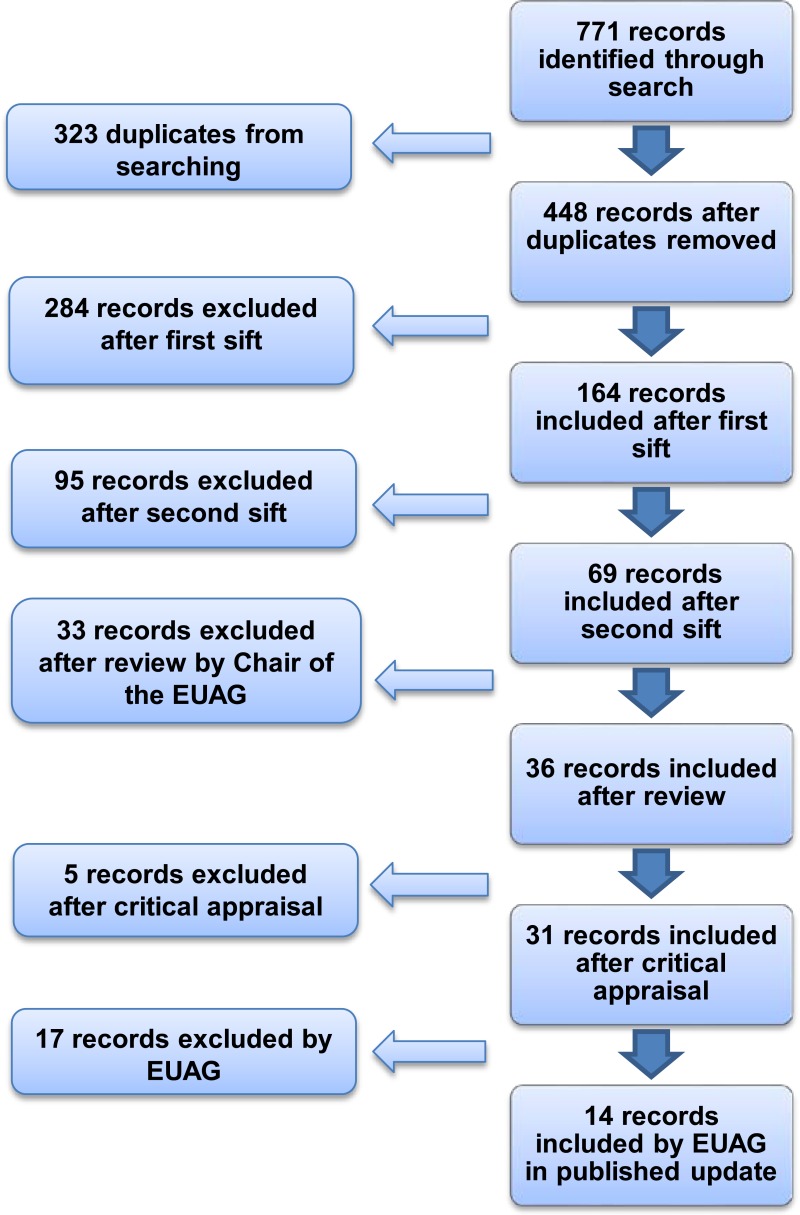
A search was conducted for new evidence published between 18 January 2010 and 6 March 2012. A total of 771 pieces of evidence were identified and assessed, of which 14 were selected for the Evidence Update (see Appendix A for details of the evidence search and selection process). An Evidence Update Advisory Group, comprised of subject experts, reviewed the prioritised evidence and provided a commentary.
Feedback
If you have any comments you would like to make on this Evidence Update, please email ku.shn.ecnedive@sutcatnoc
Key messages
The following table summarises what the Evidence Update Advisory Group (EUAG) decided were the key messages for this Evidence Update. It also indicates the EUAG’s opinion on whether new evidence identified by the Evidence Update reinforces or has potential to generate future change to the current guidance listed in the introduction.
The relevant NICE guidance development centres have been made aware of this evidence, which will be considered when guidance is reviewed. For further details of the evidence behind these key messages and the specific guidance that may be affected, please see the full commentaries.
The section headings used in the table below are taken from the guidance.
| Effect on guidance | ||
|---|---|---|
| Key message | Potential change | No change |
| Painless imaging | ||
| ✓ | |
| ✓ | |
| Painful procedures | ||
| Propofol | ||
| ✓ | |
| Propofol with ketamine | ||
| ✓ | |
| Midazolam | ||
| ✓ | |
| Midazolam versus nitrous oxide | ||
| ✓ | |
| Dental procedures | ||
| ✓ | |
| ✓ | |
| ✓ | |
| Endoscopy | ||
| ✓ | |
1. Commentary on new evidence
These commentaries analyse the key references identified specifically for the Evidence Update, which are identified in bold text. Supporting references are also provided. Section headings are taken from the guidance.
This Evidence Update contains results of studies of sedative drugs in children; many of the drugs referred to in these studies did not have UK marketing authorisation for the studied indication at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. NICE clinical guideline 112 (NICE CG112) recommended use of specific drugs that did not have UK marketing authorisation for the recommended indication because the drugs are used in UK clinical practice.
Information about licensed indications and NICE recommendations is given for each section below. Prescribers should refer to the ‘British national formulary for children’ (BNFc) and summary of product characteristics for each drug for full and up-to-date details of licensing. Informed consent should be obtained and documented for the use of any drug outside the licensed indications.
1.1. Pre-sedation assessment, communication, patient information and consent
No new key evidence was found for this section.
1.2. Fasting
No new key evidence was found for this section.
1.3. Psychological preparation
No new key evidence was found for this section.
1.4. Personnel and training
No new key evidence was found for this section.
1.5. Clinical environment and monitoring
No new key evidence was found for this section.
1.6. Discharge criteria
No new key evidence was found for this section.
1.7. Painless imaging
NICE CG112 states ‘do not routinely use ketamine or opioids for painless imaging procedures’. For children unable to tolerate painless procedures such as diagnostic imaging NICE CG112 recommends chloral hydrate (for children under 15 kg), or midazolam; if these drugs do not result in successful imaging, propofol or sevoflurane are recommended. The guideline additionally stipulates that a healthcare professional trained in delivering propofol should be available to administer this drug.
Chloral hydrate did not have UK marketing authorisation for sedation in painless procedures or for use in children younger than 2 years at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. However, the BNFc contains dosing advice for children from age 1 month.
Midazolam did not have UK marketing authorisation for use for procedural sedation in children under 6 months at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. However, the BNFc includes dosing advice for children from 1 month.
Sevoflurane did not have UK marketing authorisation for procedural sedation at the time of publication of this Evidence Update.
Specific dosing regimens were not addressed for any drug. Informed consent should be obtained and documented for the use of any drug outside the licensed indications.
Magnetic resonance imaging
In a randomised controlled trial (RCT), Cho et al. (2010) assessed the efficacy of induction of sedation with propofol (single-dose group, n = 80) compared with induction of sedation and continuous infusion of propofol (n = 80) in children undergoing magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for a duration of up to 30 minutes. The mean age of children was 28 months (range 10– 47 months) in the single-dose group and 24 months (range 12–61 months) in the continuous infusion group.
Sedation was induced with intravenous propofol 2 mg/kg with lidocaine 2 mg/ml over 30 seconds. Supplementary propofol 0.5 mg/kg was then given until the child could be aroused only with substantial stimulation (defined as University of Michigan Sedation Scale [UMSS] score of 3). If sedation was inadequate after a total dose of propofol 3 mg/kg, midazolam 0.05–0.10 mg/kg was given. After induction of sedation, the single-dose group received saline infusion, and the continuous infusion group received propofol 10 mg/ml at a rate of 0.3 ml/kg/hour. If sedation was inadequate, propofol 0.5 mg/kg was administered, and the infusion rate increased.
Induction time, defined as the time from first dose of propofol to reaching UMSS 3, was not significantly different between groups (mean = 1 minute in both groups, p = 0.289). Sedation time, defined as the time between start and end of the MRI, was not significantly different between groups (mean 25 minutes for the single-dose group vs 28 minutes for the continuous infusion group, p = 0.065). However, recovery time, defined as the time from the end of MRI to spontaneous eye-opening and vocalisation, was significantly different between groups (mean 0 minutes in the single-dose group vs 1 minute in the continuous infusion group, p < 0.001).
The authors recognised that the difference in recovery time was not clinically significant, and suggested that single-doses of propofol would be suitable for MRI durations of up to 30 minutes. They suggested that the main advantage of single-dose propofol would be not needing to use MRI-compatible infusion devices or MRI-incompatible devices with very long tubing.
Respiratory events (peripheral oxygen desaturation to ≤ 90%, or partial airway obstruction) occurred in two patients in each group. All events were resolved by neck extension and chin lift, with no additional airway support needed. No cardiovascular events (such as bradycardia, hypotension or arrhythmia) were seen.
In an RCT, Hassan et al. (2011) compared intermittent propofol infusion with continuous infusion in children aged 1 month to 18 years undergoing MRI (n = 170). Participants were randomly assigned to either initial propofol 2–4 mg/kg initial bolus, titrated to achieve UMSS score of 3, then intermittent doses of propofol 0.5–2 mg/kg as needed (n = 95), or to the same initial propofol bolus then continuous infusion titrated to effect (n = 75), with a starting dose for the infusion of 50–150 micrograms/kg/minute; a bolus of 1 mg/kg and titration were also allowed. The primary endpoint was the total dose of propofol used, adjusted for sedation time and the patient’s weight (micrograms/kg/minute).
The continuous propofol infusion group used a significantly lower dose of propofol (134 ± 54 micrograms/kg/minute) than the intermittent infusion group (162 ± 74 micrograms/kg/minute, p = 0.18). Recovery times were similar (10 ± 11 minutes vs 10 ± 12 minutes respectively).
Adverse events were mostly mild and not significantly different between groups. All adverse events were either hypotension or respiratory difficulties, but none needed the sedation to be stopped. The mean duration of procedures was 41 ± 17 minutes in the continuous infusion group and 37 minutes ± 11 minutes in the intermittent infusion group. Eleven procedures lasted longer than 1 hour, but did not seem to differ from shorter procedures in dose of propofol, recovery time or adverse events.
Taken together, evidence from Cho et al. (2010) and Hassan et al. (2011) suggest that propofol may be effective in a single dose for MRI procedures lasting up to 30 minutes, but continuous infusion might be the most effective regimen for longer procedures. The evidence from Cho et al. (2010) and Hassan et al. (2011) thus supports recommendations in NICE CG112 for use of propofol for sedation in children and young people.
Key references
- Cho JE, Kim WO, Chang DJ et al. (2010) Titrated propofol induction vs. continuous infusion in children undergoing magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 54: 453–7 [PubMed: 19930245]
- Hassan NE, Betz BW, Cole MR et al. (2011) Randomized controlled trial for intermittent versus continuous propofol sedation for pediatric brain and spine magnetic resonance imaging studies. Pediatric Critical Care Medicine 12: e262–5 [PubMed: 21263367]
Supporting reference
- Malviya S, Voepel-Lewis T, Tait AR et al. (2002) Depth of sedation in children undergoing computed tomography: validity and reliability of the University of Michigan Sedation Scale (UMSS). British Journal of Anaesthesia 88: 241–5 [PubMed: 11878656]
Auditory brainstem response testing
Avlonitou et al. (2011) undertook a retrospective case-series analysis of sedation with oral chloral hydrate in children undergoing auditory brainstem response testing in a single centre. A total of 1903 children were included, 568 were younger than 6 months and the remaining 1335 were aged up to 14 years.
Parents were instructed to bring children to the laboratory ‘awake but drowsy’. Children were given oral chloral hydrate 8% at an initial dose of 40 mg/kg; this was also the maximum dose for children younger than 6 months. The maximum dose for children of 6 months or older was 80 mg/kg. Children under 6 months were given chloral hydrate if the infant did not fall asleep spontaneously after 10–20 minutes.
Sedation with oral chloral hydrate was needed for 1586 children (83.3%), was not needed for 312 children (16.4%), and was not achieved in 5 children (0.3%). Of children younger than 6 months, 341 infants (60%) needed sedation, and 227 (40%) slept spontaneously. Of children of 6 months or older, 1245 (93.2%) needed sedation, 85 (6.4%) slept spontaneously and 5 (0.4%) did not achieve sedation with oral chloral hydrate and intravenous chloral hydrate was used.
Adverse effects were noted in 393 of children (20.6%), mainly vomiting (217 children, 11.4%) and hyperactivity (152 children, 8%). Ten cases each of rash and minor breathing distress and four cases of apnoea were also seen.
NICE CG112 recommends chloral hydrate as an option for sedation for painless imaging in children up to 15 kg; this evidence is in line with NICE CG112, although the older children in the study are likely to weigh more than the limit specified in NICE CG112. Chloral hydrate did not have UK marketing authorisation for sedation in painless procedures or for use in children younger than 2 years at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. Informed consent should be obtained and documented.
Key reference
- Avlonitou E, Balatsouras DG, Margaritis E et al. (2011) Use of chloral hydrate as a sedative for auditory brainstem response testing in a pediatric population. International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology 75: 760–3 [PubMed: 21531030]
1.8. Painful procedures
NICE CG112 recommends a local anaesthetic in addition to a sedative for all children undergoing a painful procedure. Nitrous oxide in oxygen or oral or intranasal midazolam are recommended for minimal or moderate sedation. For children in whom nitrous oxide or midazolam are unsuitable, ketamine or intravenous midazolam are recommended.
Intravenous midazolam was classed in NICE CG112 as moderate sedation and may be given with fentanyl. If ketamine or intravenous midazolam with or without fentanyl are unsuitable, a specialist sedation technique such as propofol with or without fentanyl is recommended. The guideline additionally stipulates that a healthcare professional trained in delivering ketamine, fentanyl or propofol should be available to administer these drugs.
Midazolam did not have UK marketing authorisation for use for procedural sedation in children under 6 months at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. However, the BNFc includes dosing advice for children from 1 month.
Ketamine is licensed for use in anaesthesia at all ages; the guideline noted that doses used for sedation are lower than those used for anaesthesia.
Fentanyl was not licensed for use in children younger than 2 years at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. However the BNFc gives advice for use as analgesia during operation or enhancement of anaesthesia in children with spontaneous respiration aged from 1 month.
Specific dosing regimens were not addressed for any drug. Informed consent should be obtained and documented for the use of any drug outside the licensed indications.
Propofol
In a systematic review, Lamond (2010) looked at evidence of adverse events associated with use of propofol for procedural sedation in children and young people, in all settings outside the operating theatre. Studies of patients aged 1 day to 17 years were included, as were studies of paediatric and adult patients if the data for adverse events were reported separately by age group.
A total of 60 studies (20 RCTs and 40 observational prospective and retrospective case series) with 17,066 sedations in children were included. Definitions of oxygen desaturation and hypotension varied between studies. The overall rates of adverse events were 15.4% for hypotension, 9.3% for oxygen desaturation, 5.6% for pain on injection, 1.9% for apnoea, 1.4% for assisted ventilation, 0.18% for laryngospasm, 0.13% for myoclonus, 0.1% for bradycardia, and 0.02% for unplanned intubation. No incidents of aspiration or vomiting during the procedure were reported, but 0.14% had post-procedure vomiting. No deaths were reported.
The data were confounded in some studies by use of adjunctive opioids, differing dosing regimens and use of supplemental oxygen. The authors noted that the rates of adverse events were similar to reported rates for other sedatives (cited as between 2.3% and 17.8% and mainly airway related or vomiting, no statistical comparisons reported).
The Pediatric Sedation Research Consortium database is a collective of 37 participating institutions, mainly in the USA, that use a standardised methodology to collect data for paediatric sedations from consecutive admissions. Of 123,938 sedations from July 2004 to September 2008, Mallory et al. (2011) reported on 25,433 sedations using primarily propofol in people aged under 21 years.
Adverse events were seen in 1483 sedations (5.83%, 95% confidence interval [CI] 5.55% to 6.13%); adverse events considered ‘more serious’ occurred in 581 sedations (2.28%, 95% CI 2.10% to 2.48%). No deaths were reported, and no procedures were stopped because of a sedation-related event. The most common ‘more serious’ adverse events were airway obstruction (245 [0.96%], 95% CI 0.84 to 1.08), oxygen desaturation (239 [0.94%], 95% CI 0.82 to 1.06) and apnoea (125 [0.49%], 95% CI 0.41% to 0.58%). Other ‘more serious’ adverse events were seen less commonly: laryngospasm, aspiration, unplanned admission, cardiac arrest, emergency anaesthesia call and unplanned intubation (range <0.01% to 0.11% of patients).
The consortium attempted to minimise coding variability by using largely objective endpoints, but the authors recognised that institutions may have under-reported adverse events that are considered ‘potentially embarrassing’. Additionally, the institutional source of data was anonymous meaning that institutional practices and biases could not be assessed.
NICE CG112 recommends propofol as a third-line option for sedation in children and young people undergoing painful procedures, thus evidence from these studies supports the suitability of propofol for sedation in children.
Key references
- Lamond DW (2010) Review article: safety profile of propofol for paediatric procedural sedation in the emergency department. Emergency Medicine Australasia 22: 265–86 [PubMed: 20796007]
- Mallory MD, Baxter AL, Yanosky DJ et al. (2011) Emergency physician-administered propofol sedation: a report on 25,433 sedations from the pediatric sedation research consortium. Annals of Emergency Medicine 57: 462–8 [PubMed: 21513827]
Propofol with ketamine
The combination of ketamine and propofol is not specifically recommended in NICE CG112 for procedural sedation. Ketamine alone is a second-line option for procedural sedation, and propofol with or without fentanyl is given as an example of a possible specialist sedation technique as a third-line option.
In a single-centre study in an accident and emergency department, Andolfatto and Willman (2010) collected safety and efficacy data for 219 children and young people (median age 13 years; range 1–20 years) undergoing procedural sedation with ketamine 10 mg/kg and propofol 10 mg/kg combined 1:1 in a single syringe. Sedation was titrated as needed with aliquots of 0.5 mg/kg of the drugs given every 30 seconds or 1 minute. The median dose of ketamine and propofol was 0.8 mg/kg of each drug (range 0.2 to 3.0 mg/kg).
All sedations were considered effective; that is, the procedure was completed without adjunctive procedural drugs and no sedation-related adverse events resulted in termination of the procedure, admission to hospital, or permanent complications. Most adverse events were considered to be ‘minor’, that is, needing no more than minimal intervention, although two patients had oxygen desaturation to less than 90% and two people needed intervention for unpleasant emergence reactions (neurological effects such as hallucinations, confusion or excitement).
The limitations noted by the authors included that the presence of two doctors during sedation may have reduced adverse events. Although adverse events were reported on a standardised checklist, doctors may have different ‘tolerance for events that are considered “adverse”’. The lack of a randomised trial to compare the regimen against another means that no comment on safety and efficacy against other regimens could be made. Finally, only three children receiving sedation were younger than 3 years, so the results are not applicable to this age group.
David and Shipp (2011) conducted an RCT of ketamine plus propofol versus propofol alone in 193 people undergoing procedural sedation in a single accident and emergency department. The primary outcome was respiratory depression with a definition including measures of end-tidal CO2, respiratory rate, apnoea, airway manipulation and oxygen desaturation (to < 90% for 10 seconds or longer).
All patients received an intravenous fentanyl dose of 0.5 or 1.0 mg/kg and blinded administration of either intravenous ketamine 0.5 mg/kg or placebo solution. Propofol 1 mg/kg was then given as a loading dose with 0.5 mg/kg given as needed to maintain sedation.
The median age of participants in the ketamine plus propofol group was 20 years (range 2 to 83 years, 50% aged under 18 years) and was 22 years (range 2 to 75 years, 47% aged under 18 years) in the propofol only group. The rate of respiratory depression was similar with ketamine plus propofol (21 patients [22%]) and propofol alone (27 patients [28%]; 95% CI −6 to 18), and no emergence reactions or other serious adverse events were reported in either treatment arm. A limitation of the study was potentially incomplete blinding with some patients.
Shah et al. (2011) reported a single-centre RCT in children (median age 11 years; range 2 to 17 years) needing sedation for orthopaedic reduction comparing treatment with propofol 0.5 mg/kg and ketamine 0.5 mg/kg (n = 67) and ketamine 1.0 mg/kg plus placebo (n = 69). Further doses were allowed if sedation was inadequate; 0.5 mg/kg propofol in the ketamine plus propofol group and 0.2 mg/kg ketamine for the ketamine plus placebo group. The primary outcome was total sedation time, and secondary outcomes included recovery time and adverse events.
Opioid analgesia was administered according to local protocol as needed for pain control at arrival at the hospital in 31 (46%) patients subsequently sedated with ketamine plus propofol and 27 (39%) of those in the ketamine plus placebo group.
The median sedation time was 13 minutes in the ketamine plus propofol group (interquartile range [IQR] 9 to 19 minutes), compared with 16 minutes (IQR 12 to 22 minutes) in the ketamine plus placebo group (effect size −3, 95% CI −5 to −2, p = 0.04). Median time to recovery was 10 minutes (IQR 8 to 14 minutes) and 12 minutes (IQR 9 to 18 minutes, effect size −2, 95% CI −4 to −1), and the number of adverse events was 17 (25%) and 34 (49%, effect size −24, 95% CI −39 to −8) respectively.
No patient needed airway interventions other than repositioning or increased supplemental oxygen. Limitations included the non-standard dose of opioids received by some participants and the lack of a propofol-only arm.
The results of the trials by Andolfatto and Willman (2010), David and Shipp (2011) and Shah et al. (2011) provide some evidence for the use of propofol and ketamine in specialist settings. NICE CG112 does not make specific recommendations about specialist techniques for procedural sedation, a specialist could choose to use ketamine with propofol, so this evidence does not contradict current guidance; however this combination remains a technique for specialist use only. Further studies may be needed to establish the optimum dosing regimen.
Key references
- Andolfatto G, Willman E (2010) A prospective case series of pediatric procedural sedation and analgesia in the emergency department using single-syringe ketamine–propofol combination (ketofol). Academic Emergency Medicine 17: 194–201 [PubMed: 20370749]
- David H, Shipp J (2011) A randomized controlled trial of ketamine/propofol versus propofol alone for emergency department procedural sedation. Annals of Emergency Medicine 57: 435–41 [PubMed: 21256626]
- Shah A, Mosdossy G, McLeod S et al. (2011) A blinded, randomized controlled trial to evaluate ketamine/propofol versus ketamine alone for procedural sedation in children. Annals of Emergency Medicine 57: 425–33 [PubMed: 20947210]
Midazolam
NICE CG112 recommends midazolam as an option for first-line sedation in children and young people undergoing painful procedures. Midazolam did not have UK marketing authorisation for use for procedural sedation in children under 6 months at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. However, the BNFc includes dosing advice for children from 1 month.
A single-centre RCT (Klein et al. 2011) investigated three different methods of administering midazolam (oral, intranasal and buccal) in children aged 0.5–7 years undergoing laceration repair in the accident and emergency department. Participants received oral midazolam 0.5 mg/kg (n = 56), intranasal aerosolised midazolam 0.3 mg/kg (n = 55) or buccal aerosolised midazolam 0.3 mg/kg (n = 58). The primary outcome was reduction in distress measured using the Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario Pain Scale (CHEOPS).
Buccal administration resulted in significantly less distress compared with oral administration (difference −2, 95% CI −4 to 0, p = 0.04); there was no significant difference between buccal and intranasal administration (difference −1, 95% CI −3 to 1, p = 0.08). Limitations included differences in the median age of the groups (3.7 years in the buccal midazolam group vs 2.7 years for oral and 2.9 years for intranasal midazolam), and the subjective nature of scoring to determine CHEOPS from videotape recording of the children.
This limited evidence is unlikely to affect a future update to guidance; further studies to determine the optimum method of administration of midazolam in children undergoing procedural sedation may be useful.
Key reference
- Klein EJ, Brown JC, Kobayashi A et al. (2011) A randomized clinical trial comparing oral, aerosolized intranasal, and aerosolized buccal midazolam. Annals of Emergency Medicine 58: 323–9 [PMC free article: PMC3183391] [PubMed: 21689865]
Midazolam versus nitrous oxide
Midazolam and nitrous oxide are recommended in NICE CG112 as first choice drugs for sedation in painful procedures. Midazolam did not have UK marketing authorisation for use for procedural sedation in children under 6 months at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. However, the BNFc includes dosing advice for children from 1 month.
In an RCT (n = 90), Ekbom et al. (2011) compared oral midazolam 0.3 mg/kg with 50% or 10% nitrous oxide before attempting to obtain intravenous access in children with endocrine disorders who were expected to have difficulties with intravenous line placement. Each group included 20 obese children and 10 children with growth disorders aged 5 to 18 years.
The time from the start of setting up intravenous line to the establishment of two intravenous lines (intravenous access time) and the time from establishing two lines to the patient regaining alertness (measured by a finger tapping test returning to baseline values; recovery time) were measured; the primary endpoint (total procedure time) was calculated as the sum of the intravenous access and recovery times. Successful procedures were defined as two attempts needed to fit two lines.
The total procedure time was significantly longer in patients in the midazolam group than in either nitrous oxide group (p < 0.001, time values not reported). The total number of access attempts did not differ between the three groups (p = 0.09; values not reported). The 50% nitrous oxide group had a larger proportion of successful procedures (67% vs 40% for 10% nitrous oxide and 37% for midazolam, p = 0.04).
One case of dizziness in the midazolam group and one case of nausea in the 50% nitrous oxide group were seen. Author reported limitations included: the blinding method might not have been adequate; the dose of midazolam might not have been optimised; and lack of a placebo group.
Although this evidence suggests that nitrous oxide 50% may have benefits over midazolam, the small size and limited outcome reporting of this study mean that it is unlikely to be a consideration in future updates to NICE CG112. Further studies comparing midazolam with nitrous oxide may be useful to determine the preferred first-line drug for procedural sedation in children and young people.
Key reference
- Ekbom K, Kalman S, Jakobsson J et al. (2011) Efficient intravenous access without distress: a double-blind randomized study of midazolam and nitrous oxide in children and adolescents. Archives of Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine 165: 785–91 [PubMed: 21536947]
1.9. Dental procedures
NICE CG112 recommends nitrous oxide in oxygen or midazolam for conscious sedation in children and young people who cannot tolerate dental procedures with local anaesthesia alone. If these techniques are not suitable, referral to a specialist team for an alternative sedation technique is recommended.
Midazolam did not have UK marketing authorisation for use for procedural sedation in children under 6 months at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. However, the BNFc includes dosing advice for children from 1 month.
Specific dosing regimens were not addressed for any drug. Informed consent should be obtained and documented for the use of any drug outside the licensed indications.
Midazolam and ketamine
NICE CG112 recommends midazolam or nitrous oxide (in oxygen) for dental sedation, with referral to a specialist team for alternative sedation if these sedation techniques are not suitable or sufficient.
Midazolam did not have UK marketing authorisation for use for procedural sedation in children under 6 months at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. However, the BNFc includes dosing advice for children from 1 month.
Ketamine is licensed for use in anaesthesia at all ages, but the guideline notes that doses used for sedation are lower than those used for anaesthesia.
A randomised crossover study by Bahetwar et al. (2010), compared sedation using intranasal midazolam with intranasal ketamine and with an intranasal combination of midazolam plus ketamine in 45 children undergoing dental procedures. Participants were children (mean age 4.6 years, range 2–6 years) in whom dental treatment could not be completed after administration of basic behaviour modification techniques, and whose treatment would need local anaesthesia.
The study had a three-stage crossover design, in which all participants received each regimen once in each of three visits. The regimens were midazolam 0.3 mg/kg, ketamine 6 mg/kg and midazolam 0.2 mg/kg plus ketamine 4 mg/kg administered intranasally using a syringe without needle. All dental procedures were carried out by the same dentist, and similar procedures were performed in all three visits.
Onset of sedation was longest in the midazolam group (6.8 ± 1.5 minutes), compared with ketamine (5.8 ± 1.4 minutes) or midazolam plus ketamine (6.0 ± 1.4 minutes, p < 0.0031), the difference was not significant for ketamine versus midazolam plus ketamine (p > 0.05). Recovery from sedation was longest in the midazolam plus ketamine group (41.21 ± 4.44 minutes), which was significantly longer than the ketamine group (40.0 ± 3.2 minutes, p < 0.05). Both these groups had significantly longer recovery times than midazolam (31.7 ± 3.4 minutes, p < 0.001). The only adverse event was vomiting in three children, all of whom had not followed fasting instructions before treatment. No children had emergence reactions.
Although the power calculation guiding the size of the study was for onset of sedation, the authors stated that their main outcome was whether or not the treatment was successful. Success was defined as: satisfactory behaviour during treatment, adequate sedation, physiological parameters remaining within 10% of baseline, oxygen saturation remaining above 90%, no need for physical restraint and no major side effects. According to these criteria, ketamine was successful in 40 of 45 sessions (89%), midazolam plus ketamine was successful in 38 of 45 sessions (84%) and midazolam was successful in 31 of 45 sessions (69%); the difference between ketamine and midazolam was significant (p < 0.01). The authors concluded that ketamine was the most effective drug regimen.
Using ketamine for dental sedation is an advanced technique, which is likely to be used only by specialist teams, so this study is unlikely to affect a future update to NICE CG112.
Key reference
- Bahetwar SK, Pandey RK, Saksena AK et al. (2010) A comparative evaluation of intranasal midazolam, ketamine and their combination for sedation of young uncooperative pediatric dental patients: a triple blind randomized crossover trial. The Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry 35: 415–20 [PubMed: 22046702]
Midazolam and fentanyl
NICE CG112 recommends midazolam alone as an option for sedation in children and young people undergoing dental procedures. Alternative sedation techniques may be available on referral to a specialist team.
Midazolam did not have UK marketing authorisation for use for procedural sedation in children under 6 months at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. However, the BNFc includes dosing advice for children from 1 month.
Fentanyl was not licensed for use in children younger than 2 years at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. However, the BNFc gives advice for use as analgesia during operation or enhancement of anaesthesia in children with spontaneous respiration aged from 1 month.
Specific dosing regimens were not addressed for any drug. Informed consent should be obtained and documented for the use of any drug outside the licensed indications.
Pandey et al. (2010) conducted a pilot randomised crossover study of oral midazolam 0.5 mg/kg plus fentanyl 3 micrograms/kg injected into the oral mucosa compared with 0.5 mg/kg midazolam with saline placebo injected submucosally in 23 children aged 2–6 years. Children were eligible for inclusion if basic behaviour modification techniques did not result in successful dental treatment and they needed treatment on both sides of an arch that would need local anaesthetic adjacent to the maxillary primary molar.
All injections of fentanyl or placebo were mixed with 0.5 ml of 2% lidocaine (with 1:200,000 adrenaline), and topical benzocaine 20% was applied to local injection sites (but not submucosal injection site). This study was conducted by most of the same investigators as Bahetwar et al. (2010) discussed above, and used a similar measure of treatment success as listed above with small differences, namely that adequate sedation needed to be achieved during the first 45 minutes of treatment, physiological parameters remaining within 20% of baseline, and oxygen saturation remaining at 95% or more.
‘Successful’ treatment was achieved in 17 of 23 children (73.91%) on midazolam plus fentanyl compared with 11 of 23 children (47.83%) on midazolam (p = 0.031). Recovery time was significantly slower with midazolam plus fentanyl (mean 72.4 minutes, 95% CI 67.6 to 77.1) compared with midazolam (mean 55.8 minutes, 95% CI 52.1 to 59.5, p < 0.0001).
Transient oxygen desaturation (to < 95% for less than 2 minutes) was seen four times with midazolam plus fentanyl, and one patient in each group vomited after returning home. The authors discussed the oxygen desaturation, noting that it was resolved by verbal or physical stimulation, and that this adverse effect had been seen in a previous study of these drugs.
Further research is needed to establish the safety of this combination of sedatives for dental procedures. This evidence is unlikely to affect a future update to NICE CG112, because the combination of midazolam and fentanyl would be considered a specialist sedation technique, which is not covered in NICE CG112.
Key reference
- Pandey RK, Padmanabhan MY, Saksena AK et al. (2010) Midazolam-fentanyl analgo-sedation in pediatric dental patients – a pilot study. The Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry 35: 105–10 [PubMed: 21189774]
Nitrous oxide and sevoflurane
Nitrous oxide in oxygen is recommended in NICE CG112 as an option for sedation in children and young people undergoing dental procedures. Specific dosing regimens were not addressed in the guideline for any drug.
Sevoflurane did not have UK marketing authorisation for procedural sedation at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. Informed consent should be obtained and documented for the use of any drug outside the licensed indications.
Soldani et al. (2010) conducted a randomised controlled crossover trial comparing inhaled nitrous oxide with inhaled nitrous oxide plus sevoflurane in 30 children and young people (mean age 10.6 years, range 7–15 years) undergoing dental extractions. The primary outcome measures were successful treatment and patient preference between sedation techniques. Patients needing identical extractions on contralateral sides of the dental arch were included, and each patient received both regimens once in a random order.
The authors stated that a calculation of sample size was attempted but was not possible because of lack of previous research, so a pilot study of 30 patients was designed. The treating dentist, dental nurse, patient, and guardian were kept blind to treatment method by use of a covering on the inhalation machine, so that only the consultant anaesthetist knew which method was used for each procedure.
When receiving nitrous oxide only, patients were started on 100% oxygen, and then titrated to a maximum of 30% nitrous oxide. When receiving nitrous oxide plus sevoflurane, patients were started on oxygen then titrated to 10% nitrous oxide and 0.1% sevoflurane, 20% nitrous oxide and 0.2% sevoflurane or 30% nitrous oxide and 0.3% sevoflurane. All patients received topical anaesthetic with 20% benzocaine, then local 2% lidocaine with adrenaline 1:80,000. Supplemental anaesthesia with 3% prilocaine with felypressin was used if initial anaesthesia was insufficient. At completion (or abandonment) of treatment, all patients received 100% oxygen for a minimum of 2 minutes.
Overall, 30 patients enrolled and 26 completed two rounds of treatment. In an intention-to-treat analysis, successfully completed treatment was seen in 87% of those on nitrous oxide-only and 83% of those on nitrous oxide and sevoflurane (p = 1.00).
Nine patients preferred nitrous oxide plus sevoflurane and one preferred nitrous oxide only; the remainder had no preference. Five patient carers preferred nitrous oxide plus sevoflurane and eight preferred nitrous oxide only; the remainder had no preference.
All patients had oxygen saturation above 98% throughout the procedure; reported side effects included nausea (five patients on nitrous oxide vs none on nitrous oxide plus sevoflurane), and drowsiness (eight patients vs one patient respectively).
The authors acknowledged that this study was limited by the small number of people in the dental team, the small number and wide age range of patients, and the range of extraction types.
The authors noted that the inconsistent preferences of patients and carers, and similarity in treatment completion rates between the two groups meant that use of sevoflurane was difficult to justify because of increased drug costs and the need for a consultant anaesthetist. Sevoflurane is not recommended in NICE CG112 for use in dental treatment; this evidence is unlikely to affect current guidance.
Key reference
- Soldani F, Manton S, Stirrups DR et al. (2010) A comparison of inhalation sedation agents in the management of children receiving dental treatment: a randomized, controlled, cross-over pilot trial. International Journal of Paediatric Dentistry 20: 65–75 [PubMed: 20059594]
1.10. Endoscopy
NICE CG112 recommends intravenous midazolam for minimal or moderate sedation in upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Fentanyl or equivalent opioid in combination with intravenous midazolam is recommended for moderate sedation in lower gastrointestinal endoscopy, but propofol is not recommended. The guideline additionally stipulated that a healthcare professional trained in delivering fentanyl should be available to administer this drug.
Midazolam did not have UK marketing authorisation for use for procedural sedation in children under 6 months at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. However, the BNFc includes dosing advice for children from 1 month.
Fentanyl was not licensed for use in children younger than 2 years at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. However the BNFc gives advice for use as analgesia during operation or enhancement of anaesthesia in children with spontaneous respiration aged from 1 month.
Specific dosing regimens were not addressed for any drug. Informed consent should be obtained and documented for the use of any drug outside the licensed indications.
In an RCT, Hirsh et al. (2010) compared remifentanil with fentanyl, both in combination with propofol for sedation in children (mean age 7.1 years) undergoing elective diagnostic oesophagogastroduodenoscopy. Remifentanil did not have UK marketing authorisation for use in children at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. In the fentanyl plus propofol group (n = 20), patients received a bolus of fentanyl 1 microgram/kg then propofol 2 mg/kg. In the remifentanil plus propofol group (n = 22), patients received a bolus of remifentanil 0.5 micrograms/kg plus propofol 2 mg/kg. Additional doses of propofol 0.5 mg/kg were given as needed, and all patients received oxygen via a nasal cannula during the procedure.
The average time to awakening was significantly shorter in the remifentanil plus propofol group (9.5 ± 5.6 minutes vs 16.5 ± 10.5 minutes, p = 0.01). The total dose of propofol used was significantly higher in the fentanyl plus propofol group; doses were reported only in graph form, but were around: 4 mg/kg for the fentanyl plus propofol group (range 2.5 to 8.5 mg/kg) and 3.5 mg/kg for the remifentanil plus propofol group (range 2 to 5 mg/kg, p = 0.034).
No clinically significant differences in heart rate or blood pressure were seen between groups. Oxygen desaturation to less than 90% was seen in six children (27.3%) of those in the remifentanil and propofol group, and in one (5%) of those in the fentanyl plus propofol group; this difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.096). Occurrences of apnoea lasting longer than 20 seconds were seen in seven patients (31.8%) in the remifentanil plus propofol group and no patients in the fentanyl plus propofol group; this difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.009).
The authors concluded that, because of the increased respiratory depression in the remifentanil group, this drug should only be used for sedation by an anaesthetist. Further studies are needed to establish the safety of remifentanil with propofol for procedural sedation in children, thus this limited evidence is unlikely to affect an update to the guidance.
Key reference
- Hirsh I, Lerner A, Shnaider I et al. (2010) Remifentanil versus fentanyl for esophagogastroduodenoscopy in children. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 51: 618–21 [PubMed: 20808251]
2. New evidence uncertainties
No new evidence uncertainties were identified during the Evidence Update process, however current uncertainties for sedation in children can be found in the NHS Evidence UK Database of Uncertainties about the Effects of Treatments (UK DUETs) and in the NICE research recommendations database.
UK DUETs was established to publish uncertainties about the effects of treatment that cannot currently be answered by referring to reliable up-to-date systematic reviews of existing research evidence.
Appendix A. Methodology
Scope
The scope of this Evidence Update is taken from the scope of the reference guidance:
- Sedation in children and young people. NICE clinical guideline 112 (2010)
Searches
The literature was searched to identify studies and reviews relevant to the scope. Searches were conducted of the following databases, covering the dates 18 January 2010 (the end of the search period of NICE CG112) to 6 March 2012:
- CINAHL
- Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews – Cochrane Library
- Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL)
- NHS Economic Evaluation Database
- Embase
- MEDLINE
Table 1 provides details of the MEDLINE search strategy used, which was adapted to search the other databases listed above. The searches aimed to identify relevant systematic reviews and RCTs on all aspects of sedation in children, and cohort studies with a focus on adverse effects of drugs used for sedation in children. The search strategy was used in conjunction with validated Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network search filters for RCTs and systematic reviews.
Figure 1 provides details of the evidence selection process. The long list of evidence excluded after review by the Chair of the EUAG, and the full search strategies, are available on request from ku.shn.ecnedive@sutcatnoc
Table 1MEDLINE search strategy (adapted for individual databases)
| 1 | Conscious Sedation/ |
| 2 | Deep Sedation/ |
| 3 | sedat$.ti,ab. |
| 4 | Dental Anxiety/ |
| 5 | ((minimal or light) adj (anesthesia or anaesthesia)).tw. |
| 6 | 1 or 2 or 3 or 4 or 5 |
| 7 | exp Child/ |
| 8 | child$.tw. |
| 9 | exp Infant/ |
| 10 | infan$.tw. |
| 11 | (baby or babies).tw. |
| 12 | Adolescent/ |
| 13 | adolescen$.tw. |
| 14 | (pediatric$ or paediatric$).tw. |
| 15 | 7 or 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 |
| 16 | 6 and 15 |
| 17 | Ketamine/ae,to |
| 18 | Propofol/ ae,to |
| 19 | Midazolam/ ae,to |
| 20 | Diazepam/ ae,to |
| 21 | Morphine/ ae,to |
| 22 | Heroin/ ae,to |
| 23 | Fentanyl/ ae,to |
| 24 | Alfentanil/ ae,to |
| 25 | Meperidine/ ae,to |
| 26 | Nitrous Oxide/ ae,to |
| 27 | Chloral Hydrate/ ae,to |
| 28 | Isoflurane/ae, to |
| 29 | sevoflurane.ti,ab,hw |
| 30 | triclofos. ti,ab,hw |
| 31 | (ae or to).fs. |
| 32 | 29 or 30 |
| 33 | 31 and 32 |
| 34 | exp Analgesics, Opioid/ ae,to |
| 35 | exp Anesthetics/ ae,to |
| 36 | exp “Hypnotics and Sedatives”/ ae,to |
| 37 | exp Analgesics/ ae,to |
| 38 | exp Anti-Anxiety Agents/ ae,to |
| 39 | 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 or 21 or 22 or 23 or 24 or 25 or 26 or 27 or 28 or 33 or 34 or 35 or 36 or 37 or 38 |
| 40 | 16 and SRs/RCTs filter |
| 41 | 16 and 39 and observational studies filter |
| 42 | 40 or 41 |
Appendix B. The Evidence Update Advisory Group and NHS Evidence project team
Evidence Update Advisory Group
The Evidence Update Advisory Group is a group of subject experts who review the prioritised evidence obtained from the literature search and provide the commentary for the Evidence Update.
- Dr Ranjit Verma – ChairConsultant Anaesthetist, Derby Hospitals Foundation Trust
- Professor Nick GirdlerProfessor and Consultant in Sedation Dentistry, Newcastle University and Newcastle Hospitals NHS Trust
- Dr Christina LiossiSenior Lecturer in Health Psychology, University of Southampton
- Heather McClellandNurse Consultant, Calderdale and Huddersfield NHS Foundation Trust
- Dr Peter MurphyConsultant in Paediatric Anaesthesia and Intensive Care, Bristol Royal Hospital for Children
- Dr Anna-Maria RollinProfessional Standards Adviser, Royal College of Anaesthetists
- Dr Mike SuryConsultant Anaesthetist, Great Ormond Street Hospital, London
NHS Evidence project team
- Alan LovellEvidence Hub Manager
- Janet ClaptonSenior Information Specialist
- Anelia BoshnakovaInformation Specialist
- Charles LaneMedical Editor, NICE Medicines and Prescribing Centre
- Lynne KincaidEditor
Footnotes
- 1
NICE-accredited guidance is denoted by the Accreditation Mark

- 2
Chloral hydrate did not have UK marketing authorisation for sedation in children younger than 2 years at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. Informed consent should be obtained and documented.
- 3
Midazolam did not have UK marketing authorisation for use for procedural sedation in children under 6 months at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. Informed consent should be obtained and documented.
- 4
Remifentanil did not have UK marketing authorisation for use in children at the time of publication of this Evidence Update. Informed consent should be obtained and documented.
Evidence Updates provide a regular, often annual, summary of selected new evidence published since the literature search was last conducted for the accredited guidance they update. They reduce the need for individuals, managers and commissioners to search for new evidence and inform guidance developers of new evidence in their field. In particular, Evidence Updates highlight any new evidence that might reinforce or generate future change to the practice described in the most recent, accredited guidance, and provide a commentary on the potential impact. Any new evidence that may impact current guidance will be notified to the appropriate NICE guidance development centres. For contextual information, this Evidence Update should be read in conjunction with Sedation in children (NICE clinical guideline 112). NHS Evidence is a service provided by NICE to improve use of, and access to, evidence-based information about health and social care.
Evidence Updates do not replace current accredited guidance and do not provide formal practice recommendations.
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence
Level 1A
City Tower
Piccadilly Plaza
Manchester M1 4BT
- Sedation in children and young peopleSedation in children and young people
- Homo sapiens lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (LPAR1), transcript variant 5, mRN...Homo sapiens lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 (LPAR1), transcript variant 5, mRNAgi|1677498152|ref|NM_001351399.2|Nucleotide
- maturase K, partial (chloroplast) [Oenothera nuttallii]maturase K, partial (chloroplast) [Oenothera nuttallii]gi|2718040982|gb|WZK92001.1|Protein
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
See more...