Summary
Clinical characteristics.
ELN-related cutis laxa is characterized by generalized cutis laxa (ranging from generalized skin redundancy causing excessive skin folds to skin hyperextensibility without obvious skin folds) and distinctive facial features that may become more prominent with age. Other common findings are joint hyperlaxity in infancy and increasing risk of inguinal hernia at all ages. Progressive findings that may be present as early as childhood include ptosis, aortic root dilatation, and emphysema.
Diagnosis/testing.
The diagnosis of ELN-related cutis laxa is established in a proband with suggestive findings and a heterozygous pathogenic (or likely pathogenic) variant in ELN identified by molecular genetic testing.
Management.
Treatment of manifestations: There is no cure for ELN-related cutis laxa. Experience in treating individuals with ELN-related cutis laxa is very limited. Supportive care to improve quality of life, maximize function, and reduce complications is recommended and ideally involves multidisciplinary care by specialists in general surgery, cardiothoracic surgery, cardiology, pulmonology, urology, physical therapy, ophthalmology, and medical genetics.
Surveillance: Monitor for known problems (e.g., inguinal hernias, joint hypermobility and pain) and new issues that may require interventions (e.g., ptosis, aortic root dilatation, emphysema, bladder diverticula).
Agents/circumstances to avoid: Positive pressure ventilation unless needed for life-threatening conditions; contact with people with respiratory infections; tobacco smoking; isometric exercise (which causes an increase in blood pressure); contact sports or activities that increase the risk for blunt abdominal trauma and/or joint injury or pain; sunbathing or tanning in order to preserve residual skin elasticity.
Pregnancy management: Perinatal complications for mothers with ELN-related cutis laxa or affected neonates have not been reported to date. Nonetheless, recommended evaluations for women with ELN-related cutis laxa before conception and during pregnancy are pulmonary function testing and cardiovascular assessment (including aortic root diameter). Continued cardiac surveillance for six months post partum is also recommended. Additionally, women taking a beta-blocker should continue it during pregnancy; however, some other classes of medications, such as angiotensin receptor-blocking agents, are teratogenic and should be discontinued or changed to beta-blocking agents, given the increased risk for teratogenicity typically related to second- and third-trimester exposure.
Genetic counseling.
ELN-related cutis laxa is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. About one third of individuals diagnosed with ELN-related cutis laxa have an affected parent; about two thirds of affected individuals have the disorder as the result of a de novo ELN pathogenic variant. Each child of an individual with ELN-related cutis laxa has a 50% chance of inheriting the pathogenic variant. Once the ELN pathogenic variant has been identified in an affected family member, prenatal and preimplantation genetic testing are possible.
Diagnosis
No consensus clinical diagnostic criteria for ELN-related cutis laxa have been published.
Suggestive Findings
ELN-related cutis laxa should be suspected in individuals with the following clinical findings and family history.
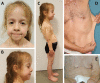
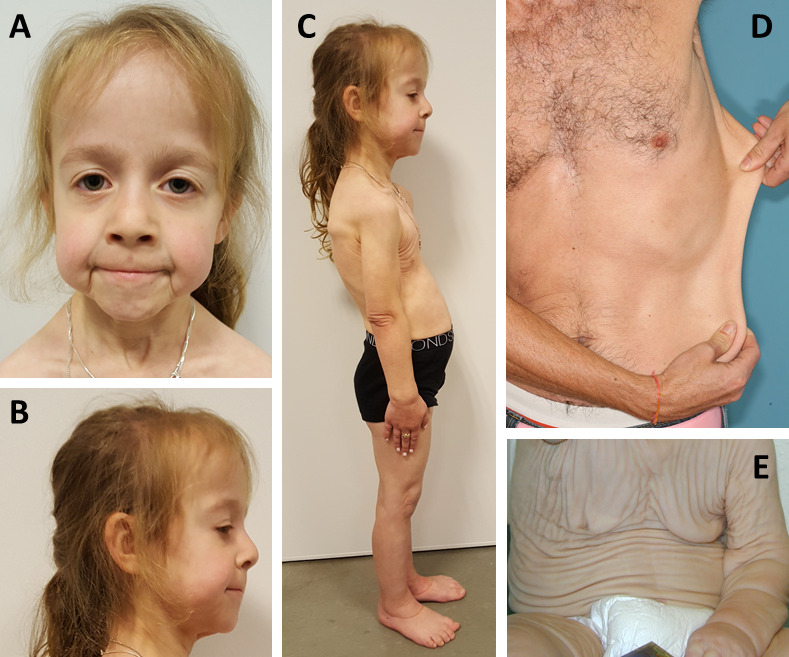
Clinical findings include generalized cutis laxa (ranging from generalized skin redundancy causing excessive skin folds to skin hyperextensibility without obvious skin folds) (Figure 1) with or without the following:
- Present at birth
- Inguinal hernia, with increased risk at all ages
- Joint hyperlaxity
- Progressive (may be present as early as childhood)
- Aortic root dilatation
- Emphysema
- Ptosis (eyelid drooping that can be caused by skin laxity)
- Facial characteristics that may become more prominent with age: large ears, convex nasal ridge, long philtrum, aged appearance (Figure 1)
Note: The skin is hyperextensible if it can be stretched more than a standardized cutoff in three of the following areas: 1.5 cm for the distal part of the forearms and the dorsum of the hands; 3 cm for neck, elbows, and knees.
Family history is consistent with autosomal dominant inheritance (e.g., affected males and females in multiple generations). Absence of a known family history does not preclude the diagnosis.
Establishing the Diagnosis
The diagnosis of ELN-related cutis laxa is established in a proband with suggestive findings and a heterozygous pathogenic (or likely pathogenic) variant in ELN identified by molecular genetic testing (see Table 1).
Note: (1) Per ACMG/AMP variant interpretation guidelines, the terms "pathogenic variants" and "likely pathogenic variants" are synonymous in a clinical setting, meaning that both are considered diagnostic, and both can be used for clinical decision making [Richards et al 2015]. Reference to "pathogenic variants" in this section is understood to include any likely pathogenic variants. (2) Identification of a heterozygous ELN variant of uncertain significance does not establish or rule out a diagnosis.
Because the phenotype of ELN-related cutis laxa may be difficult to distinguish from many other inherited disorders with cutis laxa, recommended molecular genetic testing approaches include use of a multigene panel or comprehensive genomic testing.
Note: Single-gene testing (sequence analysis of ELN, followed by gene-targeted deletion/duplication analysis) is rarely useful and typically NOT recommended.
- A cutis laxa multigene panel that includes ELN and other genes of interest (see Differential Diagnosis) is most likely to identify the genetic cause of the condition while limiting identification of variants of uncertain significance and pathogenic variants in genes that do not explain the underlying phenotype. Note: (1) The genes included in the panel and the diagnostic sensitivity of the testing used for each gene vary by laboratory and are likely to change over time. (2) Some multigene panels may include genes not associated with the condition discussed in this GeneReview. (3) In some laboratories, panel options may include a custom laboratory-designed panel and/or custom phenotype-focused exome analysis that includes genes specified by the clinician. (4) Methods used in a panel may include sequence analysis, deletion/duplication analysis, and/or other non-sequencing-based tests.
- Comprehensive genomic testing does not require the clinician to determine which gene is likely involved. Exome sequencing is most commonly used; genome sequencing is also possible.
Table 1.
Molecular Genetic Testing Used in ELN-Related Cutis Laxa
Clinical Characteristics
Clinical Description
ELN-related cutis laxa is characterized by generalized cutis laxa (ranging from generalized skin redundancy causing excessive skin folds to skin hyperextensibility without obvious skin folds) and distinctive facial features that may become more prominent with age. Other common findings are joint hyperlaxity in infancy and increasing risk of inguinal hernia at all ages. Progressive findings that may be present as early as childhood include ptosis, aortic root dilatation, and emphysema.
To date, more than 46 individuals from 23 families have been identified with a pathogenic variant in ELN [Tassabehji et al 1998, Zhang et al 1999, Rodriguez-Revenga et al 2004, Urban et al 2005, Szabo et al 2006, Callewaert et al 2011, Hadj-Rabia et al 2013, Vodo et al 2015, Duz et al 2017, Okuneva et al 2019, Xiao et al 2019]. The following description (Table 2) of the phenotypic features associated with ELN-related cutis laxa is based on these reports. The phenotype is present at birth and affects males and females equally.
Findings in Nearly All Individuals
Skin features in ELN-related cutis laxa include generalized loose and redundant skin, most prominent in the lower face, axillar, and inguinal regions, usually present at birth [Callewaert et al 2011]. Milder skin manifestations have been reported in adults as skin hyperlaxity [Szabo et al 2006, Hadj-Rabia et al 2013].
Nevertheless, all affected individuals have an aged appearance (see Figure 1), often with sagging eyelids, a convex nasal ridge, a long philtrum, prominent nasolabial folds, and skin redundancy in the chin and neck area. The external ears tend to be large.
Voice. The voice usually sounds hoarse and lower than expected.
Common Findings
Joint hypermobility. Affected individuals may show remarkable joint hypermobility of the small and large joints.
Aortic root dilatation. It has been estimated that up to 55% of affected individuals may develop aortic root aneurysm, with the risk increasing with age [Beyens et al 2021a, Beyens et al 2021b]. Aortic root dilatation has been observed in the first decade [Callewaert et al 2011]. Large diameters of the aortic root (up to 85 mm) and ascending aorta have been described [Szabo et al 2006, Callewaert et al 2011, Hadj-Rabia et al 2013].
Aortic aneurysms are amenable to surgery and there is no evidence of vascular fragility during surgery [Szabo et al 2006, Hadj-Rabia et al 2013].
Aortic dissection has been reported in multiple families as early as in the third decade [Szabo et al 2006]. The risk for aortic dissection has not been established.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and emphysema. Up to 35% of all affected individuals develop obstructive lung disease and emphysema, predisposing to airway infections [Beyens et al 2021a, Beyens et al 2021b].
Severe emphysema requiring lung transplantation has been observed in the context of concomitant excessive use of tobacco [Urban et al 2005, Hadj-Rabia et al 2013].
Inguinal hernias may occur and are prone to recurrence after surgery. Wound healing is normal.
Infrequent Findings
Arterial tortuosity. Increased tortuosity of the arteries (mainly of the supra-aortic vasculature) has been incidentally noted but not systematically assessed [Zhang et al 1999].
Bicuspid aortic valve. Three individuals had a bicuspid aortic valve associated with aneurysm formation of the ascending aorta [Callewaert et al 2011].
Other Observations
A splice site variant was reported in exon 25 of ELN (c.1708C>T) in an individual with cutis laxa, congenital emphysema, and epilepsy [Graul-Neumann et al 2008]. The facial characteristics do not fit with typical ELN-related cutis laxa. The variant was also present in the unaffected father. The variant results in exclusion of exon 25, containing lysine residues important for elastin crosslinking. Alternatively, if exon 25 is not spliced out, the variant creates a stop codon at position 541. The authors hypothesized that differences in expression of the mutated gene accounted for the interfamilial clinical variability. Of note, the c.1708C>T variant has been reported multiple times in individuals with supravalvular aortic stenosis (SVAS) (see Genetically Related Disorders). It is unclear if the variant explains all or part of the phenotype observed in the proband.
Genotype-Phenotype Correlations
No genotype-phenotype correlations have been identified in individuals with ELN-related cutis laxa.
Penetrance
ELN-related cutis laxa has 100% penetrance on detailed clinical observation [Hadj-Rabia et al 2013].
Prevalence
ELN-related cutis laxa is extremely rare; fewer than 50 individuals with a molecularly confirmed diagnosis have been reported to date.
While affected individuals have been mostly of European descent, individuals of other ethnicities have been reported, and there is no evidence to suspect ethnic preponderance.
Genetically Related (Allelic) Disorders
Supravalvular aortic stenosis (SVAS, OMIM 185500) is an autosomal dominant condition characterized by the variable presence of arterial stenoses. Stenoses are typically localized above the aortic valve, but may occur elsewhere on large and middle-sized arteries of both systemic and pulmonary circulation. Stenoses can be progressive. There is increased vascular wall stiffness, and affected individuals are prone to arterial hypertension. Associated connective tissue manifestations that may occur include a hoarse voice, inguinal/umbilical hernia, bowel/bladder diverticula, rectal prolapse, joint limitation or laxity, and soft, hyperextensible (rather than lax) skin. Neuromotor development and intellectual capacities are normal [Merla et al 2012].
Pathogenic variants in ELN causing SVAS result in haploinsufficiency, and typically induce premature truncation of the ELN transcript through introduction of a stop codon or an out-of-frame splicing defect. Most variants are in the first 19 exons, but variants at the C terminus have been reported [Mefford et al 2008, Merla et al 2012].
This differs from the variants causing ELN-related cutis laxa, which result in a transcript coding a 3' extended protein that is deposited in the extracellular matrix and acts via a dominant-negative effect [Callewaert et al 2011].
An ELN intronic deletion, c.2132-14_2161del (NM_000501.3), has been reported in an individual without features of ELN-related cutis laxa but with features of SVAS [Velandia-Piedrahita et al 2020]. The variant was also present in the unaffected father. Two other children of the father died prematurely, probably in the context of SVAS. Complementary DNA analysis indicated three transcripts. Transcript 1 skips the coding region of exon 33 and uses a cryptic splice site in the 3' UTR predicting a protein with a C terminus containing 49 additional residues and lacking the conserved KxxxRKRK motif. Transcript 2 shows the presence of 92 bp of intronic sequence adjacent to exon 32, indicating intron 32 retention. The predicted protein has 17 additional amino acids at the C terminus and disrupts the KxxxRKRK motif. The third transcript predicts consequences at the protein level similar to transcript 2, but shows physiologic splicing of exon 31. Nevertheless, abundance of the different RNA molecules has not been investigated and no protein expression analysis was performed; thus, a haploinsufficiency mechanism for the c.2132-14_2161del variant cannot be ruled out. Familial segregation was incomplete, as the variant was not assessed in the paternal grandparents of the proband.
Williams syndrome (WS) is an autosomal dominant disorder characterized by cardiovascular disease (including SVAS), distinctive facies, connective tissue abnormalities, intellectual disability, a specific cognitive profile, unique personality characteristics, and growth and endocrine abnormalities. WS is caused by a recurrent 7q11.23 contiguous gene deletion of the Williams-Beuren syndrome critical region (WBSCR) that encompasses ELN. Hence, deletion of ELN contributes to the phenotype of Williams-Beuren syndrome.
7q11.23 duplication syndrome (Williams syndrome region duplication syndrome) is caused by duplication of the 1.5-Mb region most commonly deleted in Williams syndrome. Vascular disease in the 7q11.23 duplication syndrome may include aortic root dilatation.
Differential Diagnosis
Table 3.
Disorders to Consider in the Differential Diagnosis of ELN-Related Cutis Laxa
Neurometabolic Cutis Laxa
The term "neurometabolic cutis laxa" has been suggested for a group of diseases related to inborn errors of metabolism. These disorders combine cutis laxa and skeletal defects with neurometabolic findings and result from pathogenic variants causing aberrant intracellular processing of extracellular matrix proteins as well as other proteins necessary for neurometabolic homeostasis.
Known genetic defects involved in neurometabolic cutis laxa include:
- Defects in transporters for cofactors necessary for enzymes in the glycosylation pathway (ATP7A, encoding a copper transporter);
- Defects in proteins involved in retrograde Golgi-to-ER transport (COG7 [see Congenital Disorders of N-Linked Glycosylation and Multiple Pathway Overview], GORAB, NBAS, RIN2);
- Defects in enzymes involved in mitochondrial processes that include proline synthesis (PYCR1, encoding pyrroline-5-carboxylate reductase 1, and ALDH18A1, encoding delta-1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthase);
- Defects in enzymes involved in the synthesis of reducing equivalents to protect the cell from reactive oxygen species (TALDO1 [OMIM 606003]);
- Defects in phosphatidylserine synthesis (PTDSS1) and mitochondrial fatty acid beta-oxidation (ECHS1).
Note: For simplicity and clarity, not all of the growing list of genes involved in neurometabolic cutis laxa have been included in Table 3.
Management
No clinical practice guidelines for ELN-related cutis laxa have been published.
Evaluations Following Initial Diagnosis
To establish the extent of disease and needs in an individual diagnosed with ELN-related cutis laxa, the evaluations summarized in Table 4 (if not performed as part of the evaluation that led to the diagnosis) are recommended.
Table 4.
Recommended Evaluations Following Initial Diagnosis in Individuals with ELN-Related Cutis Laxa
Treatment of Manifestations
There is no cure for ELN-related cutis laxa.
Supportive treatment. Experience in treating individuals with ELN-related cutis laxa is very limited. Treatment is largely symptomatic and serves to improve quality of life, maximize function, and reduce complications. It ideally involves multidisciplinary care by specialists in relevant fields (Table 5).
Table 5.
Supportive Treatment of Manifestations in Individuals with ELN-Related Cutis Laxa
Surveillance
Table 6.
Recommended Surveillance for Individuals with ELN-Related Cutis Laxa
Agents/Circumstances to Avoid
Avoid the following:
- Positive pressure ventilation unless needed to treat life-threatening conditions. No data exist on the potential risk of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) for the treatment of sleep apnea. Close follow up is warranted when CPAP is started.
- Contracting respiratory infections
- Tobacco smoking, which can result in rapid, severe loss of lung function in persons with ELN-related cutis laxa
- Isometric exercise (which causes an increase in blood pressure)
- Contact sports. The increased risk for joint injury or pain related to contact sports should be discussed. In case of arterial aneurysms reaching diameters necessitating surgery, blunt trauma should be prevented as much as possible (similar to Marfan syndrome guidelines).
- Sunbathing or tanning, to preserve residual skin elasticity. Vitamin D supplementation should be considered in this context, and monitored annually.
Evaluation of Relatives at Risk
See Genetic Counseling for issues related to testing of at-risk relatives for genetic counseling purposes.
Pregnancy Management
At least 21 pregnancies have been reported in affected females. No perinatal complications for the affected mother or the neonate were reported [Zhang et al 1999, Rodriguez-Revenga et al 2004, Urban et al 2005, Szabo et al 2006, Hadj-Rabia et al 2013, Vodo et al 2015, Okuneva et al 2019, Xiao et al 2019, Velandia-Piedrahita et al 2020].
Per guidelines used for women with Marfan syndrome who are planning a pregnancy, women with ELN-related cutis laxa require preconception cardiovascular evaluation, including assessment of the aortic root diameter, as well as increased surveillance throughout the pregnancy and six months post partum.
Additionally, pulmonary evaluation and follow up are warranted before and during pregnancy. Pregnancy may aggravate respiratory symptoms as a result of reduced lung volume, resulting in increased respiratory effort in the third trimester.
Uterine prolapse may occur [Urban et al 2005].
Affected women who anticipate pregnancy or become pregnant and are taking a beta-blocker should continue it during pregnancy; however, some other classes of medications, such as angiotensin receptor-blocking agents, are teratogenic and should be discontinued or changed to beta-blocking agents, given the increased risk for teratogenicity (i.e., increased risk for fetal loss, oligohydramnios, and abnormal fetal development) typically related to second- and third-trimester exposure. Women who are planning a pregnancy or who become pregnant while taking an angiotensin receptor blocker can be transitioned to a beta-blocker.
See MotherToBaby for further information on medication use during pregnancy.
Therapies Under Investigation
Search ClinicalTrials.gov in the US and EU Clinical Trials Register in Europe for access to information on clinical studies for a wide range of diseases and conditions. Note: There may not be clinical trials for this disorder.
Genetic Counseling
Genetic counseling is the process of providing individuals and families with information on the nature, mode(s) of inheritance, and implications of genetic disorders to help them make informed medical and personal decisions. The following section deals with genetic risk assessment and the use of family history and genetic testing to clarify genetic status for family members; it is not meant to address all personal, cultural, or ethical issues that may arise or to substitute for consultation with a genetics professional. —ED.
Mode of Inheritance
ELN-related cutis laxa is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.
Risk to Family Members
Parents of a proband
- About one third of individuals diagnosed with ELN-related cutis laxa have an affected parent.
- About two thirds of individuals diagnosed with ELN-related cutis laxa have the disorder as the result of a de novo ELN pathogenic variant.
- If the proband appears to be the only affected family member (i.e., a simplex case), molecular genetic testing is recommended for the parents of the proband to confirm their genetic status and to allow reliable recurrence risk counseling.
- If the pathogenic variant identified in the proband is not identified in either parent and parental identity testing has confirmed biological maternity and paternity, the following possibilities should be considered:
- The proband has a de novo pathogenic variant.
- The proband inherited a pathogenic variant from a parent with germline (or somatic and germline) mosaicism. Thus far, germline mosaicism has not been reported in ELN-related cutis laxa. Note: Testing of parental leukocyte DNA may not detect all instances of somatic mosaicism and will not detect a pathogenic variant that is present in the germ cells only.
- The family history of some individuals diagnosed with ELN-related cutis laxa may appear to be negative because of a milder personal appreciation of a phenotypic presentation in the affected parent. Therefore, an apparently negative family history cannot be confirmed unless molecular genetic testing has demonstrated that neither parent is heterozygous for the pathogenic variant identified in the proband.
Sibs of a proband. The risk to the sibs of the proband depends on the clinical/genetic status of the proband's parents:
- If a parent of the proband is affected and/or is known to have the pathogenic variant identified in the proband, the risk to the sibs of inheriting the pathogenic variant is 50%.
- A sib who inherits a pathogenic variant is expected to have manifestations of the disorder; however, intrafamilial clinical variability is observed in ELN-related cutis laxa.
- If the ELN pathogenic variant identified in the proband cannot be detected in the leukocyte DNA of either parent, the recurrence risk to sibs is estimated to be 1% because of the theoretic possibility of parental germline mosaicism [Rahbari et al 2016].
- If the parents have not been tested for the ELN pathogenic variant but are clinically unaffected, the risk to the sibs of a proband appears to be low. However, sibs of a proband with clinically unaffected parents are still presumed to be at increased risk for ELN-related cutis laxa because of the possibility of a mild presentation in a heterozygous parent or the theoretic possibility of parental germline mosaicism.
Offspring of a proband. Each child of an individual with ELN-related cutis laxa has a 50% chance of inheriting the ELN pathogenic variant.
Other family members. The risk to other family members depends on the status of the proband's parents: if a parent has the ELN pathogenic variant, the parent's family members may be at risk.
Related Genetic Counseling Issues
Family planning
- The optimal time for determination of genetic risk and discussion of the availability of prenatal/preimplantation genetic testing is before pregnancy.
- It is appropriate to offer genetic counseling (including discussion of potential risks to offspring and reproductive options) to young adults who are affected or at risk.
Prenatal Testing and Preimplantation Genetic Testing
Once the ELN pathogenic variant has been identified in an affected family member, prenatal and preimplantation genetic testing are possible.
Differences in perspective may exist among medical professionals and within families regarding the use of prenatal testing. While most centers would consider use of prenatal testing to be a personal decision, discussion of these issues may be helpful.
Resources
GeneReviews staff has selected the following disease-specific and/or umbrella support organizations and/or registries for the benefit of individuals with this disorder and their families. GeneReviews is not responsible for the information provided by other organizations. For information on selection criteria, click here.
- DermNet NZNew Zealand
- MedlinePlus
- Genodermatoses Network - Fondation René TouraineThe network on rare genetic skin diseases for professionals and patients.France
Molecular Genetics
Information in the Molecular Genetics and OMIM tables may differ from that elsewhere in the GeneReview: tables may contain more recent information. —ED.
Table A.
ELN-Related Cutis Laxa: Genes and Databases
Table B.
OMIM Entries for ELN-Related Cutis Laxa (View All in OMIM)
Molecular Pathogenesis
ELN pathogenic variants causing ELN-related cutis laxa result in a shift in the reading frame in the last four exons of the ELN transcript, causing an elongated sequence at the C terminus of the protein tropoelastin. The altered tropoelastin is stable and secreted [Szabo et al 2006, Callewaert et al 2011]. When in the secretory pathway, the abnormal protein interacts with wild type tropoelastin increasing self-aggregation (coacervation) and clump formation that impedes proper crosslinking in elastic fibers by lysyl oxidases [Callewaert et al 2011]. As a result, electron microscopy of skin biopsies shows abnormal elastic fibers that appear as amorphic clumps without parallel directionality to the microfibrils [Callewaert et al 2011].
Mechanism of disease causation. ELN pathogenic variants that cause ELN-related cutis laxa result in an abnormal protein with an extended C terminal. The pathogenic variant may result in a frameshift with a readthrough in the 3' untranslated region or result in inclusion of noncoding sequences in the mature mRNA. Mutated tropoelastin has been shown to aggregate with wild type elastin. Hence, the likely mechanism is a dominant-negative effect [Callewaert et al 2011].
Although other mechanisms of ELN variants have been described, confirmation is necessary to establish a causal relationship with typical ELN-related cutis laxa [Graul-Neumann et al 2008, Velandia-Piedrahita et al 2020].
ELN-specific laboratory technical considerations. Most identified pathogenic variants in ELN-related cutis laxa cause an ELN frameshift affecting exons 30-34 and result in an extended open reading frame.
A more complex gene duplication/triplication was reported in one family by Urban et al [2005]. The predicted open reading frame similarly extended beyond the typical stop codon.
Molecular testing should include analysis for deep intronic variants. One reported intronic splice variant (c.2272+20), causing inclusion of a 19-base pair intronic sequence in the mature ELN mRNA resulting in a frameshift, was reported in a boy age five years with a phenotype indistinguishable from other individuals with ELN-related cutis laxa [Vodo et al 2015].
Table 7.
Notable ELN Pathogenic Variants
Chapter Notes
Author Notes
Bert Callewaert is an Associate Professor at Ghent University and a pediatrician/clinical geneticist at the Center for Medical Genetics of the Ghent University Hospital. His research focuses on connective tissue disorders (including arterial tortuosity syndrome, cutis laxa syndromes, and familial thoracic aortic aneurysms). Both zebra fish and mouse models are used to gain insight into the pathogenesis of these disorders.
Dr Callewaert is actively involved in clinical research regarding individuals with ELN-related cutis laxa. He would be happy to communicate with persons who have any questions regarding diagnosis of ELN-related cutis laxa or other considerations.
Contact Dr Callewaert to inquire about the interpretation of ELN variants of uncertain significance.
Dr Callewaert is also interested in hearing from clinicians treating families affected by cutis laxa in whom no causative variant has been identified through molecular genetic testing of the genes known to be involved in this group of disorders.
Email: eb.tnegu@treawellac.treb
Website: Center for Medical Genetics, Ghent University Hospital
Zsolt Urban is an Associate Professor of Human Genetics at the Graduate School of Public Health of the University of Pittsburgh. His research is focused on cutis laxa and related disorders. His research team pursues clinical, cell culture, and animal model studies to characterize the natural history of cutis laxa and identify the genetic causes and underlying molecular mechanisms responsible for this group of disorders.
For more information, go to the Cutis Laxa Research Study website or email ude.ttip@znabru.
Acknowledgments
Bert Callewaert is a Senior Clinical Investigator of the Fund for Scientific Research-Flanders. Zsolt Urban is funded by a National Institutes of Health grant HL090648.
Revision History
- 29 September 2022 (bp) Review posted live
- 25 January 2022 (bc) Original submission
References
Literature Cited
- Basel-Vanagaite L, Sarig O, Hershkovitz D, Fuchs-Telem D, Rapaport D, Gat A, Isman G, Shirazi I, Shohat M, Enk CD, Birk E, Kohlhase J, Matysiak-Scholze U, Maya I, Knopf C, Peffekoven A, Hennies HC, Bergman R, Horowitz M, Ishida-Yamamoto A, Sprecher E. RIN2 deficiency results in macrocephaly, alopecia, cutis laxa, and scoliosis: MACS syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2009;85:254–63. [PMC free article: PMC2725231] [PubMed: 19631308]
- Beyens A, Boel A, Symoens S, Callewaert B. Cutis laxa: a comprehensive overview of clinical characteristics and pathophysiology. Clinical genetics. 2021a;99:53–66. [PubMed: 33058140]
- Beyens A, Pottie L, Sips P, Callewaert B. Clinical and molecular delineation of cutis laxa syndromes: paradigms for homeostasis. Advances in experimental medicine and biology. 2021b;1348:273–309. [PubMed: 34807425]
- Beyens A, Van Meensel K, Pottie L, De Rycke R, De Bruyne M, Baeke F, Hoebeke P, Plasschaert F, Loeys B, De Schepper S, Symoens S, Callewaert B. Defining the clinical, molecular and ultrastructural characteristics in occipital horn syndrome: two new cases and review of the literature. Genes. 2019;10:528. [PMC free article: PMC6678539] [PubMed: 31336972]
- Callewaert B, Renard M, Hucthagowder V, Albrecht B, Hausser I, Blair E, Dias C, Albino A, Wachi H, Sato F, Mecham RP, Loeys B, Coucke PJ, De Paepe A, Urban Z. New insights into the pathogenesis of autosomal-dominant cutis laxa with report of five ELN mutations. Hum Mutat. 2011;32:445–55. [PMC free article: PMC3383654] [PubMed: 21309044]
- Callewaert BL, Willaert A, Kerstjens-Frederikse WS, De Backer J, Devriendt K, Albrecht B, Ramos-Arroyo MA, Doco-Fenzy M, Hennekam RC, Pyeritz RE, Krogmann ON, Gillessen-kaesbach G, Wakeling EL, Nik-zainal S, Francannet C, Mauran P, Booth C, Barrow M, Dekens R, Loeys BL, Coucke PJ, De Paepe AM. Arterial tortuosity syndrome: clinical and molecular findings in 12 newly identified families. Hum Mutat. 2008;29:150–8. [PubMed: 17935213]
- Duz MB, Kirat E, Coucke PJ, Koparir E, Gezdirici A, Paepe A, Callewaert B, Seven M. A novel case of autosomal dominant cutis laxa in a consanguineous family: report and literature review. Clin Dysmorphol. 2017;26:142–7. [PubMed: 28383366]
- Graul-Neumann LM, Hausser I, Essayie M, Rauch A, Kraus C. Highly variable cutis laxa resulting from a dominant splicing mutation of the elastin gene. Am J Med Genet A. 2008;146A:977–83. [PubMed: 18348261]
- Hadj-Rabia S, Callewaert BL, Bourrat E, Kempers M, Plomp AS, Layet V, Bartholdi D, Renard M, De Backer J, Malfait F, Vanakker OM, Coucke PJ, De Paepe AM, Bodemer C. Twenty patients including 7 probands with autosomal dominant cutis laxa confirm clinical and molecular homogeneity. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2013;8:36. [PMC free article: PMC3599008] [PubMed: 23442826]
- McKenzie F, Mina K, Callewaert B, Beyens A, Dickinson JE, Jevon G, Papadimitriou J, Diness BR, Steensberg JN, Ek J, Baynam G. Severe congenital cutis laxa: Identification of novel homozygous LOX gene variants in two families. Clin Genet. 2021;100:168–75. [PubMed: 33866545]
- Mefford HC, Sharp AJ, Baker C, Itsara A, Jiang Z, Buysse K, Huang S, Maloney VK, Crolla JA, Baralle D, Collins A, Mercer C, Norga K, de Ravel T, Devriendt K, Bongers EM, de Leeuw N, Reardon W, Gimelli S, Bena F, Hennekam RC, Male A, Gaunt L, Clayton-Smith J, Simonic I, Park SM, Mehta SG, Nik-Zainal S, Woods CG, Firth HV, Parkin G, Fichera M, Reitano S, Lo Giudice M, Li KE, Casuga I, Broomer A, Conrad B, Schwerzmann M, Raber L, Gallati S, Striano P, Coppola A, Tolmie JL, Tobias ES, Lilley C, Armengol L, Spysschaert Y, Verloo P, De Coene A, Goossens L, Mortier G, Speleman F, van Binsbergen E, Nelen MR, Hochstenbach R, Poot M, Gallagher L, Gill M, McClellan J, King MC, Regan R, Skinner C, Stevenson RE, Antonarakis SE, Chen C, Estivill X, Menten B, Gimelli G, Gribble S, Schwartz S, Sutcliffe JS, Walsh T, Knight SJ, Sebat J, Romano C, Schwartz CE, Veltman JA, de Vries BB, Vermeesch JR, Barber JC, Willatt L, Tassabehji M, Eichler EE. Recurrent rearrangements of chromosome 1q21.1 and variable pediatric phenotypes. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1685–99. [PMC free article: PMC2703742] [PubMed: 18784092]
- Merla G, Brunetti-Pierri N, Piccolo P, Micale L, Loviglio MN. Supravalvular aortic stenosis: elastin arteriopathy. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2012;5:692–6. [PubMed: 23250899]
- Okuneva EG, Kozina AA, Baryshnikova NV, Krasnenko AY, Tsukanov KY, Klimchuk OI, Surkova EI, Ilinsky VV. A novel elastin gene frameshift mutation in a Russian family with cutis laxa: a case report. BMC dermatology. 2019;19:4. [PMC free article: PMC6357400] [PubMed: 30704477]
- Piard J, Lespinasse J, Vlckova M, Mensah MA, Iurian S, Simandlova M, Malikova M, Bartsch O, Rossi M, Lenoir M, Nugues F, Mundlos S, Kornak U, Stanier P, Sousa SB, Van Maldergem L. Cutis laxa and excessive bone growth due to de novo mutations in PTDSS1. Am J Med Genet A. 2018;176:668–75. [PMC free article: PMC5838527] [PubMed: 29341480]
- Pottie L, Adamo CS, Beyens A, Lutke S, Tapaneeyaphan P, De Clercq A, Salmon PL, De Rycke R, Gezdirici A, Gulec EY, Khan N, Urquhart JE, Newman WG, Metcalfe K, Efthymiou S, Maroofian R, Anwar N, Maqbool S, Rahman F, Altweijri I, Alsaleh M, Abdullah SM, Al-Owain M, Hashem M, Houlden H, Alkuraya FS, Sips P, Sengle G, Callewaert B. Bi-allelic premature truncating variants in LTBP1 cause cutis laxa syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2021;108:1095–114. [PMC free article: PMC8206382] [PubMed: 33991472]
- Rahbari R, Wuster A, Lindsay SJ, Hardwick RJ, Alexandrov LB, Turki SA, Dominiczak A, Morris A, Porteous D, Smith B, Stratton MR, Hurles ME, et al. Timing, rates and spectra of human germline mutation. Nat Genet. 2016;48:126–33. [PMC free article: PMC4731925] [PubMed: 26656846]
- Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S, Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, Voelkerding K, Rehm HL, et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. 2015;17:405–24. [PMC free article: PMC4544753] [PubMed: 25741868]
- Rodriguez-Revenga L, Iranzo P, Badenas C, Puig S, Carrio A, Mila M. A novel elastin gene mutation resulting in an autosomal dominant form of cutis laxa. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:1135–9. [PubMed: 15381555]
- Sousa SB, Jenkins D, Chanudet E, Tasseva G, Ishida M, Anderson G, Docker J, Ryten M, Sa J, Saraiva JM, Barnicoat A, Scott R, Calder A, Wattanasirichaigoon D, Chrzanowska K, Simandlova M, Van Maldergem L, Stanier P, Beales PL, Vance JE, Moore GE. Gain-of-function mutations in the phosphatidylserine synthase 1 (PTDSS1) gene cause Lenz-Majewski syndrome. Nat Genet. 2014;46:70–6. [PubMed: 24241535]
- Stenson PD, Mort M, Ball EV, Chapman M, Evans K, Azevedo L, Hayden M, Heywood S, Millar DS, Phillips AD, Cooper DN. The Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD®): optimizing its use in a clinical diagnostic or research setting. Hum Genet. 2020;139:1197–207. [PMC free article: PMC7497289] [PubMed: 32596782]
- Szabo Z, Crepeau MW, Mitchell AL, Stephan MJ, Puntel RA, Yin Loke K, Kirk RC, Urban Z. Aortic aneurysmal disease and cutis laxa caused by defects in the elastin gene. J Med Genet. 2006;43:255–8. [PMC free article: PMC2563239] [PubMed: 16085695]
- Tassabehji M, Metcalfe K, Hurst J, Ashcroft GS, Kielty C, Wilmot C, Donnai D, Read AP, Jones CJ. An elastin gene mutation producing abnormal tropoelastin and abnormal elastic fibres in a patient with autosomal dominant cutis laxa. Hum Mol Genet. 1998;7:1021–8. [PubMed: 9580666]
- Urban Z, Gao J, Pope FM, Davis EC. Autosomal dominant cutis laxa with severe lung disease: synthesis and matrix deposition of mutant tropoelastin. J Invest Dermatol. 2005;124:1193–9. [PubMed: 15955094]
- Velandia-Piedrahita CA, Morel A, Fonseca-Mendoza DJ, Huertas-Quinones VM, Castillo D, Bonilla JD, Hernandez-Toro CJ, Miranda-Fernandez MC, Restrepo CM, Cabrera R. A novel splice-site mutation in the ELN gene suggests an alternative mechanism for vascular elastinopathies. Appl Clin Genet. 2020;13:233–40. [PMC free article: PMC7751611] [PubMed: 33364810]
- Verlee M, Beyens A, Gezdirici A, Gulec EY, Pottie L, De Feyter S, Vanhooydonck M, Tapaneeyaphan P, Symoens S, Callewaert B. Loss-of-function variants in EFEMP1 cause a recognizable connective tissue disorder characterized by cutis laxa and multiple herniations. Genes. 2021;13:12. [PMC free article: PMC8066907] [PubMed: 33807164]
- Vodo D, Sarig O, Peled A, Frydman M, Greenberger S, Sprecher E. Autosomal-dominant cutis laxa resulting from an intronic mutation in ELN. Exp Dermatol. 2015;24:885–7. [PubMed: 26121527]
- Xiao H, Zhang Z, Lyu X, Li T, Guo Q, Wang H, Zhang Q, Su J, Liao S. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2019;36:785–8. [Analysis of ELN gene mutation in a pedigree affected with cutis laxa] [PubMed: 31400128]
- Zhang MC, He L, Giro M, Yong SL, Tiller GE, Davidson JM. Cutis laxa arising from frameshift mutations in exon 30 of the elastin gene (ELN). J Biol Chem. 1999;274:981–6. [PubMed: 9873040]
Publication Details
Author Information and Affiliations
University of Pittsburgh Graduate School of Public Health
Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania
Publication History
Initial Posting: September 29, 2022.
Copyright
GeneReviews® chapters are owned by the University of Washington. Permission is hereby granted to reproduce, distribute, and translate copies of content materials for noncommercial research purposes only, provided that (i) credit for source (http://www.genereviews.org/) and copyright (© 1993-2024 University of Washington) are included with each copy; (ii) a link to the original material is provided whenever the material is published elsewhere on the Web; and (iii) reproducers, distributors, and/or translators comply with the GeneReviews® Copyright Notice and Usage Disclaimer. No further modifications are allowed. For clarity, excerpts of GeneReviews chapters for use in lab reports and clinic notes are a permitted use.
For more information, see the GeneReviews® Copyright Notice and Usage Disclaimer.
For questions regarding permissions or whether a specified use is allowed, contact: ude.wu@tssamda.
Publisher
University of Washington, Seattle, Seattle (WA)
NLM Citation
Callewaert BL, Urban Z. ELN-Related Cutis Laxa. 2022 Sep 29. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, et al., editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993-2024.