A condition in which abnormal cells that look like cancer cells under a microscope are found only in the place where they first formed and haven’t spread to nearby tissue. At some point, these cells may become cancerous and spread into nearby normal tissue. There are many different types of carcinoma in situ depending on the type of tissue in which it began. These include adenocarcinoma in situ (of the cervix, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract), ductal carcinoma in situ (of the breast), and squamous cell carcinoma in situ (of the skin, mouth, and larynx). Also called stage 0 disease.
Figure
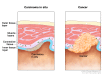
Carcinoma in situ (CIS) is a group of abnormal cells that are found only in the place where they first formed in the body (see left panel). These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread to nearby normal tissue (see right panel).