| Maternal anaemia (third trimester Hb <110 g/L) |
|---|
| 8 | randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | none | 27 832 | 27 731 | RR 1.03 (0.92 to 1.15) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗⊗ HIGH | CRITICAL |
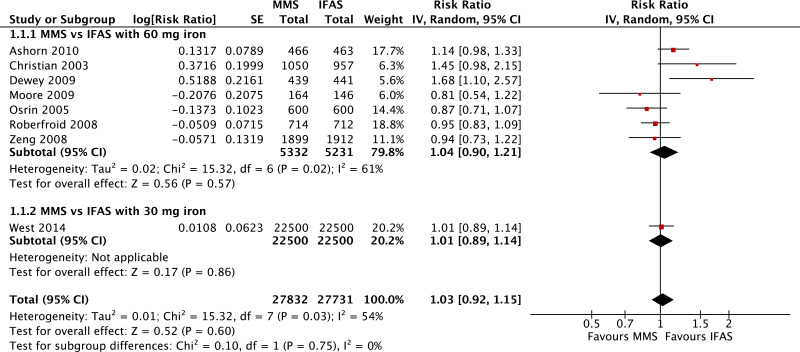
| Maternal anaemia (third trimester Hb <110 g/L) - versus 60 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 7 | randomized trials | not serious | seriousa | not serious | not serious | none | 5332 | 5231 | RR 1.04 (0.90 to 1.21) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗◯ MODERATE | CRITICAL |
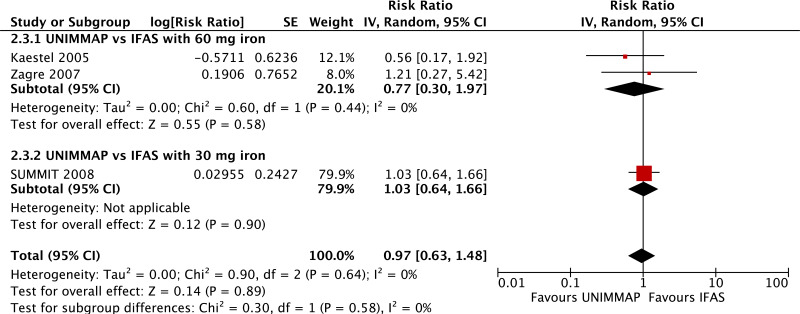
| Maternal anaemia (third trimester Hb <110 g/L) - versus 30 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 1 | randomized trial | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | none | 22 500 | 22 500 | RR 1.01 (0.89 to 1.14) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗⊗ HIGH | CRITICAL |
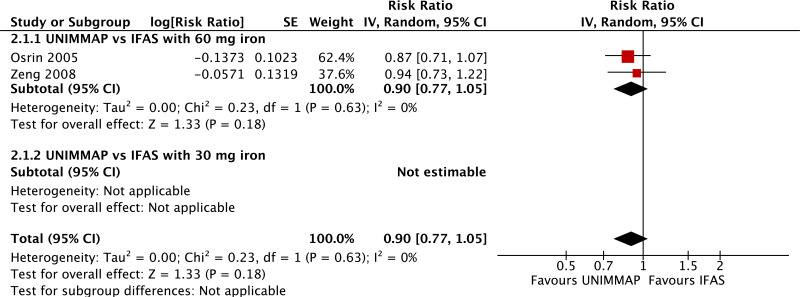
| Mode of delivery: Caesarean section |
|---|
| 4 | randomized trials | seriousb | not serious | not serious | seriousc | none | 3299 | 3374 | RR 1.04 (0.76 to 1.43) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗◯◯ LOW | CRITICAL |
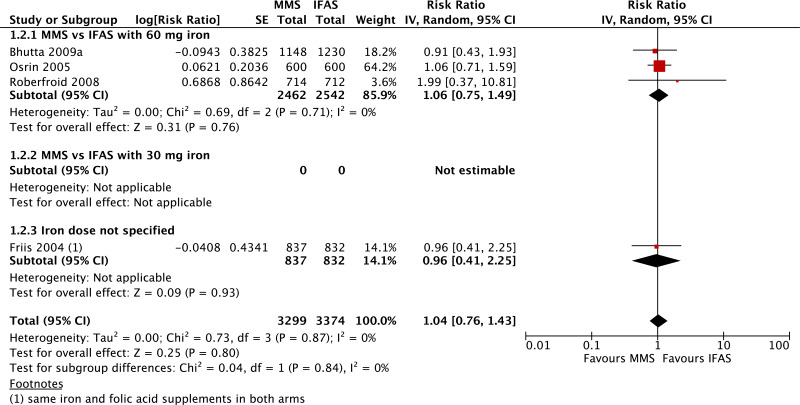
| Mode of delivery: Caesarean section - versus 60 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 3 | randomized trials | seriousb | not serious | not serious | seriousc | none | 2462 | 2542 | RR 1.06 (0.75 to 1.49) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗◯◯ LOW | CRITICAL |
| Mode of delivery: Caesarean section - versus 30 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 0d | | | | | | | 0 | 0 | not pooled | not pooled | - | CRITICAL |
| Mode of delivery: Caesarean section - iron dose not specified |
|---|
| 1 | randomized trial | seriousb | not serious | not serious | seriousc | none | 837 | 832 | RR 0.96 (0.41 to 2.25) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗◯◯ LOW | CRITICAL |
| Maternal mortality |
|---|
| 6 | randomized trials | seriousb | not serious | not serious | seriousc | none | 42 494 | 41 375 | RR 1.06 (0.72 to 1.54) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗◯◯ LOW | CRITICAL |
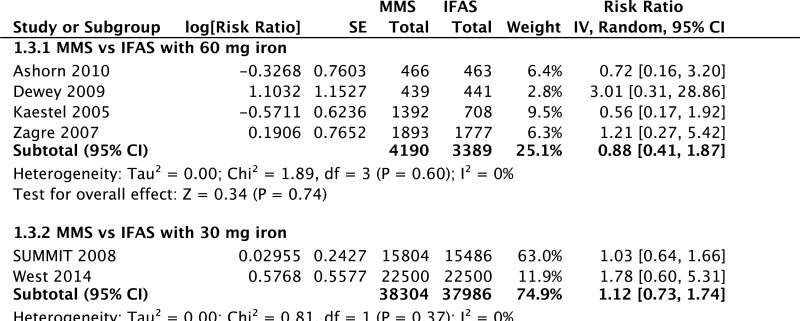
| Maternal mortality - versus 60 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 4 | randomized trials | very seriouse | not serious | not serious | seriousc | none | 4190 | 3389 | RR 0.88 (0.41 to 1.87) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗◯◯◯ VERY LOW | CRITICAL |
| Maternal mortality - versus 30 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 2 | randomized trials | seriousb | not serious | not serious | seriousc | none | 38 304 | 37 986 | RR 1.12 (0.73 to 1.74) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗◯◯ LOW | CRITICAL |
| Small for gestational age |
|---|
| 15 | randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | publication bias strongly suspectedf | 50 562 | 49 423 | RR 0.98 (0.96 to 1.00) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗◯ MODERATE | CRITICAL |
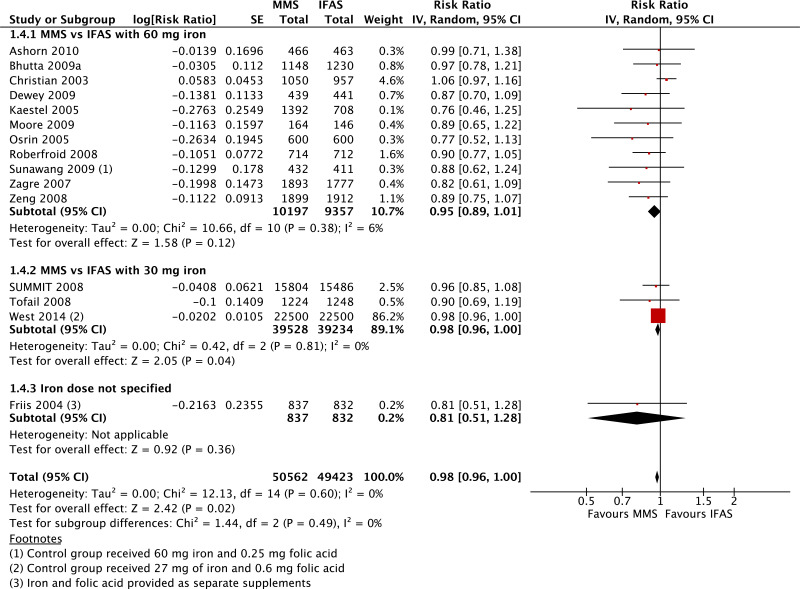
| Small for gestational age - versus 60 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 11 | randomized trials | seriousb | not serious | not serious | not serious | publication bias strongly suspectedf | 10 197 | 9357 | RR 0.95 (0.89 to 1.01) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗◯◯ LOW | CRITICAL |
| Small for gestational age - versus 30 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 3 | randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | none | 39 528 | 39 234 | RR 0.98 (0.96 to 1.00) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗⊗ HIGH | CRITICAL |
| Small for gestational age - iron dose not specified |
|---|
| 1 | randomized trial | seriousb | not serious | not serious | seriousc | none | 837 | 832 | RR 0.81 (0.51 to 1.28) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗◯◯ LOW | CRITICAL |
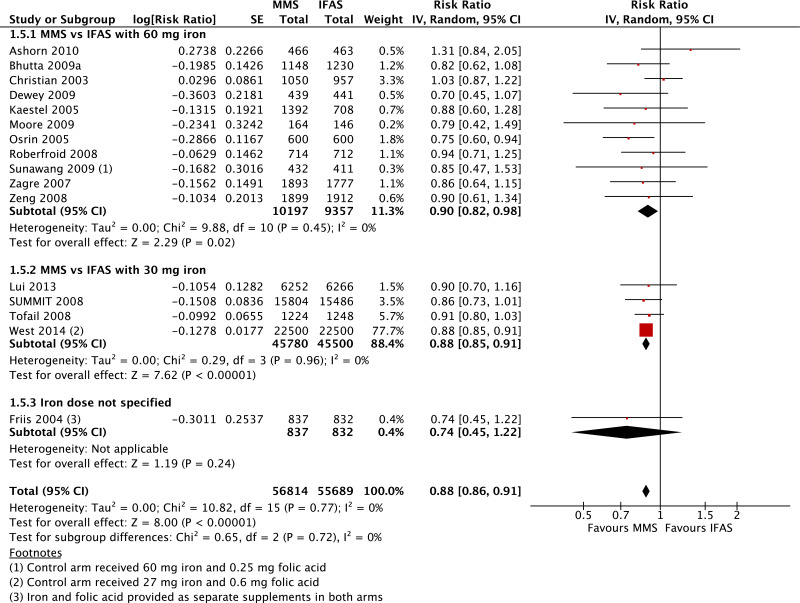
| Low birthweight |
|---|
| 16 | randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | none | 56 814 | 55 689 | RR 0.88 (0.86 to 0.91) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗⊗ HIGH | CRITICAL |
| Low birthweight - versus 60 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 11 | randomized trials | seriousb | not serious | not serious | not serious | publication bias strongly suspectedf | 10 197 | 9357 | RR 0.90 (0.82 to 0.98) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗◯◯ LOW | CRITICAL |
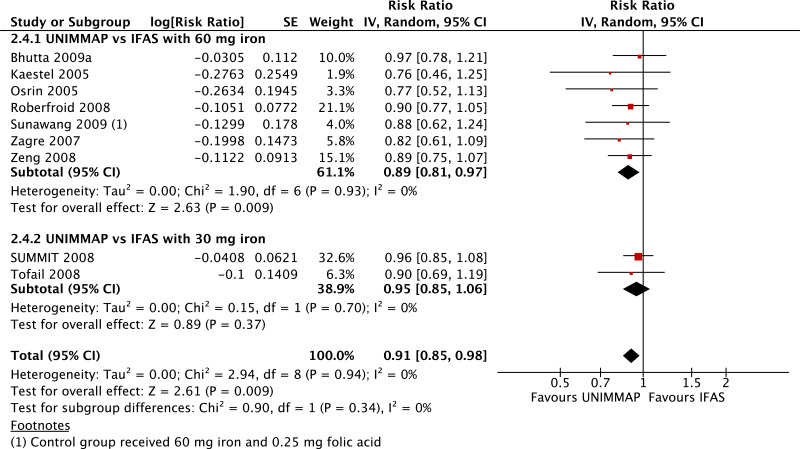
| Low birthweight - versus 30 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 4 | randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | none | 45 780 | 45 500 | RR 0.88 (0.85 to 0.91) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗⊗ HIGH | CRITICAL |
| Low birthweight - iron dose not specified |
|---|
| 1 | randomized trial | seriousb | not serious | not serious | seriousc | none | 837 | 832 | RR 0.74 (0.45 to 1.22) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗◯◯ LOW | CRITICAL |
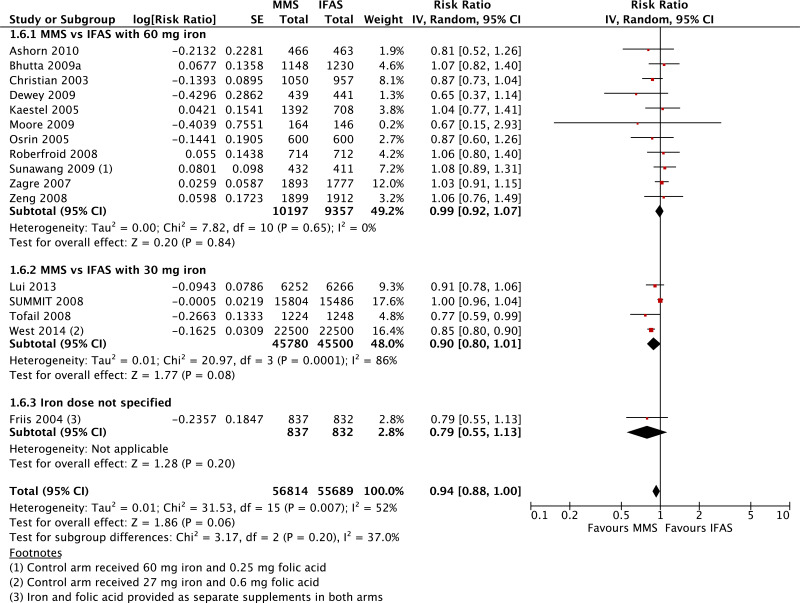
| Preterm births |
|---|
| 16 | randomized trials | seriousb | not serious | not serious | not serious | none | 56 814 | 55 689 | RR 0.94 (0.88 to 1.00) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗◯ MODERATE | CRITICAL |
| Preterm births - versus 60 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 11 | randomized trials | seriousb | not serious | not serious | not serious | publication bias strongly suspectedf | 10 197 | 9357 | RR 0.99 (0.92 to 1.07) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗◯◯ LOW | CRITICAL |
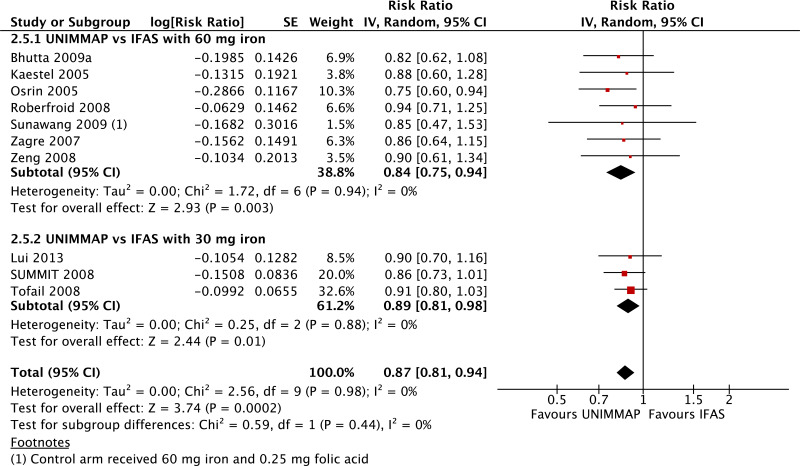
| Preterm births - versus 30 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 4 | randomized trials | not serious | seriousg | not serious | not serious | none | 45 780 | 45 500 | RR 0.90 (0.80 to 1.01) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗◯ MODERATE | CRITICAL |
| Preterm births - iron dose not specified |
|---|
| 1 | randomized trial | seriousb | not serious | not serious | seriousc | none | 837 | 832 | RR 0.79 (0.55 to 1.13) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗◯◯ LOW | CRITICAL |
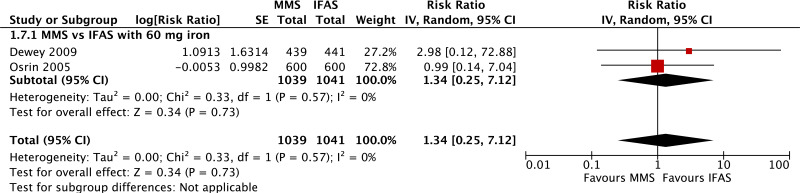
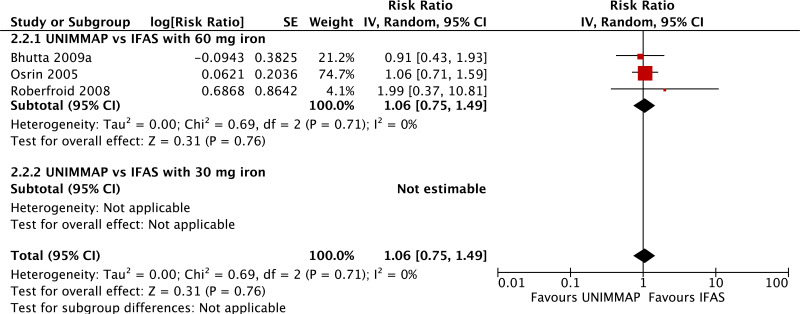
| Congenital anomalies - versus 60 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 2 | randomized trials | seriousb | not serious | not serious | seriousc | none | 1039 | 1041 | RR 1.34 (0.25 to 7.12) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗◯◯ LOW | CRITICAL |
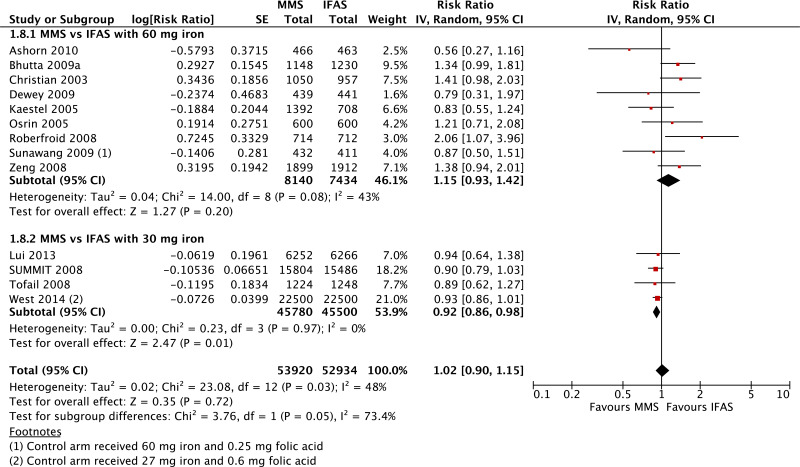
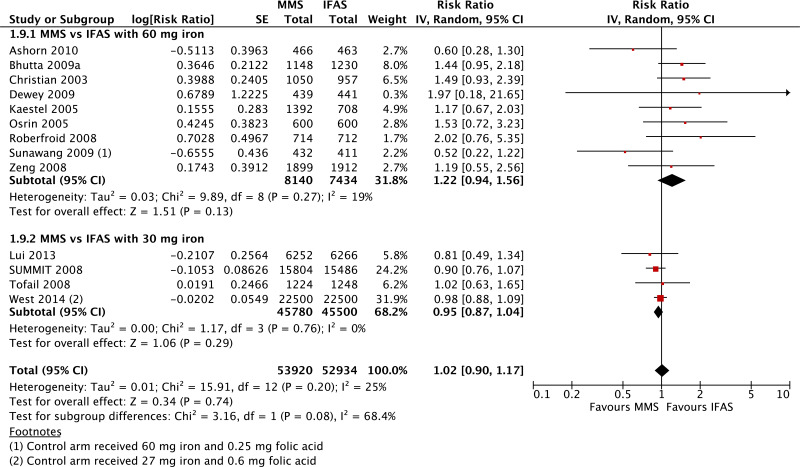
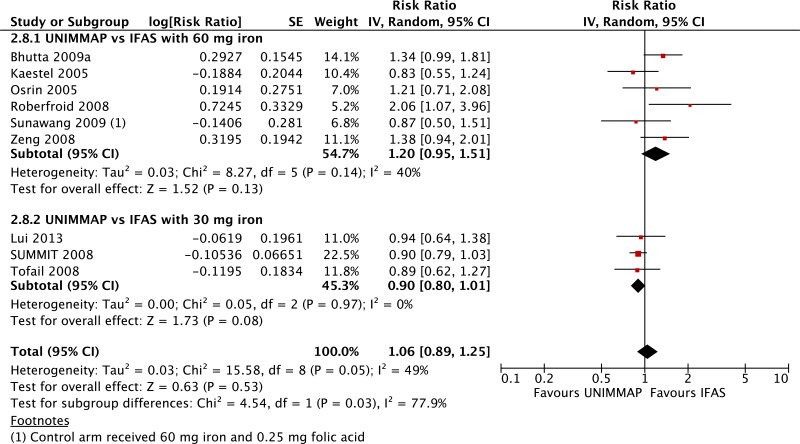
| Perinatal mortality |
|---|
| 13 | randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | seriousi | 53 920 | 52 934 | Subgroup data not pooled (tests for subgroup differences P = 0.05, I2 = 73.4%) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | - | CRITICAL |
| Perinatal mortality - versus 60 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 9 | randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | seriousc | none | 8140 | 7434 | RR 1.15 (0.93 to 1.42) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗◯ MODERATE | CRITICAL |
| Perinatal mortality - versus 30 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 4 | randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | serioush | 45 780 | 45 500 | RR 0.92 (0.86 to 0.98) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗◯ MODERATE | CRITICAL |
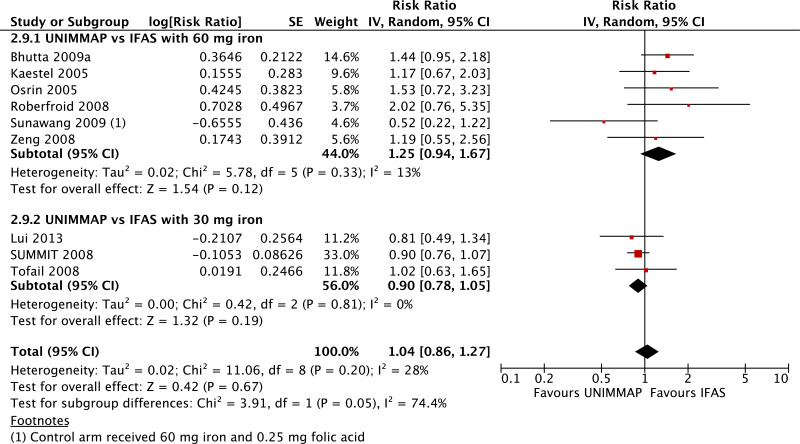
| Neonatal mortality |
|---|
| 13 | randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | seriousi | 53 920 | 52 934 | Subgroup data not pooled (tests for subgroup differences P = 0.08, I2 = 68.4%) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | - | CRITICAL |
| Neonatal mortality - versus 60 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 9 | randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | seriousc | none | 8140 | 7434 | RR 1.22 (0.94 to 1.56) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗◯ MODERATE | CRITICAL |
| Neonatal mortality - versus 30 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 4 | randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | serioush | 45 780 | 45 500 | RR 0.95 (0.87 to 1.04) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗◯ MODERATE | CRITICAL |
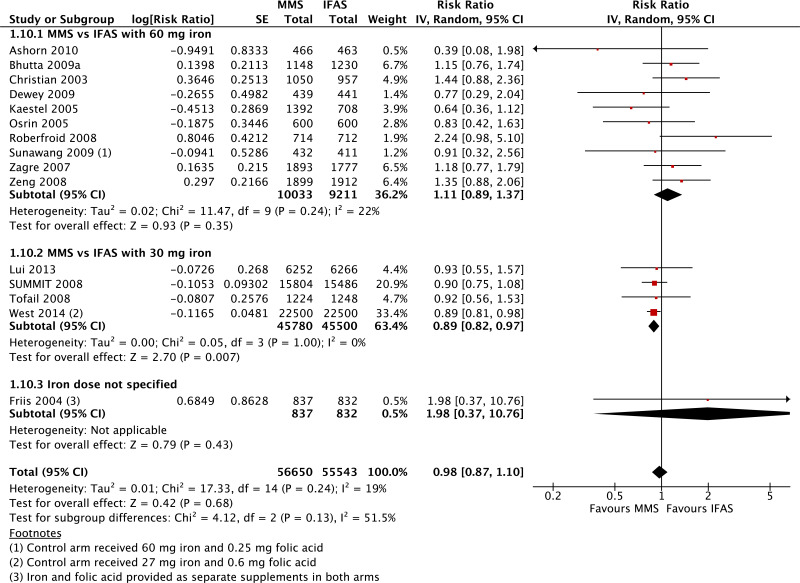
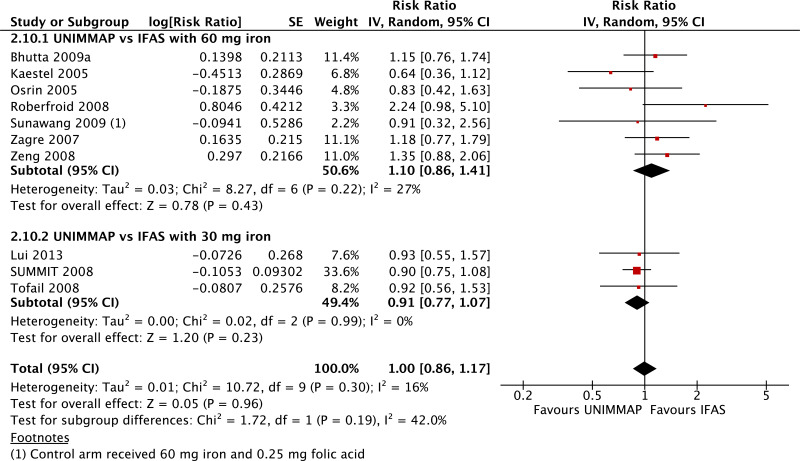
| Stillbirths |
|---|
| 15 | randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | none | 56 650 | 55 543 | RR 0.98 (0.87 to 1.10) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗⊗ HIGH | CRITICAL |
| Stillbirths - versus 60 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 10 | randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | seriousc | none | 10 033 | 9211 | RR 1.11 (0.89 to 1.37) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗◯ MODERATE | CRITICAL |
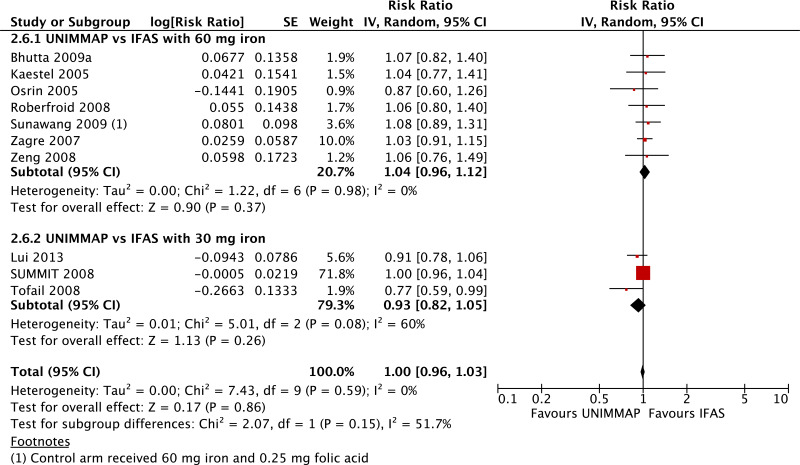
| Stillbirths - versus 30 mg iron plus folic acid |
|---|
| 4 | randomized trials | not serious | not serious | not serious | not serious | serioush | 45 780 | 45 500 | RR 0.89 (0.82 to 0.97) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗⊗◯ MODERATE | CRITICAL |
| Stillbirths - iron dose not specified |
|---|
| 1 | randomized trials | seriousb | not serious | not serious | seriousc | none | 837 | 832 | RR 1.98 (0.37 to 10.76) | 0 fewer per 1000 (from 0 fewer to 0 fewer) | ⊗⊗◯◯ LOW | CRITICAL |