Getting started with BigQuery
Pathogen Detection Resources at Google Cloud Platform
- Pathogen Detection Resources at Google Cloud Platform
- MicroBIGG-E table in BigQuery
- MicroBIGG-E contig sequences in Google Storage buckets
- MicroBIGG-E protein sequences in Google Storage buckets
- Isolates Browser table in BigQuery
- Isolate Exceptions table in BigQuery
Set up account 

To access BigQuery, you will need to set up a Google cloud account: https://cloud.google.com/
Once you have set up the account, you will need to create your project: https://cloud.google.com/resource-manager/docs/creating-managing-projects
Payment 

The user pays for running queries against public data sets and you should review the payment requirements for on-demand queries from Google BigQuery. Google BigQuery provides 1TB per month free for querying data.
Access methods 

We recommend starting with the BigQuery SQL Workspace to become familiar with with BigQuery SQL and writing queries before attempting to use the command line tools or client libraries.
BigQuery can be accessed through a web browser query editor:
https://console.cloud.google.com/bigquery
BigQuery client library documentation is also available for reference if you
plan to access it through the supported programming languages:
https://cloud.google.com/bigquery/docs/reference/libraries
BigQuery command line tools can be downloaded and set up from here
https://cloud.google.com/sdk/docs/quickstarts
(see Using the bq command-line tool below for more)
Using the SQL Workspace 

We recommend starting with the BigQuery SQL Workspace to become familiar with BigQuery SQL and the pathogen resources.
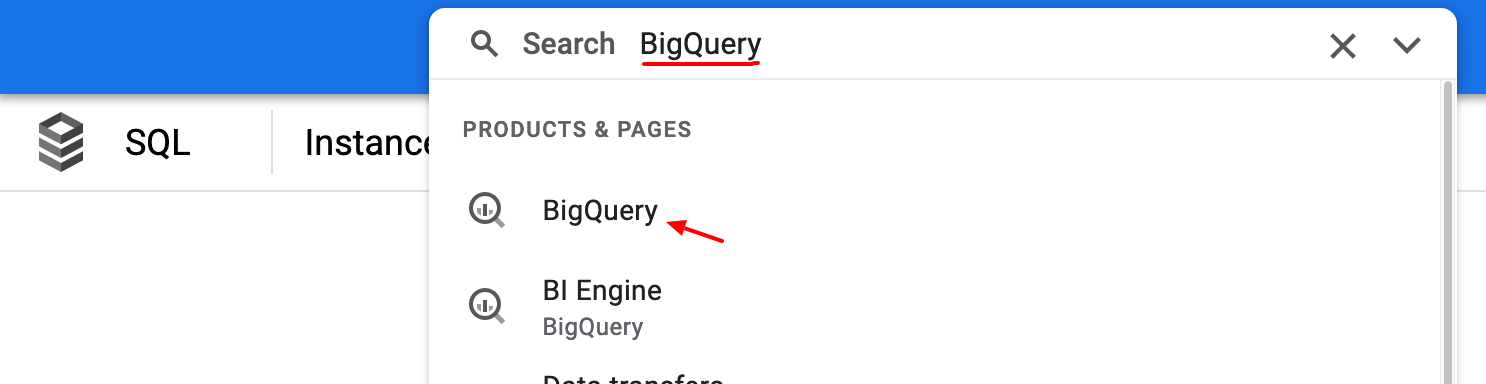 Click the search bar and enter BigQuery as the search term and click on the BigQuery search result.
Click the search bar and enter BigQuery as the search term and click on the BigQuery search result.
Add ncbi-pathogen-detect to the Data Explorer 

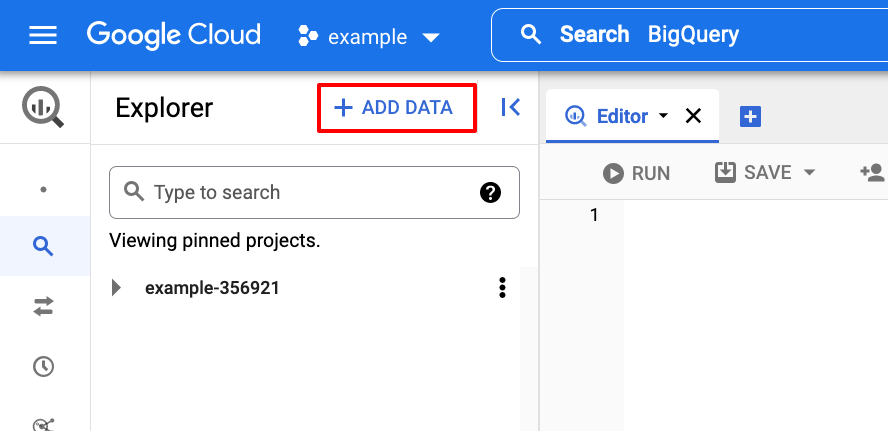
Adding the project ncbi-pathogen-detect to the Data Explorer makes it much
more convenient to get started with the dataset. Click the ADD DATA button
on the left side of the screen, in the Explorer panel.
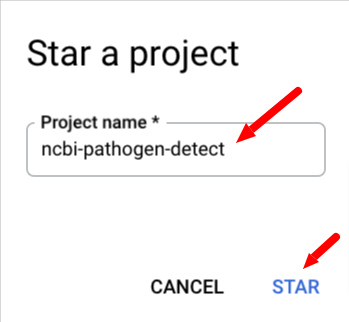
Next, select Star a project by name and paste ncbi-pathogen-detect into the Pin a project box and click STAR.

You can get to a view of the structure of a table by clicking on the tables in the Data Explorer, for example ncbi-pathogen-detect.pdbrowser.microbigge.
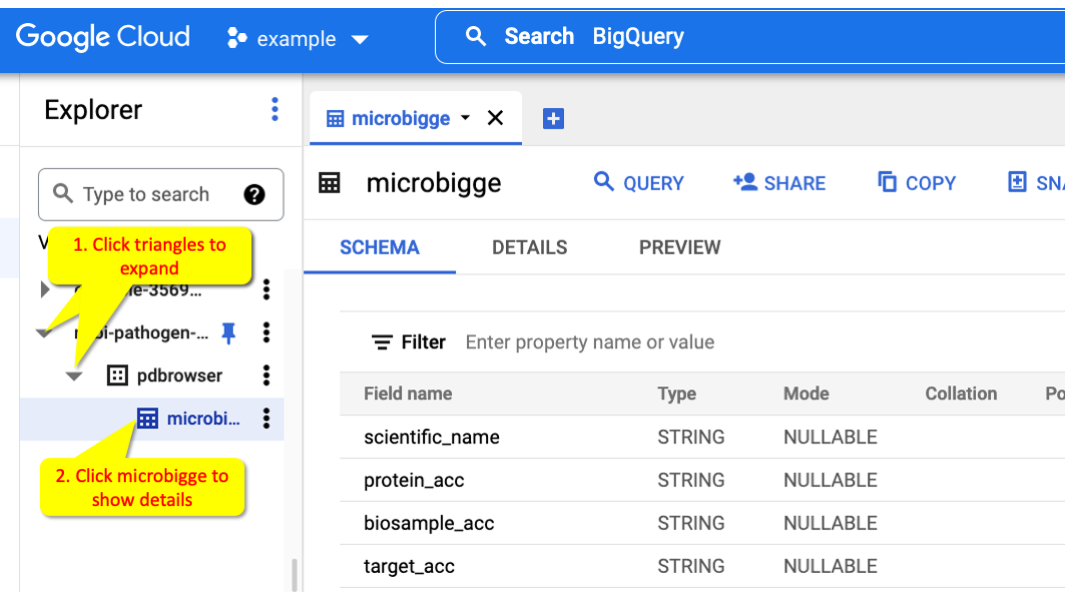
Click the Triangles (1) to expand and show the collection. Click the microbigge table (2) to view information about that table.
Within the table information panel you can click SCHEMA to list the fields and PREVIEW to show some sample data from the table.
Search in BigQuery 

To search the table click QUERY or the + symbol to open a new query editor tab and enter the query in the text box.
The area outlined in red shows how much data will be searched with your SQL query so that you can estimate the cost of running that query.
Click the RUN button to execute the query. Note that there may be a small charge associated with running the query. See above and Google's BigQuery pricing page for more information.
Using the bq command-line tool
- Create your account and project through the Google web interface (see above).
- Download install the Cloud SDK from https://cloud.google.com/sdk/docs/install-sdk.
- Sign into your account by entering the command below and following the instructions. gcloud auth login --no-launch-browser
-
Once you're logged into your account, you should set your project ID. Where
<PROJECT_ID>is the ID that was set when you created your project (this is different from your project name).gcloud config set project <PROJECT_ID> -
You should now be able to execute the following query to get the most common AMR genes:
bq query --nouse_legacy_sql --format=csv 'SELECT element_symbol, count(*) num_found FROM `ncbi-pathogen-detect.pdbrowser.microbigge` WHERE scope="core" GROUP BY element_symbol ORDER BY num_found DESC LIMIT 5'
Exporting large tables
Many people want to download the table data in bulk from our resources. See Google's Export table data documentation for details. As an example of one way, you can use a query like the following to export all MicroBIGG-E data to a google cloud storage bucket:
EXPORT DATA
OPTIONS (
uri = 'gs://<storage-bucket>/microbigge/*.tsv.gz',
format = 'CSV',
overwrite = true,
header = true,
field_delimiter = '\t',
compression = 'GZIP')
AS (
SELECT *
FROM `ncbi-pathogen-detect.pdbrowser.microbigge`
ORDER BY scientific_name, target_acc, contig_acc, start_on_contig
);
The above query will export all data from the
ncbi-pathogen-detect.pdbrowser.microbigge table to the storage bucket (named
<storage-bucket> above) in a series of gzipped tab-delimited files which you
can then download to your computer using
gsutil or other cloud
storage access methods.
What Pathogen Detection Pipeline data is available at BigQuery?
NCBI Pathogen Detection has four tables available in GCP BigQuery:
ncbi-pathogen-detect.pdbrowser.isolatescontains information and analysis results on isolate sequences in the NCBI Pathogen Detection Pipeline.- See Isolates Browser data at GCP for details
- The web interface is at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pathogens/isolates
- Isolates Browser Documentation
ncbi-pathogen-detect.pdbrowser.isolate_exceptionscontains information on isolate sequences or assemblies that failed Quality Control (QC) checks in the pipeline.- See Isolates Browser data at GCP for details
- The web interface is at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pathogens/isolates
- Exceptions table documentation
ncbi-pathogen-detect.pdbrowser.microbigge- The Microbial Browser for the Identification of Genetic and Genomic Elements (MicroBIGG-E) contains the results of running AMRFinderPlus on assemblies in the Isolates Browser.- See MicroBIGG-E at GCP for details
- The web interface is at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pathogens/microbigge
- MicroBIGG-E Documentation
ncbi-pathogen-detect.pdbrowser.bioproject_hierarchy- Bioprojects and their parent umbrella bioprojects for all isolates in the Pathogen Detection System- See BioProject Hierarchy documentation for details
