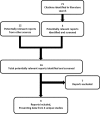
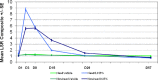
3.2.1. Description of studies
Four multicentre, randomized, parallel-group, double-blind, vehicle-controlled trials met the inclusion criteria for this systematic review. PEP005-014 (N = 255) and PEP005-028 (N = 203) evaluated the efficacy and safety of ingenol mebutate gel, 0.05% for the treatment of AK on non-head locations (trunk and extremities; non-head studies).11,14 PEP005-016 (N = 269) and PEP005-025 (N = 278) evaluated the efficacy and safety of ingenol mebutate gel, 0.015% for the treatment of AK on the head (face and scalp; head studies).12,13
All of the included trials were 57 days in duration and patients who achieved complete clearance of AK lesions were followed up for 12 months in study PEP005-032 (follow-up of PEP005-025) and study PEP005-030 (follow-up of PEP005-016 and PEP005-028). Results of these long-term follow-up trials are summarized in APPENDIX 6: LONG-TERM EFFICACY AND HARMS FROM EXTENSION STUDIES.
Patients were randomized in a 1:1 ratio with stratification by study site and anatomical location (arm, back of hand, chest, other locations; face or scalp) to ingenol mebutate gel or vehicle gel. In the non-head studies (PEP005-014 and PEP005-028), ingenol mebutate gel, 0.05% was applied topically once daily for two consecutive days to the selected treatment area by the patient at home. In the head studies (PEP005-016 and PEP005-025), ingenol mebutate gel, 0.015% was applied topically once daily for three consecutive days to the selected treatment area by the patient at home.
3.2.2. Populations
a. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
The main inclusion criterion was the presence of four to eight clinically typical, visible, and discrete AK lesions within a 25 cm2 contiguous treatment area on the trunk and extremities (PEP005-014 and PEP005-028) or on the face and scalp (PEP005-016 and PEP005-025). The target treatment area was identified and documented using a three-point landmark technique study transparency, where three anatomical landmarks (e.g., scars, moles, birthmarks), the 25 cm2 treatment area, and AK lesions were marked on a transparency using a marker.
Patients were excluded from the trial if the selected treatment area was within 5 cm of an incompletely healed wound or within 10 cm of a suspected basal cell or SCC, if they had been previously treated with ingenol mebutate, if the target treatment area contained hypertrophic or hyperkeratotic lesions, or if they had a history of other skin conditions or treatments that could interfere with the evaluation of study medication (e.g., topical medications, artificial tanners, immunosuppressive medications, immunomodulation agents, cytotoxic drugs, ultraviolet B phototherapy, other therapies for AK, or oral retinoids).
Patients who had received treatment with topical therapies such as 5-FU, imiquimod, and diclofenac within 2 cm of a selected treatment area within eight weeks before screening were excluded.
b. Baseline Characteristics
Baseline characteristics were generally well-balanced across treatment groups in the non-head studies () and head studies (). In all studies, patients had a mean age of around 65 years and the majority of them were male (approximately 60% in non-head studies; approximately 80% in head studies).
Summary of Baseline Characteristics of Non-Head Studies.
Summary of Baseline Characteristics of Head Studies.
All patients were white and their skin type was categorized according to the Fitzpatrick Scale, which is a numerical classification schema for the colour of skin with the following definitions: type I = burns easily, rarely tans; type II = burns easily, tans minimally; type III = burns moderately, tans gradually; type IV = burns minimally, tans well; type V = rarely burns, tans profusely; type VI = never burns, deeply pigmented.18 In the non-head studies, the majority of patients had Fitzpatrick skin type II, followed by types I and III. In the head studies, the majority of patients had Fitzpatrick skin type II, followed by type III and then type I.
In the non-head studies, the location of AK treatment area was evenly distributed between ingenol mebutate and vehicle groups, with the majority of patients having lesions on the arm (approximately 60%) and back of the hand (20% to 30%). In the head studies, approximately 80% of patients had lesions on the face and 20% had lesions on the scalp.
More than 75% of patients in all of the studies had received previous treatment for AK with cryotherapy on any previous AK lesion, and a smaller percentage had received treatment with topical therapies. Approximately 20% of patients had previously received treatment with topical 5-FU. Subsequent to a request from the CDR, the manufacturer confirmed that the prior AK treatments and procedures were not specific to the lesions studied in the reviewed trials.
3.2.3. Outcomes
The primary efficacy outcome was the proportion of patients achieving complete clearance of all clinically visible AK lesions in the target treatment area at day 57. Clinical AK lesion assessment was performed by a board certified dermatologist. The same dermatologist performing screening assessments was to perform all subsequent study assessments for each individual patient and across enrolled patients.
Secondary outcomes of interest included the following:
Proportion of patients achieving partial clearance of AK lesions at day 57, defined as a reduction of 75% or more in the number of clinically visible AK lesions in the target treatment area.
Percentage change from baseline in the total number of AK lesions (not pre-specified in the trial protocol). Change in Skindex-16 Dermatological Survey score from baseline at day 8, day 29, and day 57.
The Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire for Medication (TSQM) scores at day 57.
The Skindex-16 Dermatological Survey is a validated, 16-item, self-administered instrument that measures the effect of skin disease on patient quality of life. There are three domains: Symptoms (four items), Emotions (seven items), and Functioning (five items), and items are rated on a seven-point Likert-type scale, with higher scores indicating increased “bothersomeness.” Each of the items was transformed to a 0 to 100-point scale, and the mean of the transformed scores was calculated for each domain.
TSQM is a validated, 14-item, self-administered instrument with four domains: Effectiveness (three items), Side Effects (five items), Convenience (three items), and Global Satisfaction (three items). Items were rated on a five or seven-point Likert-type scale, and the sum of the individual items comprising each of the four domains was transformed to a 0 to 100-point scale (least favourable to most favourable).
Adverse events were defined as any unfavourable and unintended sign, symptom, or disease temporarily associated with the use of a study medication, whether or not related to the investigational product. Pre-existing conditions that worsened during the treatment period were reported as adverse events. The relationship of an adverse event to the study medication was assessed by the investigator (treatment-related adverse events). An adverse event was considered a serious adverse event if it was fatal, life-threatening, required participant hospitalization or prolonged existing hospitalization, resulted in persistent or significant disability/incapacity, a congenital anomaly/birth defect, or a medically significant event.
Local skin responses (LSRs), including erythema, flaking/scaling, crusting, swelling, vesiculation/pustulation, or erosion/ulceration, were assigned a grade of 0 to 4 according to the LSR Grading Scale, with higher numbers indicating greater severity. A composite LSR score was calculated based on the sum of the six individual LSR scores and ranged from 0 to 24. A summary of the LSR grading criteria is presented in .
Local Skin Response Grading Criteria.
Pigmentation and scarring were assessed by presence and then graded. Hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation were assigned a grade of 0 (not present) to 3 (darker pigment or depigmented); scarring was assigned a grade of 0 (not present) to 2 (entire treatment area).
For a more detailed description of study outcomes, see APPENDIX 5: VALIDITY OF OUTCOME MEASURES.