This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of neuroblastoma. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
Editorial Boards write the PDQ cancer information summaries and keep them up to date. These Boards are made up of experts in cancer treatment and other specialties related to cancer. The summaries are reviewed regularly and changes are made when there is new information. The date on each summary ("Date Last Modified") is the date of the most recent change. The information in this patient summary was taken from the health professional version, which is reviewed regularly and updated as needed, by the PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board.
General Information About Neuroblastoma
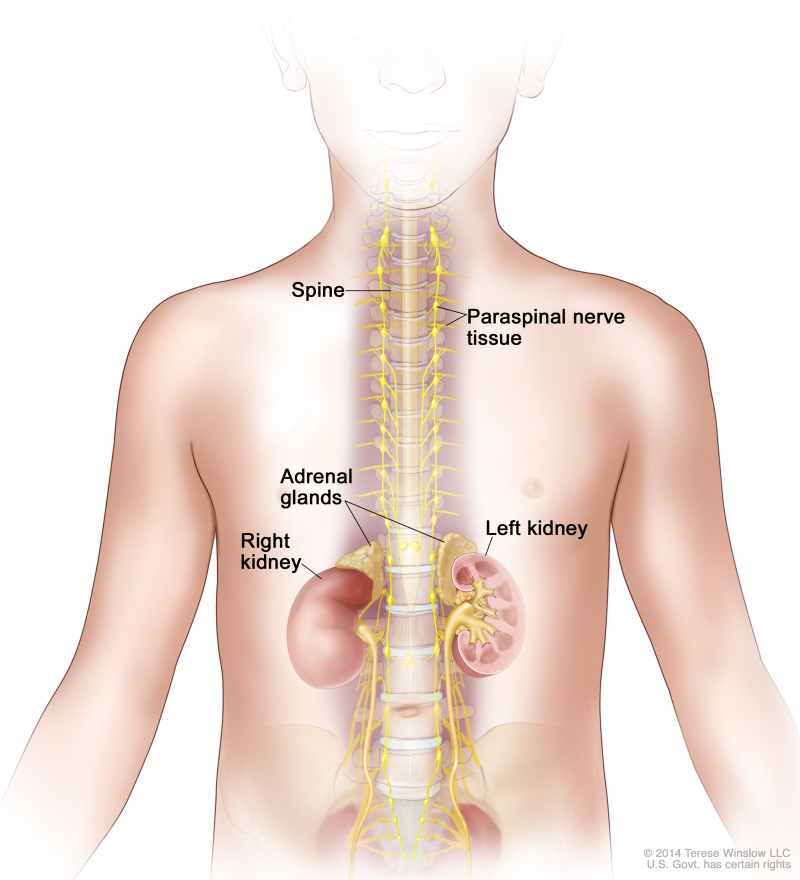
Neuroblastoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in nerve tissue of the adrenal gland, neck, chest, or spinal cord.
Neuroblastoma often begins in the nerve tissue of the adrenal glands. There are two adrenal glands, one on top of each kidney in the back of the upper abdomen. The adrenal glands make important hormones that help control heart rate, blood pressure, blood sugar, and the way the body reacts to stress. Neuroblastoma may also begin in the abdomen, in the chest, in nerve tissue near the spine in the neck, or in the spinal cord.
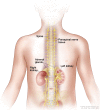
Figure
Neuroblastoma may be found in the adrenal glands and paraspinal nerve tissue from the neck to the pelvis.
Neuroblastoma most often begins during early childhood, usually in children younger than 5 years of age. It is found when the tumor begins to grow and cause signs or symptoms. Sometimes it forms before birth and is found during a fetal ultrasound.
By the time neuroblastoma is diagnosed, the cancer has usually metastasized (spread). Neuroblastoma spreads most often to the lymph nodes, bones, bone marrow, liver, and in infants, skin.
See the PDQ summary on Neuroblastoma Screening for more information.
Neuroblastoma is sometimes caused by a gene mutation (change) passed from the parent to the child.
The gene mutation that increases the risk of neuroblastoma is sometimes inherited (passed from the parent to the child). In patients with this gene mutation, neuroblastoma usually occurs at a younger age and more than one tumor may form in the adrenal medulla.
Signs and symptoms of neuroblastoma include bone pain and a lump in the abdomen, neck, or chest.
The most common signs and symptoms of neuroblastoma are caused by the tumor pressing on nearby tissues as it grows or by cancer spreading to the bone. These and other signs and symptoms may be caused by neuroblastoma or by other conditions.
Check with your child’s doctor if your child has any of the following:
- Lump in the abdomen, neck, or chest.
- Bulging eyes.
- Dark circles around the eyes ("black eyes").
- Bone pain.
- Swollen stomach and trouble breathing (in infants).
- Painless, bluish lumps under the skin (in infants).
- Weakness or paralysis (loss of ability to move a body part).
Less common signs and symptoms of neuroblastoma include the following:
Tests that examine many different body tissues and fluids are used to detect (find) and diagnose neuroblastoma.
The following tests and procedures may be used:
- Physical exam and history: An exam of the body to check general signs of health, including checking for signs of disease, such as lumps or anything else that seems unusual. A history of the patient’s health habits and past illnesses and treatments will also be taken.
- Neurological exam: A series of questions and tests to check the brain, spinal cord, and nerve function. The exam checks a person’s mental status, coordination, and ability to walk normally, and how well the muscles, senses, and reflexes work. This may also be called a neuro exam or a neurologic exam.
- Urine catecholamine studies: A procedure in which a urine sample is checked to measure the amount of certain substances, vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) and homovanillic acid (HVA), that are made when catecholamines break down and are released into the urine. A higher than normal amount of VMA or HVA can be a sign of neuroblastoma.
- Blood chemistry studies: A procedure in which a blood sample is checked to measure the amounts of certain substances released into the blood by organs and tissues in the body. An unusual (higher or lower than normal) amount of a substance can be a sign of disease.
- Hormone test: A procedure in which a blood sample is checked to measure the amount of hormones released into the blood by the adrenal medulla. A higher than normal amount of the hormones dopamine and norepinephrine may be a sign of neuroblastoma.
- mIBG (metaiodobenzylguanidine) scan: A procedure used to find neuroendocrine tumors, such as neuroblastoma and pheochromocytoma. A very small amount of a substance called radioactive mIBG is injected into a vein and travels through the bloodstream. Neuroendocrine tumor cells take up the radioactive mIBG and are detected by a scanner. Scans may be taken over 1-3 days. An iodine solution may be given before or during the test to keep the thyroid gland from absorbing too much of the mIBG. This test is also used to find out how well the tumor is responding to treatment. mIBG is used in high doses to treat neuroblastoma.
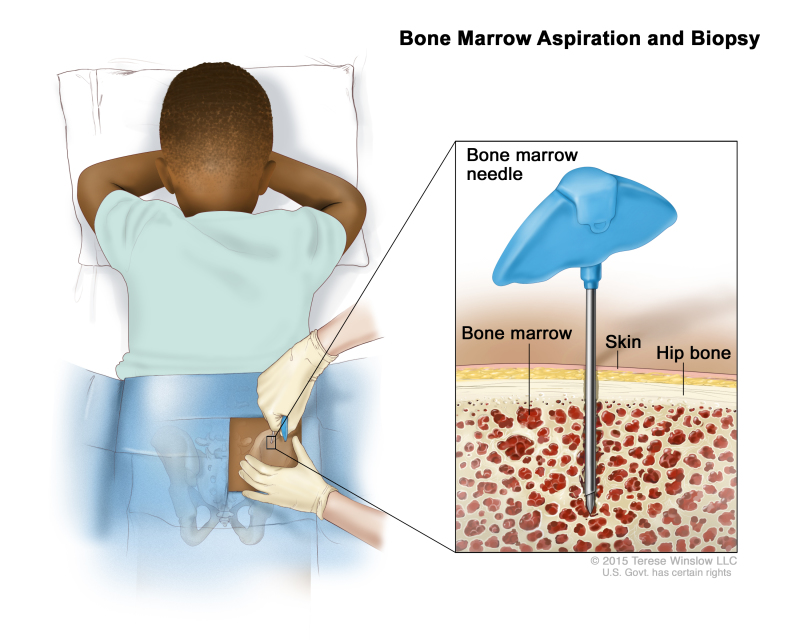
- Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy: The removal of bone marrow, blood, and a small piece of bone by inserting a hollow needle into the hipbone or breastbone. A pathologist views the bone marrow, blood, and bone under a microscope to look for signs of cancer.

Figure
Bone marrow aspiration and biopsy. After a small area of skin is numbed, a bone marrow needle is inserted into the child’s hip bone. Samples of blood, bone, and bone marrow are removed for examination under a microscope.
- X-ray: An x-ray is a type of energy beam that can go through the body and onto film, making a picture of areas inside the body.
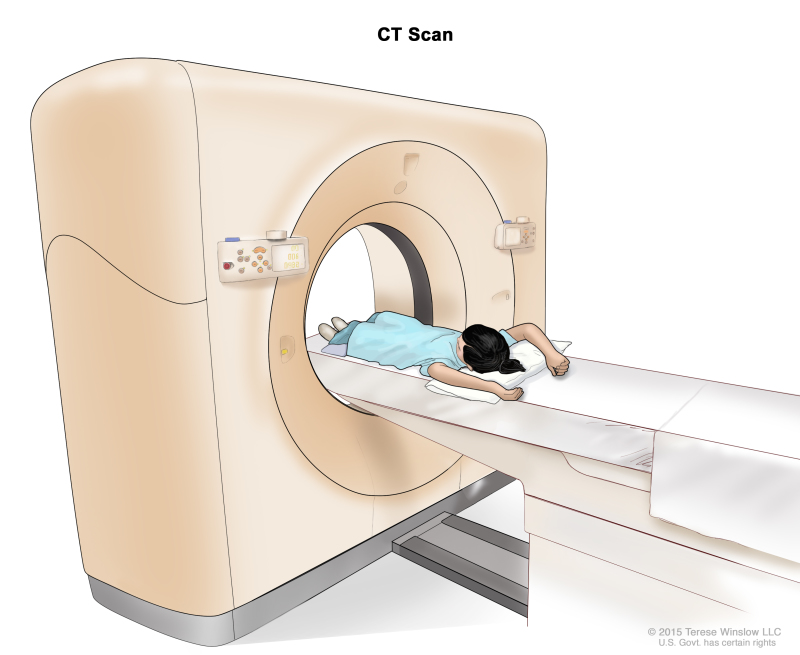
- CT scan (CAT scan): A procedure that makes a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body, taken from different angles. The pictures are made by a computer linked to an x-ray machine. A dye may be injected into a vein or swallowed to help the organs or tissues show up more clearly. This procedure is also called computed tomography, computerized tomography, or computerized axial tomography.

Figure
Computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen. The child lies on a table that slides through the CT scanner, which takes x-ray pictures of the inside of the abdomen.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) with gadolinium: A procedure that uses a magnet, radio waves, and a computer to make a series of detailed pictures of areas inside the body. A substance called gadolinium is injected into a vein. The gadolinium collects around the cancer cells so they show up brighter in the picture. This procedure is also called nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMRI).
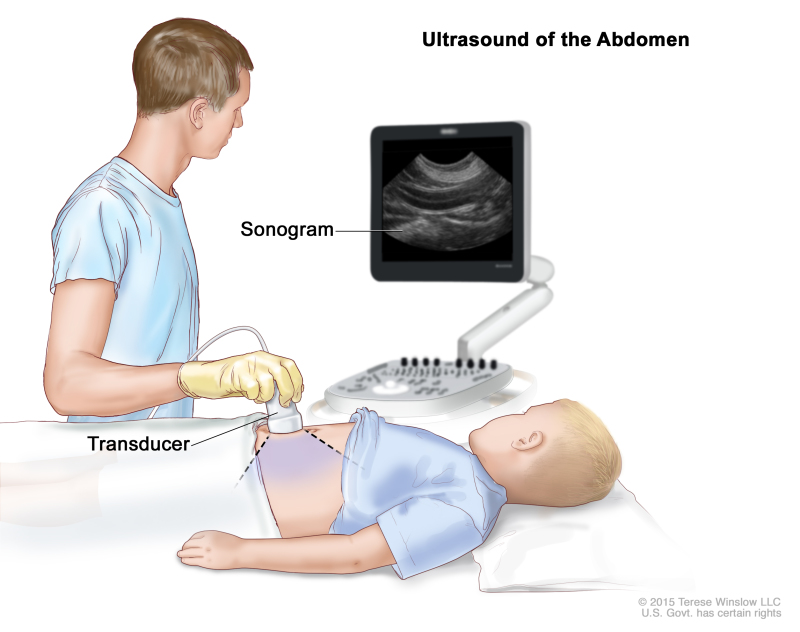
- Ultrasound exam: A procedure in which high-energy sound waves (ultrasound) are bounced off internal tissues or organs and make echoes. The echoes form a picture of body tissues called a sonogram. The picture can be printed to be looked at later.
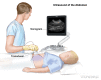
Figure
Abdominal ultrasound. An ultrasound transducer connected to a computer is pressed against the skin of the abdomen. The transducer bounces sound waves off internal organs and tissues to make echoes that form a sonogram (computer picture).
A biopsy is done to diagnose neuroblastoma.
Cells and tissues are removed during a biopsy so they can be viewed under a microscope by a pathologist to check for signs of cancer. The way the biopsy is done depends on where the tumor is in the body. Sometimes the whole tumor is removed at the same time the biopsy is done.
The following tests may be done on the tissue that is removed:
- Cytogenetic analysis: A laboratory test in which cells in a sample of tissue are viewed under a microscope to look for certain changes in the chromosomes.
- Light and electron microscopy: A laboratory test in which cells in a sample of tissue are viewed under regular and high-powered microscopes to look for certain changes in the cells.
- Immunohistochemistry: A test that uses antibodies to check for certain antigens in a sample of tissue. The antibody is usually linked to a radioactive substance or a dye that causes the tissue to light up under a microscope. This type of test may be used to tell the difference between different types of cancer.
- MYC-N amplification study: A laboratory study in which tumor or bone marrow cells are checked for the level of MYC-N. MYC-N is important for cell growth. A higher level of MYC-N (more than 10 copies of the gene) is called MYC-N amplification. Neuroblastoma with MYC-N amplification is more likely to spread in the body and less likely to respond to treatment.
Children who are 6 months old or younger may not need a biopsy or surgery to remove the tumor because the tumor may disappear without treatment.
Certain factors affect prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options.
The prognosis (chance of recovery) and treatment options depend on the following:
- Age of the child at diagnosis.
- Stage of the cancer.
- Where in the body the tumor started.
- Tumor histology (the shape, function, and structure of the tumor cells).
- Whether there is cancer in the lymph nodes on the same side of the body as the cancer or whether there is cancer in the lymph nodes on the opposite side of the body.
- How the tumor responds to treatment.
- Whether there are certain changes in the chromosomes.
- How much time passed between diagnosis and when the cancer recurred (for recurrent cancer).
Prognosis and treatment options for neuroblastoma are also affected by tumor biology, which includes:
- The patterns of the tumor cells.
- How different the tumor cells are from normal cells.
- How fast the tumor cells are growing.
- Whether the tumor shows MYC-N amplification.
The tumor biology is said to be favorable or unfavorable, depending on these factors. A favorable tumor biology means there is a better chance of recovery.
In some children who are 6 months old and younger, neuroblastoma may disappear without treatment. The child is closely watched for signs or symptoms of neuroblastoma. If signs or symptoms occur, treatment may be needed.
Stages of Neuroblastoma
After neuroblastoma has been diagnosed, tests are done to find out if cancer has spread from where it started to other parts of the body.
The process used to find out the extent or spread of cancer is called staging. The information gathered from the staging process helps determine the stage of the disease. For neuroblastoma, stage is one of the factors used to plan treatment. The results of tests and procedures used to diagnose neuroblastoma may also be used for staging. See the General Information section for a description of these tests and procedures.
The following tests and procedures also may be used to determine the stage:
- Lumbar puncture: A procedure used to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the spinal column. This is done by placing a needle between two bones in the spine and into the CSF around the spinal cord and removing a sample of the fluid. The sample of CSF is checked under a microscope for signs that the cancer has spread to the brain and spinal cord. This procedure is also called an LP or spinal tap.
- Lymph node biopsy: The removal of all or part of a lymph node. A pathologist views the tissue under a microscope to look for cancer cells. One of the following types of biopsies may be done:
- -
Excisional biopsy: The removal of an entire lymph node.
- -
Incisional biopsy: The removal of part of a lymph node.
- -
Core biopsy: The removal of tissue from a lymph node using a wide needle.
- -
Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy: The removal of tissue or fluid from a lymph node using a thin needle.
- Bone scan: A procedure to check if there are rapidly dividing cells, such as cancer cells, in the bone. A very small amount of radioactive material is injected into a vein and travels through the bloodstream. The radioactive material collects in the bones with cancer and is detected by a scanner.
There are three ways that cancer spreads in the body.
Cancer can spread through tissue, the lymph system, and the blood:
- Tissue. The cancer spreads from where it began by growing into nearby areas.
- Lymph system. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the lymph system. The cancer travels through the lymph vessels to other parts of the body.
- Blood. The cancer spreads from where it began by getting into the blood. The cancer travels through the blood vessels to other parts of the body.
Cancer may spread from where it began to other parts of the body.
When cancer spreads to another part of the body, it is called metastasis. Cancer cells break away from where they began (the primary tumor) and travel through the lymph system or blood.
- Lymph system. The cancer gets into the lymph system, travels through the lymph vessels, and forms a tumor (metastatic tumor) in another part of the body.
- Blood. The cancer gets into the blood, travels through the blood vessels, and forms a tumor (metastatic tumor) in another part of the body.
The metastatic tumor is the same type of cancer as the primary tumor. For example, if neuroblastoma spreads to the liver, the cancer cells in the liver are actually neuroblastoma cells. The disease is metastatic neuroblastoma, not liver cancer.
The following stages are used for neuroblastoma:
Stage 1
In stage 1, the tumor is in only one area and all of the tumor that can be seen is completely removed during surgery.
Stage 3
In stage 3, one of the following is true:
- the tumor cannot be completely removed during surgery and has spread from one side of the body to the other side and may also have spread to nearby lymph nodes; or
- the tumor is in only one area, on one side of the body, but has spread to lymph nodes on the other side of the body; or
- the tumor is in the middle of the body and has spread to tissues or lymph nodes on both sides of the body, and the tumor cannot be removed by surgery.
Stage 4
Stage 4 is divided into stages 4 and 4S.
- In stage 4S:
- -
the child is younger than 12 months; and
- -
the cancer has spread to the skin, liver, and/or bone marrow; and
- -
the tumor is in only one area and all of the tumor that can be seen may be completely removed during surgery; and/or
- -
cancer cells may be found in the lymph nodes near the tumor.
Treatment of neuroblastoma is based on risk groups.
For many types of cancer, stages are used to plan treatment. For neuroblastoma, treatment depends on risk groups. The stage of neuroblastoma is one factor used to determine risk group. Other factors are the age of the child, tumor histology, and tumor biology.
There are three risk groups: low risk, intermediate risk, and high risk.
- Low-risk and intermediate-risk neuroblastoma have a good chance of being cured.
- High-risk neuroblastoma may be hard to cure.
Recurrent Neuroblastoma
Recurrent neuroblastoma is cancer that has recurred (come back) after it has been treated. The cancer may come back in the same place or in other parts of the body.
Treatment Option Overview
There are different types of treatment for patients with neuroblastoma.
Different types of treatment are available for patients with neuroblastoma. Some treatments are standard (the currently used treatment), and some are being tested in clinical trials. A treatment clinical trial is a research study meant to help improve current treatments or obtain information on new treatments for patients with cancer. When clinical trials show that a new treatment is better than the standard treatment, the new treatment may become the standard treatment.
Because cancer in children is rare, taking part in a clinical trial should be considered. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Children with neuroblastoma should have their treatment planned by a team of doctors who are experts in treating childhood cancer, especially neuroblastoma.
Treatment will be overseen by a pediatric oncologist, a doctor who specializes in treating children with cancer. The pediatric oncologist works with other pediatric health care providers who are experts in treating children with neuroblastoma and who specialize in certain areas of medicine. These may include the following specialists:
Children who are treated for neuroblastoma may have an increased risk of second cancers.
Some cancer treatments cause side effects that continue or appear years after cancer treatment has ended. These are called late effects. Late effects of cancer treatment may include:
- Physical problems.
- Changes in mood, feelings, thinking, learning, or memory.
- Second cancers (new types of cancer).
Some late effects may be treated or controlled. It is important that parents of children who are treated for neuroblastoma talk with their doctors about the possible late effects caused by some treatments. See the PDQ summary on Late Effects of Treatment for Childhood Cancer for more information.
Five types of standard treatment are used:
Observation
Observation is closely monitoring a patient's condition without giving any treatment until signs or symptoms appear or change.
Surgery
Surgery is used to treat neuroblastoma unless it has spread to other parts of the body. Depending on where the tumor is, as much of the tumor as is safely possible will be removed. If the tumor cannot be removed, a biopsy may be done instead.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is a cancer treatment that uses high-energy x-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or keep them from growing. There are two types of radiation therapy. External radiation therapy uses a machine outside the body to send radiation toward the cancer. Internal radiation therapy uses a radioactive substance sealed in needles, seeds, wires, or catheters that are placed directly into or near the cancer.
The way the radiation therapy is given depends on the type and stage of the cancer being treated. External radiation therapy is used to treat neuroblastoma.
High-risk neuroblastoma that comes back after initial treatment is sometimes treated with mIBG (radioactive iodine therapy). Radioactive iodine is given through an intravenous (IV) line and enters the bloodstream which carries radiation directly to tumor cells. Radioactive iodine collects in neuroblastoma cells and kills them with the radiation that is given off.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a cancer treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by killing the cells or by stopping them from dividing. When chemotherapy is taken by mouth or injected into a vein or muscle, the drugs enter the bloodstream and can reach cancer cells throughout the body (systemic chemotherapy). When chemotherapy is placed directly into the cerebrospinal fluid, an organ, or a body cavity such as the abdomen, the drugs mainly affect cancer cells in those areas (regional chemotherapy). The way the chemotherapy is given depends on the type and stage of the cancer being treated.
The use of two or more anticancer drugs is called combination chemotherapy.
See Drugs Approved for Neuroblastoma for more information.
High-dose chemotherapy and radiation therapy with stem cell rescue
High-dose chemotherapy and radiation therapy with stem cell rescue is a way of giving high doses of chemotherapy and radiation therapy and replacing blood-forming cells destroyed by cancer treatment for high-risk neuroblastoma. Stem cells (immature blood cells) are removed from the blood or bone marrow of the patient and are frozen and stored. After chemotherapy and radiation therapy are completed, the stored stem cells are thawed and given back to the patient through an infusion. These reinfused stem cells grow into (and restore) the body's blood cells.
Maintenance therapy is given after high-dose chemotherapy and radiation therapy with stem cell rescue to kill any cancer cells that may regrow and cause the disease to come back. Maintenance therapy is given for 6 months and includes the following treatments:
- Isotretinoin: A vitamin-like drug that slows the cancer's ability to make more cancer cells and changes how these cells look and act. This drug is taken by mouth.
- Anti-GD2 antibody ch14.18: A type of monoclonal antibody therapy that uses an antibody (ch14.18) made in the laboratory from a single type of immune system cell. ch14.18 identifies and attaches to a substance, called GD2, on the surface of neuroblastoma cells. Once the ch14.18 attaches to the GD2, a signal is sent to the immune system that a foreign substance has been found and needs to be killed. Then the body's immune system kills the neuroblastoma cell. This drug is given by infusion.
- Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF): A cytokine that helps make more immune system cells, especially granulocytes and macrophages (white blood cells), which can attack and kill cancer cells.
- Interleukin-2 (IL-2): A type of biologic therapy that boosts the growth and activity of many immune cells, especially lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Lymphocytes can attack and kill cancer cells.
New types of treatment are being tested in clinical trials.
This summary section describes treatments that are being studied in clinical trials. It may not mention every new treatment being studied. Information about clinical trials is available from the NCI website.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs or other substances to identify and attack specific cancer cells without harming normal cells. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) therapy is one type of targeted therapy being studied in the treatment of neuroblastoma.
TKI therapy blocks signals needed for tumors to grow. TKIs block the enzyme, tyrosine kinase, that causes stem cells to become more white blood cells (granulocytes or blasts) than the body needs. Crizotinib is one of the TKIs being studied to treat neuroblastoma that has come back after treatment. TKIs may be used in combination with other anticancer drugs as adjuvant therapy (treatment given after the initial treatment, to lower the risk that the cancer will come back).
Vaccine therapy
Vaccine therapy is a type of biologic therapy. Biologic therapy is a treatment that uses the patient’s immune system to fight cancer. Substances made by the body or made in a laboratory are used to boost, direct, or restore the body’s natural defenses against cancer. This type of cancer treatment is also called biotherapy or immunotherapy.
Other drug therapy
Lenalidomide is a type of angiogenesis inhibitor. It prevents the growth of new blood vessels that are needed by a tumor to grow.
Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial.
For some patients, taking part in a clinical trial may be the best treatment choice. Clinical trials are part of the cancer research process. Clinical trials are done to find out if new cancer treatments are safe and effective or better than the standard treatment.
Many of today's standard treatments for cancer are based on earlier clinical trials. Patients who take part in a clinical trial may receive the standard treatment or be among the first to receive a new treatment.
Patients who take part in clinical trials also help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future. Even when clinical trials do not lead to effective new treatments, they often answer important questions and help move research forward.
Patients can enter clinical trials before, during, or after starting their cancer treatment.
Some clinical trials only include patients who have not yet received treatment. Other trials test treatments for patients whose cancer has not gotten better. There are also clinical trials that test new ways to stop cancer from recurring (coming back) or reduce the side effects of cancer treatment.
Clinical trials are taking place in many parts of the country. See the Treatment Options section that follows for links to current treatment clinical trials. These have been retrieved from NCI's listing of clinical trials.
Follow-up tests may be needed.
Some of the tests that were done to diagnose the cancer or to find out the stage of the cancer may be repeated. Some tests will be repeated in order to see how well the treatment is working. Decisions about whether to continue, change, or stop treatment may be based on the results of these tests.
Some of the tests will continue to be done from time to time after treatment has ended. The results of these tests can show if your child's condition has changed or if the cancer has recurred (come back). These tests are sometimes called follow-up tests or check-ups.
Treatment Options for Neuroblastoma
Low-Risk Neuroblastoma
Treatment of low-risk neuroblastoma may include the following:
- Surgery followed by observation.
- Chemotherapy with or without surgery, for some patients.
- Observation alone for infants who do not have signs or symptoms of neuroblastoma. More studies are needed before this is considered a standard treatment.
- A clinical trial of treatment guided by the tumor's response to treatment and whether there are certain changes in the tumor cells.
Intermediate-Risk Neuroblastoma
Treatment of intermediate-risk neuroblastoma may include the following:
- Chemotherapy with or without surgery.
- Surgery alone for infants.
- Observation alone for certain infants.
- Radiation therapy to treat tumors that are causing serious problems and do not respond quickly to chemotherapy or surgery.
- Radiation therapy for tumors that do not respond to other treatment.
- A clinical trial of treatment guided by the tumor's response to treatment and whether there are certain changes in the tumor cells.
High-Risk Neuroblastoma
Treatment of high-risk neuroblastoma may include the following:
- A regimen of combination chemotherapy, surgery, stem cell rescue, radiation therapy, and anti-GD2 ch14.18 with interleukin-2 (IL-2), granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), and isotretinoin.
- A clinical trial of chemotherapy combined with mIBG, followed by surgery, more chemotherapy, stem cell rescues, radiation therapy, and isotretinoin.
- A clinical trial of chemotherapy and stem cell rescue followed by isotretinoin with or without monoclonal antibody therapy and biologic therapy.
Stage 4S Neuroblastoma
There is no standard treatment for stage 4S neuroblastoma but treatment options include the following:
- Observation with supportive care for certain patients who have favorable tumor biology and do not have signs or symptoms.
- Chemotherapy, for children who have signs or symptoms of neuroblastoma or unfavorable tumor biology, or for very young infants.
- A clinical trial of treatment guided by the tumor's response to treatment and whether there are certain changes in the tumor cells.
Recurrent Neuroblastoma
Patients First Treated for Low-Risk Neuroblastoma
Treatment for recurrent neuroblastoma that is found in one place in the body may include the following:
- Chemotherapy that may be followed by surgery.
Treatment for recurrent neuroblastoma that has spread to other parts of the body may include the following:
- Observation for certain infants.
- Chemotherapy.
- Surgery followed by chemotherapy.
Patients First Treated for Intermediate-Risk Neuroblastoma
Treatment for recurrent neuroblastoma that is found in one place in the body may include the following:
- Surgery that may be followed by chemotherapy.
Recurrent neuroblastoma that has spread to other parts of the body is treated the same way as newly diagnosed high-risk neuroblastoma.
Patients First Treated for High-Risk Neuroblastoma
Treatment for recurrent neuroblastoma may include the following:
- mIBG therapy to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. It may be given alone or in combination with other therapy, or after stem cell rescue.
- A second course of high-dose chemotherapy and stem cell rescue.
Because there is no standard treatment for recurrent neuroblastoma in patients first treated for high-risk neuroblastoma, patients may want to consider a clinical trial. For information about clinical trials, please see the NCI website.
Patients with Recurrent CNS Neuroblastoma
Treatment for neuroblastoma that recurs (comes back) in the central nervous system (CNS; brain and spinal cord) may include the following:
- A clinical trial of a new therapy.
Treatments in Clinical Trials for Progressive/Recurrent Neuroblastoma
Some of the treatments being studied in clinical trials for neuroblastoma that recurs (comes back) or progresses (grows, spreads, or does not respond to treatment) include the following:
- Lenalidomide and ch14.18 monoclonal antibody therapy with or without isotretinoin.
- A tyrosine kinase inhibitor (crizotinib) with or without combination chemotherapy.
Check the list of NCI-supported cancer clinical trials that are now accepting patients with neuroblastoma. For more specific results, refine the search by using other search features, such as the location of the trial, the type of treatment, or the name of the drug. Talk with your child's doctor about clinical trials that may be right for your child. General information about clinical trials is available from the NCI website.
To Learn More About Neuroblastoma
For more information from the National Cancer Institute about neuroblastoma, see the following:
For more childhood cancer information and other general cancer resources, see the following:
Changes to This Summary (10/01/2015)
The PDQ cancer information summaries are reviewed regularly and updated as new information becomes available. This section describes the latest changes made to this summary as of the date above.
Images were added to this summary.
About This PDQ Summary
About PDQ
Physician Data Query (PDQ) is the National Cancer Institute's (NCI's) comprehensive cancer information database. The PDQ database contains summaries of the latest published information on cancer prevention, detection, genetics, treatment, supportive care, and complementary and alternative medicine. Most summaries come in two versions. The health professional versions have detailed information written in technical language. The patient versions are written in easy-to-understand, nontechnical language. Both versions have cancer information that is accurate and up to date and most versions are also available in Spanish.
PDQ is a service of the NCI. The NCI is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). NIH is the federal government’s center of biomedical research. The PDQ summaries are based on an independent review of the medical literature. They are not policy statements of the NCI or the NIH.
Purpose of This Summary
This PDQ cancer information summary has current information about the treatment of neuroblastoma. It is meant to inform and help patients, families, and caregivers. It does not give formal guidelines or recommendations for making decisions about health care.
Reviewers and Updates
Editorial Boards write the PDQ cancer information summaries and keep them up to date. These Boards are made up of experts in cancer treatment and other specialties related to cancer. The summaries are reviewed regularly and changes are made when there is new information. The date on each summary ("Date Last Modified") is the date of the most recent change.
The information in this patient summary was taken from the health professional version, which is reviewed regularly and updated as needed, by the PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board.
Clinical Trial Information
A clinical trial is a study to answer a scientific question, such as whether one treatment is better than another. Trials are based on past studies and what has been learned in the laboratory. Each trial answers certain scientific questions in order to find new and better ways to help cancer patients. During treatment clinical trials, information is collected about the effects of a new treatment and how well it works. If a clinical trial shows that a new treatment is better than one currently being used, the new treatment may become "standard." Patients may want to think about taking part in a clinical trial. Some clinical trials are open only to patients who have not started treatment.
Clinical trials are listed in PDQ and can be found online at NCI's website. Many cancer doctors who take part in clinical trials are also listed in PDQ. For more information, call the Cancer Information Service 1-800-4-CANCER (1-800-422-6237).
Permission to Use This Summary
PDQ is a registered trademark. The content of PDQ documents can be used freely as text. It cannot be identified as an NCI PDQ cancer information summary unless the whole summary is shown and it is updated regularly. However, a user would be allowed to write a sentence such as “NCI’s PDQ cancer information summary about breast cancer prevention states the risks in the following way: [include excerpt from the summary].”
The best way to cite this PDQ summary is:
National Cancer Institute: PDQ® Neuroblastoma Treatment. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute. Date last modified <MM/DD/YYYY>. Available at: http://www.cancer.gov/types/neuroblastoma/patient/neuroblastoma-treatment-pdq. Accessed <MM/DD/YYYY>.
Images in this summary are used with permission of the author(s), artist, and/or publisher for use in the PDQ summaries only. If you want to use an image from a PDQ summary and you are not using the whole summary, you must get permission from the owner. It cannot be given by the National Cancer Institute. Information about using the images in this summary, along with many other images related to cancer can be found in Visuals Online. Visuals Online is a collection of more than 2,000 scientific images.
Disclaimer
The information in these summaries should not be used to make decisions about insurance reimbursement. More information on insurance coverage is available on Cancer.gov on the Managing Cancer Care page.
Contact Us
More information about contacting us or receiving help with the Cancer.gov website can be found on our Contact Us for Help page. Questions can also be submitted to Cancer.gov through the website’s E-mail Us.
Get More Information From NCI
Call 1-800-4-CANCER
For more information, U.S. residents may call the National Cancer Institute's (NCI's) Cancer Information Service toll-free at 1-800-4-CANCER (1-800-422-6237) Monday through Friday from 8:00 a.m. to 8:00 p.m., Eastern Time. A trained Cancer Information Specialist is available to answer your questions.
Chat online
The NCI's LiveHelp® online chat service provides Internet users with the ability to chat online with an Information Specialist. The service is available from 8:00 a.m. to 11:00 p.m. Eastern time, Monday through Friday. Information Specialists can help Internet users find information on NCI websites and answer questions about cancer.
Write to us
For more information from the NCI, please write to this address:
- NCI Public Inquiries Office
- 9609 Medical Center Dr.
- Room 2E532 MSC 9760
- Bethesda, MD 20892-9760
Search the NCI websites
The NCI website provides online access to information on cancer, clinical trials, and other websites and organizations that offer support and resources for cancer patients and their families. For a quick search, use the search box in the upper right corner of each web page. The results for a wide range of search terms will include a list of "Best Bets," editorially chosen web pages that are most closely related to the search term entered.
There are also many other places to get materials and information about cancer treatment and services. Hospitals in your area may have information about local and regional agencies that have information on finances, getting to and from treatment, receiving care at home, and dealing with problems related to cancer treatment.
Find Publications
The NCI has booklets and other materials for patients, health professionals, and the public. These publications discuss types of cancer, methods of cancer treatment, coping with cancer, and clinical trials. Some publications provide information on tests for cancer, cancer causes and prevention, cancer statistics, and NCI research activities. NCI materials on these and other topics may be ordered online or printed directly from the NCI Publications Locator. These materials can also be ordered by telephone from the Cancer Information Service toll-free at 1-800-4-CANCER (1-800-422-6237).
Publication Details
Author Information and Affiliations
Authors
PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board.Publication History
Published online: October 1, 2015.
Version History
- NBK65838.27 October 23, 2024
- NBK65838.26 March 1, 2024
- NBK65838.25 September 28, 2023
- NBK65838.24 July 26, 2023
- NBK65838.23 June 10, 2021
- NBK65838.22 January 6, 2021
- NBK65838.21 September 10, 2020
- NBK65838.20 April 20, 2020
- NBK65838.19 March 10, 2020
- NBK65838.18 October 30, 2019
- NBK65838.17 October 11, 2019
- NBK65838.16 March 28, 2019
- NBK65838.15 September 18, 2018
- NBK65838.14 July 6, 2018
- NBK65838.13 March 16, 2018
- NBK65838.12 October 6, 2017
- NBK65838.11 August 18, 2017
- NBK65838.10 June 23, 2017
- NBK65838.9 January 19, 2017
- NBK65838.8 December 9, 2016
- NBK65838.7 November 21, 2016
- NBK65838.6 January 20, 2016
- NBK65838.5 December 4, 2015
- NBK65838.4 October 7, 2015
- NBK65838.3 October 1, 2015 (Displayed Version)
- NBK65838.2 September 21, 2015
- NBK65838.1 August 6, 2015
Copyright
Publisher
National Cancer Institute (US), Bethesda (MD)
NLM Citation
PDQ Pediatric Treatment Editorial Board. Neuroblastoma Treatment (PDQ®): Patient Version. 2015 Oct 1. In: PDQ Cancer Information Summaries [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Cancer Institute (US); 2002-.