Variation Glossary
This document includes definitions and descriptions of terms used by NCBI's Variation resources. It includes Sequence Ontology (SO) terms, variation reporting terms, and descriptions of VCF file tags.
NCBI Variation Resources in collaboration with the European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI) standardize the descriptions of the type of variant, the molecular effect of the variant, and the location of the variant relative to other annotated features based on the ontology established by Sequence Ontology (SO), particularly terms treed under sequence alteration. When concepts required by NCBI are not represented in SO, we request them from SO.
Glossary Terms
Clinical Channel
Clinical channel used to indicate clinical variation submissions to dbSNP. They included variations from locus-specific databases (LSDB), genetic testing laboratories, our collaboration with LRG, and our processing of OMIM's allelic variants. It used to also apply to submissions that included a phenotype report or that were submitted as a result of any gene-specific curation process. This term has been obsoleted, and was never an indication of medical impact or clinical significance. It was replaced by a link to ClinVar to indicate that there are clinical data available for the variation.
Clinical Significance
Clinical significance is an assessment of the effect of an allele, haplotoype or genotype on a clinical phenotype. Terms include interpretations of pathogenicity, risk, and responses to drugs. For more details, refer to Clinical significance in ClinVar.
ClinVar VCF Files
Data files in the VCF format generated by ClinVar to report on human variations with clinical assertions that have been mapped to both GRCh37 and GRCh38. They are vailable at the ClinVar FTP repository ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/clinvar/.
ClinVar VCF Files currently represent all variants with precise endpoints, that have been reported to ClinVar.
ClinVar VCF files are allele-specific - each row represents a single allele at that position, rather than one row per rs number as in the dbSNP VCF files.
COMMON
Common is a category of variants representing alleles observed in the germline with a minor allele frequency (MAF) of >=0.01 in at least one 1000 Genomes Phase III major population, with at least two individuals from different families having the same minor allele. COMMON is a category (tag) used in the dbSNP VCF Files.
Common may also include alleles with an evidence of medical interest. The definition of COMMON may be based on only one population from the major populations . These major populations may or may not include the population you are studying. An allele shown to be COMMON in one of the major populations may not be common in all populations.
dbSNP VCF Files
Data files in the VCF format generated by dbSNP to report on human variations without clinical assertions that have been mapped to both GRCh37 and GRCh38. They are vailable at the dbSNP FTP repository ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp/latest_release/VCF/.
dbSNP human VCF files represent all variants that have been submitted to dbSNP.
de novo
de novo is a novel variation present for the first time in one family member as a result of a mutation in a germ cell of one of the parents, or a mutation that arises itself in the fertilized egg during early embryogenesis.
NCBI Variation resources report that a variation is of de novo origin in the following cases: (1) reported explicitly from a submitter, (2) inferred from the study because even though not observed in parents, it was observed in all tissues of the body of the proband. The evidence of occurrence in siblings is not necessary, since the event may not have occurred in parental germ cells. The assumption is that variations arising de novo are transmissible.
Filtered VCF Files
Data files in the VCF format containing subsets of variants filtered according to certain criteria, like variants per one chromosome.
Functional consequence
Functional consequence is an observed effect of a sequence change on function. Ontologies such as VariO and Sequence Ontology (SO) are used to standardize terms, which are documented here: ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pub/GTR/standard_terms/functional_consequence.txt. As used by NCBI's resources, functional consequence is experimentally determined, in contrast to molecular consequence, which is computed from sequence annotation.
Germline
Term used for representing the source of, and thus the heritability of a variation. Direct confirmation of derivation from the parental germline is possible in the case of sperm analysis of father or preimplantation genetic diagnosis (as part of assisted reproductive technologies). An acceptable proxy for direct evidence that a variation is of germline origin is the analysis of parental somatic tissue. Indirect evidence can be provided from the presence of the variant or the allele in siblings, particularly if the variant is rare in a population. Variation resources report that a variation is of germline origin when the submitter explicitly reports that the variation is of germline origin or an associated study infers that the variation is of germline origin based on observations in a pedigree consistent with inheritance.
Minor Allele Frequency (MAF)
MAF is the frequency of the minor allele. MAF is often reported in the context of allele frequencies established by the 1000 Genomes and other large sequencing projects. When there are more than two lleles, MAF refers to the second most frequent allele.
Molecular consequence
Molecular consequence represents effects on protein products from the alterations in the coding nucleotide sequence. NCBI computes molecular consequence, and also assigns location-based ontology terms established by Sequence Ontology (SO), based on where the variant is located relative to gene, RNA and/or coding regions.
Effect on protein products per transcript
For each RNA for which the variant coincides in part or completely within a coding region, we would assign one of the following molecular consequences, as a computed effect of a sequence change on a particular protein product.
Public Term |
SO id and value |
VCF Tag |
| Stop Lost | SO:0001578:stop_lost | |
| Nonsense | SO:0001587:stop_gained | NSN |
| Synonymous | SO:0001819:synonymous_variant | SYN |
| Missense | SO:0001583:missense_variant | NSM |
| Frameshift | SO:0001589 :frameshift_variant | NSF |
| Inframe Insertion | SO:0001821:inframe_insertion | |
| Inframe Deletion | SO:0001822:inframe_deletion | |
| Inframe Indel | SO:0001820:inframe_indel |
Location-based Ontology Terms
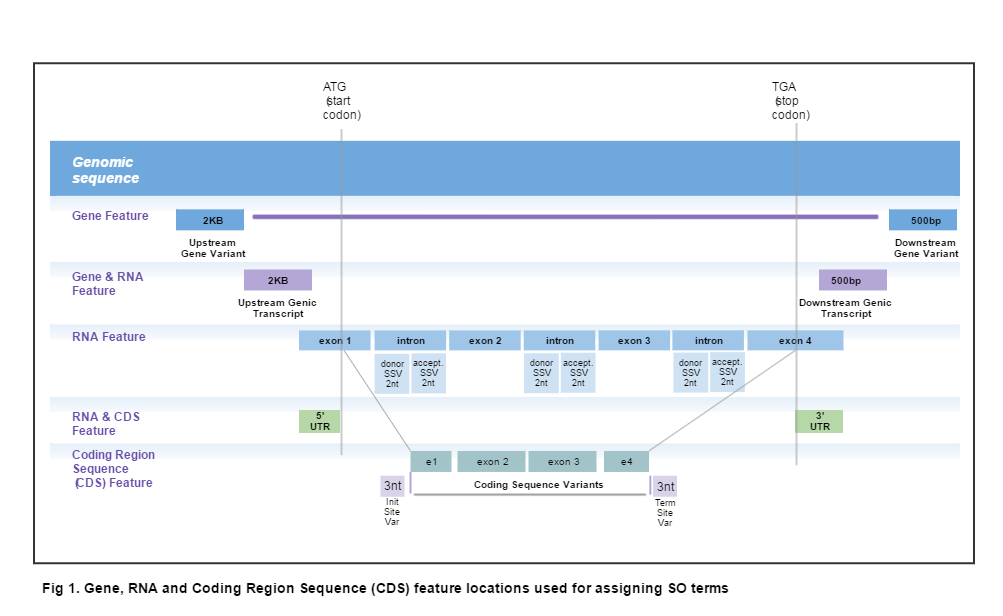
Location-based Ontology Terms are assigned to a variant whenever any part of its deletion interval (per the representation of variants that considers them to be pairs of deletion and insertion intervals on a sequence) overlaps one of the Gene, RNA Feature or Coding regions (see illustration below). If the variant overlaps more than one region or, if multiple transcripts are involved (as would be the case when the region is relative to a genomic location), all relevant SO terms are reported, in no particular order.
Public Term |
SO id and value |
VCF Tag |
| 2KB Upstream | SO:0001636 :2KB_upstream_variant | R5 |
| 500 bp Downstream | SO:0001634:500B_downstream_variant | R3 |
| 3' UTR | SO:0001624 :3_prime_UTR_variant | U3 |
| 5' UTR | SO:0001623 :5_prime_UTR_variant | U5 |
| Coding Sequence Variant | SO:0001580 :coding_sequence_variant | |
| Initiator Codon | SO:0001582 :initiator_codon_variant | |
| Terminator Codon | SO:0001590:terminator_codon_variant | |
| 500 bp Downstream Genic Variant | SO:0002152:genic_downstream_transcript_variant | |
| 2KB Upstream Genic Variant | SO:0002153:genic_upstream_transcript_variant | |
| Intron | SO:0001627:intron_variant | INT |
| Non Coding Transcript Variant | SO:0001619 :non_coding_transcript_variant | |
| Splice Acceptor | SO:0001574 :splice_acceptor_variant | ASS |
| Splice Donor | SO:0001575 : splice_donor_variant | DSS |
Somatic (origin)
Variation that arises post-zygotically and thus is not present in all cells of the body. The term is not restricted to somatic events occurring as part of the neoplastic process. NCBI Variation resources will report that a variation is of somatic origin when the submitter explicitly reports that the variation is of somatic origin or an associated study infers that the variation is of somatic origin because it was observed in a subset of somatic cells with no evidence of occurrence in siblings or parents (i.e. the observations were consistent with the interpretation that the variation arose post-zygotically).
We apply this term to variants arising post-zygotically in germ cells, so that transmission to offspring does not affect the somatic classification.
SPDI
Common data model developed at NCBI for Variation Services, to represent genetic variants as a quadruple of Sequence:Position:Deletion:Insertion (SPDI).
Variant Type
Variant type is the type of any sequence change reported relative to a reference sequence.
Public Term |
SO id and value |
| Alu Deletion | SO:0002070 :Alu_deletion |
| Alu Insertion | SO:0002063 :Alu_insertion |
| Complex Chromosomal Rearrangement | SO:0002062 :complex_chromosomal_rearrangement |
| Complex Substitution | SO:1000005 :complex_substitution |
| Copy Number Gain | SO:0001742 :copy_number_gain |
| Copy Number Loss | SO:0001743 :copy_number_loss |
| Copy Number Variation | SO:0001019 :copy_number_variation |
| Deletion | SO:0000159 :deletion |
| Duplication | SO:1000035 :duplication |
| HERV Deletion | SO:0002067 :HERV_deletion |
| Indel | SO:1000032 :indel |
| Insertion | SO:0000667 :insertion |
| Interchromosomal Translocation | SO:0002060 :interchromosomal_translocation |
| Intrachromosomal Translocation | SO:0002061 :intrachromosomal_translocation |
| Inversion | SO:1000036 :inversion |
| LINE1 Deletion | SO:0002069 :LINE1_deletion |
| LINE1 Insertion | SO:0002064 :LINE1_insertion |
| Microsatellite | SO:0000289 :microsatellite |
| Mobile Element Deletion | SO:0002066 :mobile_element_deletion |
| Mobile Element Insertion | SO:1001837 :mobile_element_insertion |
| Monomeric Repeat | SO:0001934 :monomeric_repeat |
| Multiple Nucleotide Polymorphism | SO:0001013 :MNP |
| Multiple Nucleotide Variation | SO:0002007:MNV |
| No Alteration | SO:0002073 : no_sequence_alteration |
| Novel Sequence Insertion | SO:1001838 :novel_sequence_insertion |
| Sequence Alteration | SO:0001059 :sequence_alteration |
| Single Nucleotide Variant | SO:0001483 :SNV |
| SVA Deletion | SO:0002068 :SVA_deletion |
| SVA Insertion | SO:0002065 :SVA_insertion |
| Tandem Duplication | SO:1000173 :tandem_duplication |
| Translocation | SO:0000199 :translocation |
Variation Services
Set of programs that was developed for ClinVar to compare and group genetic variants.
VCF INFO Tags
For the descriptions of INFO tags used by different Variation resources at NCBI, see:
For the descriptions of comparable INFO tags used among Variation resources at NCBI, see:
